Abstract
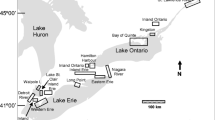
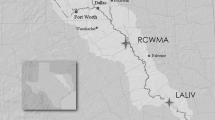
In South Carolina, U.S.A., mink have been reintroduced from two apparently healthy populations to areas where populations haveexisted in the past but have been extirpated. High mortality wasobserved during transport of mink from the source populations. Inorder to elucidate the potential effects of dioxin-like compoundson the survival and reproduction of mink, concentrations of totalpolychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), p,p′-DDE, dioxin-likePCBs, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), anddibenzofurans (PCDFs) were measured in livers of mink collectedfrom the source populations in South Carolina and Louisiana. Concentrations of total 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxinequivalents (TEQs) for the South Carolina and Louisiana mink were21 and 14 pg g-1, wet wt., respectively. PCB and TEQ concentrations were close to the threshold values that can, under laboratory conditions, elicit toxic effects in ranchmink. Therefore, any additional exposures of these populations toTEQs might adversely affect their populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aulerich, R. J. and Ringer, R. K.: 1977, ‘Current status of PCB toxicity to mink, and effect on their reproduction’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 6, 279-292.
Aulerich, R. J., Bursian, S. J., Breslin, W. J., Olson, B. A. and Ringer, R. K.: 1985, ‘Toxicological manifestations of 2,4,5,-2′,4′,5′-, 2′,3′,6′,2′,3′,6′-, and 3,4,5,3′,4′,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl and Aroclor 1254 in mink’, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 15, 63-79.
Aulerich, R. J., Ringer, R. K. and Iwamoto, S.: 1973, ‘Reproductive failure and mortality in mink fed on Great Lakes fish’, J. Repro. Fert. 19, 365-376.
Baker, O. E.: 2000, ‘The status of mink (Mustela vison) in South Carolina’, South Carolina Department of Natural Resources, Furbearer Project Publication, No. 99-01, pp. 1-47.
Champoux, L.: 1996, ‘PCBs, dioxins and furans in hooded merganser (Lophodytes cucullatus), common merganser (Mergus merganser) and mink (Mustela vison) collected along the St. Maurice River near La Tuque, Quebec’, Environ. Pollut. 92, 147-153.
Elliott, J. E., Henny, C. J., Harris, M. L., Wilson, L. K. and Norstrom R. J.: 1999, ‘Chlorinated hydrocarbons in livers of American mink (Mustela vison) and river otter (Lutra canadensis) from the Colombia and Fraser River basins, 1990-1992’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 57, 229-252.
Foley, R. E., Jackling, S. J., Sloan, R. J. and Brown, M. K.: 1988, ‘Organochlorine and mercury residues in wild mink and otter: comparison with fish’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 7, 363-374.
Giesy, J. P. and Kannan, K.: 1998, ‘Dioxin-like and non-dioxin-like toxic effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): Implications for risk assessment’, Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 28, 511-569.
Haffner, G. D., Glooschenko, V., Straughan, C. A., Hebert, C. E. and Lazar, R.: 1998, ‘Concentrations and distributions of polychlorinated biphenyls, including non-ortho congeners, in mink populations from southern Ontario’, J. Great Lakes Res. 24, 880-888.
Harding, L. E., Harris, M. L., Stephen, C. R. and Elliott J. E.: 1999, ‘Reproductive and morphological condition of wild mink (Mustela vison) and river otters (Lutra canadensis) in relation to chlorinated hydrocarbon contamination’, Environ. Health. Perspect. 107, 141-147.
Heaton, S. N., Bursian, S. J., Tillitt, D. E., Giesy, J. P., Render, J. A., Jones, P. D., Verbrugge, D. A., Kubiak, T. J. and Aulerich, R. J.: 1995, ‘Dietary exposure of mink to carp from Saginaw Bay, Michigan. 1. Effects on reproduction and survival, and the potential risks to wild mink populations’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 334-343.
Henny, C. J., Blus, L. J., Gregory, S. V. and Stafford, C. J.: 1981, ‘PCBs and Organochlorine Pesticides in Wild Mink and River Otters from Oregon’, in J. A. Chapman and Pursely (eds), Worldwide Furbearer Conference Proceedings, Frostburg, MD, pp. 1763-1780.
Hochstein, J. R., Aulerich, R. J. and Bursian, S. J.: 1988, ‘Acute toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to mink’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 17, 33-37.
Kannan, K., Tanabe, S., Borrell, A., Aguilar, A., Focardi, S. and Tatsukawa, R.: 1993, ‘Isomerspecific analysis and toxic evaluation of polychlorinated biphenyls in striped dolphins affected by an epizootic in the westernMediterranean Sea’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 25, 227-233.
