Abstract
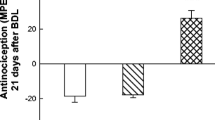
GABAergic alterations in brain stem during compensatory hyperplasia after partial hepatectomy (PH), lead nitrate (LN)-induced direct hyperplasia, and N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA)-induced neoplasia in liver were investigated. GABA content decreased in brain stem of PH- and NDEA-treated rats while it increased in LN-treated rats. GABAA receptor number and affinity in brain stem membrane preparations of rats showed a significant decrease in PH- and NDEA-treated rats. The GABAB receptor number increased in PH- and NDEA-treated rats with an increase in affinity. The results of the present study indicate that liver cell proliferation is influencing the brain stem GABAergic neurotransmission and these changes regulate the hepatic proliferation through the sympathetic stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Lautt, W. W. 1983. Afferent and efferent neural roles in liver function. Prog. Neurobiol. 21:323-348.
Frerichs, F. T. 1860. A clinical treatise on diseases of the liver. Pages 193-246. Translated by Murchison C, In The New Sydenham Society, London.
Basile, A. S., Jones, E. A., and Skolnick, P. 1991. The pathogenesis and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: Evidence for the involvement of benzodiazepine receptor ligands. Pharmacol. Rev. 43:27-71.
Butterworth, R. F. 1995. The neurobiology of hepatic encephalopathy. Semin. Liver Dis. 16:235-244.
Jones, E. A. 1995. Fatigue associated with chronic liver disease: A riddle wrapped in a mystery inside an enigma. Hepatology 22:1606-1608.
Rogers, R. C. and Hermann, G. E. 1983. Central connections of the hepatic branch of the vagus nerve: A horse radish peroxidase histochemical study. J. Auto. Nerv. Sys. 7:165-174.
Tanaka, K., Ohkawa, S., Nishino, T., Niijima, A., and Inoue, S. 1987. Role of the hepatic branch of the vagus nerve in liver regeneration in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 253:G439-G444.
Kiba, T., Tanaka, K., and Inoue, S. 1995. Lateral hypothalamic lesions facilitate hepatic regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. Pflugers Arch. 430:666-671.
Yoneda, M., Tamori, K., Sato, Y., Yokohama, S., Nakamura, K., Kono, T., and Makino, I. 1997. Central thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates hepatic DNA synthesis in rats. Hepatology 26:1203-1208.
Jones, E. A. and Yurdaydin, C. 1997. Is fatigue associated with cholestasis mediated by altered central neurotransmission? Hepatology 25:492-494.
Lapinjoki, S. P., Pulkka, A. E., Laitinen, S. I., and Pajunen, A. E. I. 1983. Possible involvement of humoral regulation in the effects of elevated cerebral 4-aminobutyric acid levels on the polyamine metabolism in brain. J. Neurochem. 41:677-683.
Biju, M. P., Pyroja, S., Rajeshkumar, N. V., and Paulose, C. S. 2001. Hypothalamic GABA receptor functional regulation and liver cell proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 216:65-70.
Coleman, M. J. and Dampney, R. A. 1998. Sympathoinhibition evoked from caudal midline medulla is mediated by GABA receptors in rostral VLM. Am. J. Physiol. 274:R318-R323.
Dimicco, J. A., Gale, K., Hamilton, B., and Gillts, R. A. 1979. GABAergic control of parasympathetic outflow to heart: Characterisation and brain stem localisation. Science 204:1106-1109.
Higgins, G. M. and Anderson, R. M. 1931. Experimental pathology of the liver: Restoration of the liver of white rat following partial surgical removal. Arch. Path. 12:186-202.
Kubo, Y., Yasunaga, M., Masuhara, M., Terai, S., Nakamura, T., and Okita, K. 1996. Hepatocyte proliferation induced in rats by lead-nitrate is suppressed by tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors. Hepatology 23:104-114.
