Abstract
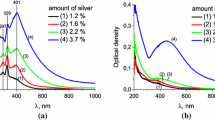
We report on the optical properties (absorption, Raman response) of thin and ultrathin phthalocyanine and amorphous silicon films with incorporated noble metal clusters. The metal clusters cause the typical absorption features originating from their surface plasmon resonance. In ultrathin films, due to the spatially close interface, the plasmon absorption may be displaced from its resonance frequency in the bulk, and its average position may be controlled by the average thickness of the ultrathin optical film. For example, we observe a shift of the plasmon resonance of silver clusters in amorphous silicon films (on fused silica) from 440 nm to 740 nm, when the silicon thickness increases from “zero” up to 9 nm. The deposition experiments are accompanied by investigations of the film structure, particularly in order to estimate the silver cluster diameter, which is around 3 nm or less.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
U. Kreibig and M. Vollmer, Optical Properties of Metal Clusters, Springer Series in Material Science 25 (Springer-Verlag, 1995).
H. Raether, Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings, Springer Tracts in Modern Physics, Vol. 111 (Springer-Verlag 1988).
M. Born and E. Wolf, Principles of Optics (Pergamon Press, 1968).
M. Quinten and U. Kreibig (1993). Appl. Opt. 32, 6173.
A. Wokaun, in H. Ehrenreich and D. Turnbull (eds.), Solid State Physics: Advances in Research and Applications, Vol. 38 (Academic Press, Orlando, Florida, 1984), p. 223 ff.
M. Cardona and G. Güntherodt (eds.), Light Scattering in Solids IV, Topics in Applied Physics, Vol. 54 (Springer-Verlag, 1984).
Surface Studies by Nonlinear Laser Spectroscopies, Materials of the 129. WE — Heraeus, Seminar, May 30–June 1, Kassel, Germany (1994).
M. Hiramoto, M. Suezak, and M. Yokoyama (1990). Chem. Lett. 327–330.
S. Hayashi, K. Kozaru, and K. Yamamoto (1991). Solid State Commun. 79, 763.
O. Stenzel, A. Stendal, K. Voigtsberger, and C. von Borczyskowski (1995). Solar Energy Mat. Solar Cells 37, 337.
T. Götz, W. Hoheisel, M. Vollmer, and F. Träger (1995). Z. Phys. D 33, 133.
D. E. Aspnes and A. A. Studna (1983). Phys. Rev. B 27, 985.
O. Stenzel, A. Stendal, M. Roder, and C. von Borczyskowski (1997). Pure Appl. Opt. 6, 577.
O. Stenzel, A. Stendal, M. Röder, S. Wilbrandt, D. Drews, T. Werninghaus, C. von Borczyskowski, and D. R. T. Zahn (1998). Nanotechnology 9.
J. P. Benedict, R. Anderson, and S. J. Klepeis (1992). Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 254, 121.
O. Stenzel, S. Wilbrandt, A. Stendal, U. Beckers, K. Voigtsberger, and C. von Borozyskowski (1995). J. Phys. D 28, 2154.
O. Stenzel, A. Stendal, D. Drews, T. Werninghaus, M. Falke, and D. R. T. Zahn, and C. von Borczyskowski (1997). Appl. Surf. Sci. 108, 71.
J. H. Dobrowolski, F. C. Ho, and A. Waldorf (1983). Appl. Opt. 22, 3191.
D. P. Arndt, R. M. A. Azzam, J. M. Bennett, J. P. Borgogno, C. K. Carniglia, W. E. Case, J. A. Dobrowolski, U. J. Gibson, T. Tuttle Hart, F. C. Ho, V. A. Hodkin, W. P. Klapp, H. A. Macleod, E. Pelletier, M. K. Purvis, D. M. Quinn, D. H. Strome, R. Swenson, P. A. Temple, and T. F. Thonn (1984). Appl. Opt. 23, and references therein.
O. Stenzel and R. Petrich (1995). J. Phys. D 28, 978.
O. Stenzel, Das Dünnschichtspektrum: Ein Zugang von den Grundlagen zur Spezialliteratur (in German, Academie-Verlag, Berlin, 1996).
A. Thelen, Design of Interference Coatings (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1989).
A. Franke, Diploma thesis (in German), Technische Universität Chemnitz, Institute of Physics, Sept. (1996).
M. Quinten, O. Stenzel, A. Stendal, and C. von Borczyskowski (1997). J. Opt. 28, 245.
C. Jennings, R. Aroca, A.-M. Hor, and R. O. Loutfy (1984). J. Raman Spectr. 15, 34.
V. Linß, Reports on Practical Studies (in German), Technische Universität (Chemnitz, Institute of Physics, July (1996).
V. R. Blok (1982). J. Exp. Teoret. Fizik. 82, 678 (in Russian).
U. Kreibig, M. Gartz, and A. Hilger, Mie Resonances: Sensors for Physical and Chemical Cluster Interface Properties (Bunsenberichte fur Physikalische Chemie, 1997).
E. J. Zeman, K. T. Carron, G. C. Schatz, and R. P. Van Duyne (1987). J. Chem. Phys. 87, 4189.
P. Dub (1983). Surf. Sci. 135, 307.
A. Bagchi, R. G. Barrera, and R. Fuchs (1982). Phys. Rev. B 25, 7086.
N. F. Mott and E. A. Davis, Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1979).
R. Zallen, The Physics of Amorphous Solids (John Wiley & Sons, 1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stenzel, O. Optical Properties of Noble Metal Clusters in Ultrathin Solid Films. Journal of Cluster Science 10, 169–193 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022664920382
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022664920382