Kannan, K., Blankenship, A. L., Jones, P. D. and Giesy, J. P.: 2000a, ‘Toxicity reference values for the toxic effects of polychlorinated biphenyls to aquatic mammals’, Human Ecolog. Risk Assess. 6, 181-201.
Kannan, K., Yamashita, N., Imagawa, T., Decoen, W., Khim, J. S., Day, R. M., Summer, C. L. and Giesy, J. P.: 2000b, ‘Polychlorinated naphthalenes and polychlorinated biphenyls in fishes from Michigan waters including the Great Lakes’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 566-572.
Kihlstrom, J. E., Olsson, M., Jensen, S., Johansson, A., Ahlbom, J. and Bergman, A.: 1992, ‘Effects of PCB and different fractions of PCB on the reproduction of the mink (Mustela vison)’, Ambio 21, 563-569.
Murk, A. J., Leonards, P. E. G, Van Hattum, B., Luit, R., Van der Weider, M. E. J. and Smit, M.: 1998, ‘Application of biomarkers for exposure and effect of polyhalogenated aromatic hydrocarbons in naturally exposed European otters (Lutra lutra)’, Environ. Toxicol. Pharamcol. 6, 91-102.
O'shea, T. J., Kaiser, T. E., Askins, G. R. and Chapman, J. A.: 1981, ‘Polychlorinated Biphenyls in a Wild Mink Population’, in J. A. Chapman, and Pursely (eds), Worldwide Furbearer Conference Proceedings, Frostburg, MD, pp. 1746-1751.
Osowski, S. L., Brewer, L. W., Baker, O. E. and Cobb, G. P.: 1995, ‘The decline of mink in Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina: The role of contaminants’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 29, 418-423.
Platonow, N. S. and Karstad, L. H.: 1973, ‘Dietary effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on mink’, Can. J. Comp. Med. 37, 391-400.
Poole, K. G., Elkin, B. T. and Bethke, R. W.: 1998, ‘Organochlorine and heavy metal contaminants in wild mink in western Northwest Territories, Canada’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 34, 406-413.
Restum, J., Bursian, S. J., Giesy, J. P., Render, J. A., Helferich, W. C., Shipp, E. B., Verbrugge, D. A. and Aulerich, R. J.: 1998, ‘Multigenerational study of the effects of consumption of PCBcontaminated carp from Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron, on mink. I. Effects of mink reproduction, kit growth and survival, and selected biological parameters’, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, A4, 343-375.
Ringer, R. K.: 1981, ‘The Effects of Environmental Contaminants on Reproduction in the Mink (Mustela vison)’, in Gilmore and B. Cook (eds), Environmental Factors in Mammal Reproduction, Macmillan, London, pp. 232-237.
Senthilkumar, K., Kannan, K., Paramasivan, O. N., Shanmugasundaram, V. P., Nakanishi, J. and Masunaga, S.: 2001, ‘Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and polychlorinated biphenyls in human tissues, meat, fish and wildlife samples from India’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 35(17), 3448-3455.
Senthilkumar, K., Kannan, K., Sinha, R. K., Tanabe, S. and Giesy, J. P.: 1999, ‘Bioaccumulation profiles of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners and organochlorine pesticides in Ganges river dolphins’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18, 1511-1520.
Tillitt, D. E., Gale, R. W., Meadows, J. C., Zajicek, J. L. Peterman, P. H., Heaton, S. N., Jones, P. D., Bursian, S. J., Kubiak, T. J., Giesy, J. P. and Aulerich, R. J.: 1996, ‘Dietary exposure of mink to carp from Saginaw Bay. 3. Characterization of dietary exposure to planar halogenated hydrocarbons, dioxin equivalents, and biomagnification’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 283-291.
Van den Berg, M., Birnbaum, L., Bosveld, A. T. C., Brunstrom, B., Cook, P., Freeley, M., Giesy, J. P., Hanberg, A., Hasegawa, R., Kennedy, S. W., Kubiak, T., Larsen, J. C., van Leeuwen, F. X., Liem, A. K., Nolt, C., Peterson, R. E., Poellinger, L., Safe, S., Schrenk, D., Tillitt, D., Tysklind, M., Younes, M., Waern, F. and Zacharewski, T.: 1998, ‘Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife’, Environ. Health Perspect. 106, 775-792.
Watanabe, M., Kannan, K., Takahashi, A., Loganathan, B. G., Odell, D. K, Tanabe S. and Giesy, J. P.: 2000, ‘Polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine pesticides, tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane and tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol in livers of small cetaceans stranded along Florida coastal waters, U.S.A.’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19, 1566-1574.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tansy, C.L., Senthilkumar, K., Pastva, S.D. et al. Concentrations and Profiles of Polychlorinated Biphenyls, -Dibenzo-p-Dioxins and -Dibenzofurans in Livers of Mink from South Carolina and Louisiana, U.S.A.. Environ Monit Assess 83, 17–33 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022450603004
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022450603004