Abstract
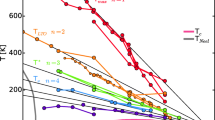
A general view has been developed to correlate spatial inhomogeneity in the carrier density over different dimensions in crystals of high-T c cuprate superconductors to basic superconducting properties such as T c , H irr and “peak effect”. Employing the BVS concept, it is shown that there are three different routes for doping the CuO 2 plane with holes, and that the more confined holes are in the middle of the CuO 2 -plane stack, the higher is T c . With the Cu(Ba,Sr) 2 (Yb,Ca)Cu 2 O 6+z system it is shown that the distribution of holes is different when holes are generated with different doping routes, and further that the more homogeneous the hole distribution along the c axis is, the better is the H irr characteristics. This agrees with observations made for Hg-1223 and Cu-1223 that the more overdoped these phases are, the more improved is the H irr characteristics. Studies on peak effect in various high-T c superconductors indicate that some mesoscopical inhomogeneity in oxygen content or hole density causes the peak. Thus control of hole density over dimensions from atomic bonds to tens of nanometers is essential in tailoring the fundamental superconducting properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamauchi, H., Karppinen, M. Control of Carrier Distribution for Tailoring Superconducting Properties of Layered Cuprates. Journal of Low Temperature Physics 117, 813–822 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022574001761
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022574001761