Narurkar, L. M. and Narurkar, M. V. 1989. Role of nicotinamide in suppression of diethylnitrosamine hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Pages 162-177, in Maru, S. V. B. a. G. B. (eds), Chemoprevention of Cancer. Omega Scientific Publishers, New Delhi.
Glowinski J. and Iversen L. L. 1966. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain: The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]DOPA in various regions of rat brain. J. Neurochem. 13:655-669.
Gaskins, H. R., Baldeon, M. E., Selassi, L., and Beverly, J. L. 1995. Glucose modulates gamma-aminobutyric acid release from the pancreatic beta TC6 cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 30286-30289.
Mohler, H. 1979. GABA receptor binding with [3H]GABA and [3H]bicuculline-methiodide: An improved method. Pages 355-362, in Mandel, P. and DeFeudis, F. V. (eds), GABABiochemistry and CNS Functions. Plenum Press, New York.
Hill, D. R., Bowery, N. G., and Hudson, A. L. 1984. Inhibition of GABA-B receptor binding by guanyl nucleotides. J. Neurochem. 42:652-657.
Scatchard, G. 1949. The attractions of proteins for small molecules and ions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 51:660-672.
Cheng, Y. and Prusoff, W. H. 1973. Relationship between the inhibition constant and the concentration of an inhibitor that cause a 50% inhibition of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 22:3099-3108.
Grisham, J. W. 1962. A morphologic study of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and cell proliferation in regenerating liver, autoradiography with thymidine-H3. Cancer Res. 22:842-849.
Kiba, T., Tanaka, K., Numata, K., Hoshino, M., and Inoue, S. 1994. Facilitation of liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy by ventromedial hypothalamic lesions in rats. Pflug. Arch. 428: 26-29.
Columbano, A. and Shinozuka, H. 1996. Liver regeneration versus direct hyperplasia. FASEB J 10:1118-1128.
Wan, Q., Xiong, Z. G., Man, H. Y., Ackerlery, C. A., Braunton, J., Lu, W. Y., Becker, L. E., MacDonald, J. F., and Wang, Y. T. 1997. Recruitment of functional GABAA receptors to postsynaptic domains by insulin. Nature 388:686-690.
Sved, A. F. and Sved, J. C. 1990. Endogenous GABA acts on GABAB receptors in nucleus tractus solitarius to increase blood pressure. Brain Res. 526:235-240.
Sieghart, W. 1995. Structure and pharmacology of gamma aminobutyric acid-A receptor subtypes. Pharmacol. Rev. 47: 182-234.
Olsen, R. W. and Snowman, A. M. 1983. [3H]Bicuculline methochloride binding to low-affinity gamma aminobutyric acid receptor sites. J. Neurochem. 41:1653-1663.
Tellioglu, T., Akin, S., Ozkutlu, U., Oktay, S., and Onat, F. 1996. The role of brain acetylcholine in GABA A receptor antagonistinduced blood-pressure changes in rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 317: 301-307.
Kerr, D. I. B., Ong, J., and Prager, R. H. 1990. GABAB receptor agonist and antagonists. Pages 29-46, in Bowery, N. G. and Bittiger, H. (eds) GABAB Receptors in Mammalian Function, John Wiley Sons, West Sussex.
Nonogaki, K., Kotomi, M., Nobuo, S., and Akihisa, I. 1994. Effect of central GABA receptors activation on catecholamine secretion in rats. Life Sci. 55:PL239-PL243.
Takenaka, K., Sasaki, S., Uchida, A., Fujita, H., Ichida, T., Itoh, H., Nakata, T., Takeda, K., and Nakagawa, M. 1995. Hypothalamic and medullary GABAA and GABAB-ergic systems differentially regulate sympathetic and cardiovascular systems. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 22:S48-S50.
Michalopoulose, G. K. and DeFrancis, M. C. 1997. Liver regeneration. Science 276:60-66.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biju, M.P., Pyroja, S., Rajeshkumar, N.V. et al. Brain Stem GABA Receptor Functional Regulation During Rat Liver Cell Proliferation. Neurochem Res 27, 905–910 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020391514995
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020391514995