Abstract
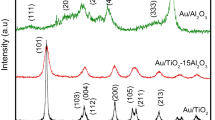
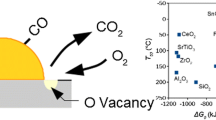
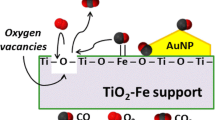
In order to elucidate the role of the contact structure between gold and metal oxide support in low-temperature CO oxidation, a mechanical mixture of colloidal gold with TiO2 powder was prepared and calcined at different temperatures. The sample calcined at 473 K, which is composed of spherical gold particles with a mean diameter of 5.1 nm and TiO2 powder, is poorly active for CO oxidation at temperatures up to 473 K. The catalytic activity appreciably increases with an increase in calcination temperature up to 873 K even though gold particles grow to larger ones, reaching a level with almost the same turnover frequency as that of Au/TiO2 prepared by a deposition–precipitation method.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsubota, S., Nakamura, T., Tanaka, K. et al. Effect of calcination temperature on the catalytic activity of Au colloids mechanically mixed with TiO2 powder for CO oxidation. Catalysis Letters 56, 131–135 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019069315071
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019069315071