Abstract
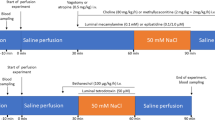
Cholera toxin-induced intestinal secretion inintact rats requires a functioning myenteric plexus. Theaim of this investigation was to determine whetherneural elements were essential for cholera toxin to produce a secretory effect in human isolatedileum. Mucosal preparations were mounted in Ussingchambers. Cholera toxin was applied apically andshort-circuit current monitored for 3 hr, at which point forskolin was given. Cholera toxin (10μg/ml) induced a tetrodotoxin-insensitive increase inshort-circuit current in muscle-stripped preparations ofhuman ileum. The increase was not additive with the action of forskolin (25 μM). Cholera toxinexerts a marked nonneural secretory effect in humanileal mucosa in vitro , probably by the same mechanismas forskolin, namely elevation of cyclic AMP.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kimberg DV, Field M, Johnson J, Henderson A, Gershon E: Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest 50:1218–1230, 1971
Field M, Fromm D, Al-Awqati Q, Greenough WB: Effect of cholera enterotoxin on ion transport across isolated ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest 51:796–804, 1972
Barrett KE, Cohn JA, Huott PA, Wasserman SL, Dharmsathaphorn K: Immune-related intestinal chloride secretion II. Effect of adenosine on T84 cell line. Am J Physiol 258:C902–C912, 1990
Field M: Regulation of small intestine ion transport by cyclic nucleotides and calcium. In Secretory Diarrhea. M Field, JS Fordtran, SG Schultz (eds). Bethesda, Maryland, American Physiological Society, 1980, pp 21–30
Cassuto J, Jodal M, Sjovall H, Lundgren O: Nervous control of intestinal secretion. Clin Res Rev 1(suppl 1):11–21, 1981
Lundgren O, Svanvik J, Jivegard L: Enteric nervous system I. Physiology and pathophysiology of the intestinal tract. Dig Dis Sci 34:264–283, 1989
Jodal M, Holmgren S, Lundgren O, Sjöqvist A: Involvement of the myenteric plexus in the cholera toxin induced net fluid secretion in the rat small intestine. Gastroenterology 105:1286–1293, 1993
Mian KB, Martin W: The inhibitory effect of 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole on relaxation induced by hydroxylamine and sodium azide but not hydrogen peroxide or glyceryl trinitrate in rat aorta. Br J Pharmacol 116:3302–3308, 1995
Izmeth A, Kirkham SE, Borman RA, Burleigh DE: The effect of atrial natriuretic peptides on ion-transport by musclestripped and full thickness preparations of rat colon. Neuropeptides 26:237–240, 1994
Burleigh DE, Borman RA: Short-circuit current responses to 5-hydroxytryptamine in human ileal mucosa are mediated by a 5-HT4 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 241:125–128, 1993
Grady GF, Madoff MA, Duhamel RC, Moore EW, Chalmers TC: Sodium transport by human ileum in vitro and its response to cholera toxin. Gastroenterology 53:737–744, 1967
Al-Awqati Q, Cameron JL, Greenough WB: Electrolyte transport in human ileum: Effect of purified cholera toxin. Am J Physiol 224:818–823, 1973
Hunt JB, Thillainayagam AV, Carnaby S, Fairclough PD, Clark ML, Farthing MJG: Absorption of a hypotonic oral rehydration solution in a human model of cholera. Gut 35:211–214, 1994
Petritsch W, Eherer AJ, Holzer-Petsche U, Hinterleitner TA, Beubler E, Krejs GJ: Effect of cholera toxin on the human jejunum. Gut 33:1174–1178, 1992
Eherer AJ, Hinterleitner TA, Petritsch W, Holzer-Petsche U, Beubler E, Krejs GJ: Effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine antagonists on cholera-toxin induced secretion in the human jejunum. Eur J Clin Invest 24:664–668, 1994
Holmgren J: Pathogenesis. In Cholera. D Barua, WB Greenough (eds). New York, Plenum Press, 1992, pp 199–208
Moriarty KJ, Higgs NB, Woodford M, Turnberg LA: An investigation of the role of possible neural mechanisms in cholera toxin-induced secretion in rabbit ileal mucosa in vitro. Clin Sci 77:161–166, 1989
Carey HV, Cooke HJ: Submucosal nerves and cholera toxin-induced secretion in guinea pig ileum in vitro. Dig Dis Sci 31:732–736, 1986
Hubel KA, Shirazi S: Human ileal transport in vitro: Changes with electrical field stimulation and tetrodotoxin. Gastroenterology 83:63–68, 1982
Sheldon RJ, Malachick ME, Fox DA, Burks TF, Porreca F: Pharmacological characterisation of neural mechanisms regulating mucosal ion transport in mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 249:572–582, 1989
Bearcroft CP, Perrett D, Farthing MJG: 5-Hydroxytryptamine release into human jejunum by cholera toxin. Gut 39:528–531, 1996
Lencer WI, Strohmeier G, Moe S, Carlsen SL, Constable CT, Madara JL: Signal transduction by cholera toxin: Processing in vesicular compartments does not require acidification. Am J Physiol 269:G548–G557, 1995
Barrett KE: Positive and negative regulation of chloride secretion in T84 cells. Am J Physiol 265:C859–C868, 1993
Binder HJ, Sandle GI: Electrolyte transport in the mammalian colon. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. LR Johnson (ed). New York, Raven Press, 1994, pp 2133–2172
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burleigh, D.E., Borman, R.A. Evidence for a Nonneural Electrogenic Effect of Cholera Toxin on Human Isolated Ileal Mucosa. Dig Dis Sci 42, 1964–1968 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018835815627
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018835815627