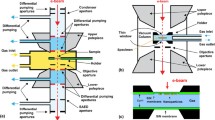
Abstract
High-resolution in situ controlled-environment electron microscopy (environmental cell TEM (ETEM) or ECELL) instrumentation and techniques, and some of the key applications to dynamic reaction studies in catalysis, are reviewed. Developments over the past decade or so have led to the novel development of ETEM for in situ studies on the atomic scale of operating catalysts under controlled environments. The powerful ETEM technique enables direct access to the important, but often metastable with respect to temperature and gas atmosphere, intermediate phases in dynamic catalysis processes. Unique insights are provided into reaction mechanisms and the sequences of microstructural and nanochemical evolution of catalyst active site structures associated with selectivity and activity, and potential deactivation and poisoning. The examples demonstrate the pivotal role of ETEM in understanding, developing and controlling novel catalysts and processes. The latest developments include wet-ETEM for in situ dynamic studies of liquid--solid reactions in polymerization and molecular electronics applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.L. Gai, Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 34 (1992) 1.
P.B. Hirsch et al., Electron Microscopy of Thin Crystals (Butterworths, London, 1965).
R. Sinclair, T. Yamashita and F. Á. Ponce, Nature 290 (1981) 386.
H. Saka et al., In situ Electron Microscopy in Materials Research, ed. P.L. Gai (Kluwer Academic, London, Boston, 1997).
D.W. Pashley, M.J. Stowell, M.H. Jacobs and T.J. Law, Phil. Mag. 10 (1964) 127.
K. Yagi et al., Thin Solid Films 126 (1985) 95.
J.M. Thomas and W.J. Thomas, Principles and Practices of Het.s Catalysis (VCH, 1997).
H. Hashimoto et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 7 (1968) 946.
P.R. Swann and N. Tighe, Jernkont. Ann. 155 (1971) 251.
E.P. Butler and K.F. Hale, Dynamic Experiments in Electron Microscopy (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1981).
D. Double, A. Hellawell and S. Perry, Proc. Roy. Soc. A359 (1978) 435.
D.F. Parsons et al., Science 186 (1974) 407.
H. Fujita et al. (eds.), In situ Experiments in HVEM (Osaka University Press, 1985).
R.C. Doole, G. Parkinson and J.M. Stead, Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 119 (1991) 161.
R.T.K. Baker, Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 19 (1979) 161.
P.L. Gai and P.B. Hirsch, Proc. Climax Mo Co. Ltd and Chemical Society (Dalton Division) Conference, University of Oxford, UK, 1976; J. Less. Comm. Metals 54 (1977) 263.
P.L. Gai, C.J. Humphreys, A.E. Webb, D.R. Pyke and J.C.J. Bart, Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 52 (1980) 317.
P.L. Gai, Phil. Mag. 43 (1981) 841.
P.L. Gai and M.J. Goringe, Proc. 39th Electron Microscopy Society of America (San Francisco Press, 1981) p. 68.
P.L. Gai, E.D. Boyes and J.C.J. Bart, Phil. Mag. A45 (1982) 531.
P.L. Gai, J. Solid State Chem. 49 (1983) 25; Phil. Mag. 48 (1983) 359.
P.L. Gai and P.A. Labun, J. Catal. 94 (1985) 79.
P.L. Gai, B.C. Smith and G. Owen, Nature 348 (1990) 430.
P.L. Gai and B.C. Smith, Ultramicroscopy 34 (1990) 17.
P.L. Gai, J. Solid State Chem. 104 (1993) 119.
K.H. Westmacott and U. Dahmen, in: Decomposition of Alloys, ed. P. Haasen et al. (Pergamon, 1984).
T.C. Lee, D. Dewald, J. Eades, I.M. Roberetson and H.K. Birnbaum, Rev. Sci. Instr. 62 (1991) 1438.
P. L. Gai et al., Science 267 (1995) 661.
P.L. Gai and E.D. Boyes, In situ Microscopy in Materials Research (Kluwer, Boston, London, 1997).
E.D. Boyes and P.L. Gai, Ultramicroscopy 67 (1997) 219.
P.L. Gai, Acta. Cryst. B53 (1997) 346.
P.L. Gai, Adv. Mater. 10 (1998) 1259.
P.L. Gai, Topics Catal. 8 (1999).
J. Haggin, Chem. Eng. News 73(30) (1995) 39.
E.D. Boyes and P.L. Gai, Electron Microscopy (ICEM 14), ed. H.A. Claderon Benavides and M.J. Yacaman (Institute of Physics Publishers, 1998) p. 511.
T.W. Hansen et al., Proc 12th Euro. Congr. on EM (Czech Electron Microscopy Society, 2000) p. 537; Science 294 (2001) 1508.
V. Oleshko, P. Crozier, R. Cantrell and A. Westwood, J. Electron Micr. 51 (2002) S27.
P. Crozier, R. Sharma and A. Datye, Proc. Micr. Soc. Am. 4 (1998) 228.
R. Sharma and P. Crozier, Electron Microsc. Anal. (1999) 569.
M.J. Goringe, A. Rawli., A. Burden, J. Hutchison and R. Doole, Faraday Disc. 105 (1996) 102.
P.L. Gai, K. Kourtakis and S. Ziemecki, Microsc. Microanal. 6 (2000) 335.
P.L. Gai, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 4 (1999) 63.
G. Centi (ed.), Catal. Today 16 (1993).
Yu.E. Gorbunova and S.A. Linde, Sov. Phy-Dockl (Engl.Trans.) 24 (1979) 138.
P.L. Gai, D.R. Coulson, K. Kourtakis and G.C. Sonnichsen, J. Phys.Chem. 101 (1997) 9916.
R.F. Service, Science 294 (2001) 2442, and references therein.
P.L. Gai and M.A. Harmer, Nano Lett. 2 (2002) 771.
M.P. Zach et al., Science 290 (2000) 2120.
M.S. Dresselhaus, Y. Lin, S.B. Cronin, O. Rabin, M. Black and G. Dresselhaus, Low Dim Thermoel: Recent Trends in Thermoel. Mater. Research, ed. T.M. Tritt (Academic Press, 2001) p. 1.
S.B. Cronin, Y. Lin, O. Rabin, M. Black, G. Dresselhaus, M.S. Dresselhaus and P.L. Gai, Microsc. Microanal. 8 (2002) 58.
N. Jana, L. Gearhart and C.J. Murphy, J. Phys. Chem. B 105 (2001) 4065.
P.L. Gai, Microsc. Microanal. 8 (2002) 21.
S. Ino, J. Phys. Soc. Japn 21 (1966) 346.
M. Gillet, Surf. Sci. 67 (1977) 139.
L.D. Marks and D.J. Smith, J. Cryst. Growth 5 (1981) 12.
M.J. Yacaman et al., Surf. Sci. Lett. 486 (2001) L449.
P.L. Gai, Curr. Opin Solid State Mater. Sci. 5 (2001) 371.
F. Nagata and I. Ishikawa, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 11 (1972) 1293.
K. Fukushima, A. Ishikawa and A. Fukami, J. Electron Micr. 34 (1985) 47.
T. Daulton, B. Little, K. Lowe and J. Jones Meehan, Proc. MSA (2001) 134.
C. De Bellefon and P. Fouilloux, Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 36 (1994) 459.
P.L. Gai and E.D. Boyes, Electron Microscopy in Heterogeneous Catalysis (Institute of Physics Publishing) (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gai, P.L. Developments in in situ Environmental Cell High-Resolution Electron Microscopy and Applications to Catalysis. Topics in Catalysis 21, 161–173 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021333310817
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021333310817