Abstract
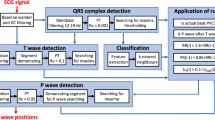
The idea of analyzing P wave inscriptions to discriminate between patients with different diseases isnot new. Whereas standard approaches deal mainly with an analysis of the duration of the P wave, there is anincreasing interest for the P wave morphology. Detailed analysis of the low voltage P wave will require ahardware setup that enables high-quality signal acquisition with low noise interference in combination with anECG subtraction technique. The feasibility of the surface ECG to detect the presence of an abnormalelectrophysiological substrate in the atrial myocardium as well as to localize ectopic atrial rhythms will beenhanced by use of P wave morphological analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dilaveris PE. Noninvasive methods in atrial fibrillation. CEPR 2001;5:177–182.
Hofmann M, Goedel-Meinen L, Beckhoff A, Rehbach K, Schomig A. Analysis of the P-wave in the signal-averaged electrocardiogram: Normal values and reproducibility. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol1996;19:1928–1932.
Dilaveris PE, Gialafos JE. P-wave dispersion: A novel predictor of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Ann Noninvas Electrocardiol 2001;6:159–165.
Opolski G, Scislo P, Stanislawska J, Gorecki A, Steckiewicz R, Torbicki A. Detection of patients at risk for recurrence of atrial fibrillation after successful electrical cardioversion by signal-averaged P-wave ECG. Int J Cardiol 1997;60:181–185.
Yamada T, Fukunami M, Ohmori M, Kumagai K, Sakai A, Kondoh N, Minamino T, Hoki N. Characteristics of frequency content of atrial signalaveraged electrocardiograms during sinus rhythm in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992;19:559–563.
Platonov PG, Carlson J, Ingemansson MP, Roijer A, Hannson A, Chireikin LV, Olsson SB. Detection of inter-atrial conduction defects with unfiltered signal-averaged P-wave ECG in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Europace 2000;2:32–41.
Carlson J, Johansson R, Olsson SB. Classification of electrocardiographic P-wave morphology. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2001;48:401–405.
Hamdan MH, Kalman JM, Barron HV, Lesh MD. P-wave morphology during right atrial pacing before and after atrial flutter ablation–Anew marker for success. Am J Cardiol 1997;79:1417–1420.
Fitzgerald DM, Hawthorne HR, Crossley GH, Simmons TW, Haisty WK Jr. P wave morphology during atrial pacing along the atrioventricular ring. ECG localization of the site of origin of retrograde atrial activation. J Electrocardiol 1996;29:1–10.
Forfang K, Erikseen J. Significance of Pwave terminal force in presumably healthy men. Am Heart J1978;96:739–743.
Ross BA, Zeigler V, Zinner A, Woodall P, Gillette PC. The effect of exercise on the atrial electrogram voltage in young patients. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol1991;14:2092–2097.
Shandling AH, Florio J, Castellanet MJ, Messenger JC, Crump R, Evans K, Rylaarsdarm A, Nolasco M. Physical determinants of the endocardial P wave. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol1990;13:1585–1589.
Dilaveris PE, Färbom P, Batchvarov V, Ghuran A, Malik M. Circadian behavior of P-wave duration, P-wave area, and PR interval in healthy subjects. Ann Noninvas Electrocardiol 2001;6:92–97.
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, Garrigue S, Le Mouroux A, Le Metayer P, Clementy J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 1998;339: 659–666.
Chen S-A, Hsieh M-H, Tai C-T, Tsai C-F, Prakash VS, Yu W-C, Hsu T-L, Ding Y-A, Chang M-S. Initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating from the pulmonary veins. Electrophysiological characteristics, pharmacological responses, and effects of radiofrequency ablation. Circulation 1999;100:1879–1886.
Abramson DI, Fenichel NM, Shookhoff C. A study of electrical activity in the auricles. Am Heart J1938;15:471–481.
Harris BC, Shaver JA, Gray S, Kroetz FW, Leonard JJ. Left atrial rhythm: Experimental production in man. Circulation 1968;37:1000–1014.
Massumi RA, Rajindra RK, Tawakkol AA, Rios JC, Jackson H. Time sequence of right and left atrial depolarization as a guide to the origin of P waves. Am J Cardiol 1969;24:28–36.
Leon DF, Lancaster JF, Shaver JA, Kroetz FW, Leonard JJ. Right atrial ectopic rhythms: Experimental production in man. Am J Cardiol1970;25:6–10.
Mirowski M. Left atrial rhythm, diagnostic criteria and differentiation from nodal arrhythmias. Am J Cardiol 1966;17:203–210.
Scherf D, Schott A. The localization of the site of origin and the spread of extrasystoles. In: Scherf D, Schott A, eds. Extrasystoles and Allied Arrhythmias,2nd ed. London, UK: Heinemann, 1973: 529–559.
Josephson ME. Ectopic rhythms and premature depolarizations. In: Josephson ME(ed). Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology: Techniques and Interpretations. Malvern, PA: Lea & Febiger, 1993: 167–180.
Maclean WAH, Karp RB, Kouchoukos NT, James TN, Waldo AL. P waves during ectopic atrial rhythms in man: A study utilizing atrial pacing with fixed electrodes. Circulation 1975;52:426–434.
Man KC, Chan KK, Kovacek P, Goyal R, Bogun F, Harvey M, Daoud E, Strickberger SA, Morady F. Spatial resolution of atrial pace mapping as determined by unipolar atrial pacing at adjacent sites. Circulation 1996;94:1357–1363.
Kawano S, Hiraoka M. P wave mapping in ectopic atrial rhythm. In: Yasui S, Abildskov JA, Yamada K, Harumi K(eds). Advances in Body Surface Mapping and High Resolution ECG. Nagoya, Japan: Life Medicom, 1995:47–56.
SippensGroenewegen A, Peeters HAP, Jessurun ER, Linnenbank AC, Robles de Medina EO, Lesh MD, van Hemel NM. Body surface mapping during pacing at multiple sites in the human atrium. P-wave morphology of ectopic right atrial activation. Circulation 1998;97:369–380.
Saksena S, Prakash A, Krol RB, Shankar A. Regional endocardial mapping of spontaneous and induced atrial fibrillation in patients with heart disease and refractory atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol1999;84:880–889.
Yamane T, Shah DC, Peng J-T, Jaïs P, Hocini M, Deisenhofer I, Choi K-J, Macle L, Clémenty J, Haïssaguerre M. Morphological characteristics of P waves during selective pulmonary vein pacing. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;38:1505–1510.
Lu T-M, Tai C-T, Hsieh M-H, Tsai CF, Lin YK, Yu WC, Tsao HM, Lee SH, Ding YA, Chang MS, Chen SA. Electrophysiological characteristics in initiation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation from a focal area. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;37: 1658–1664.
Gritzali F, Frangakis G, Papakonstantinou G. Detection of the P and T waves in an ECG. Comput Biomed Res 1989;22:83–91.
Thakor N, Yi-Sheng Z. Applications of adaptive filtering to ECG analysis: Noise cancellation and arrhythmia detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng1991;38:785–794.
Sippensgroenewegen A, Mlynach MD, Roithinger FX, Goseki Y, Lesh MD. Electrocardiographic analysis of ectopic atrial activity obscured by ventricular repolarization: P wave isolation using an automatic 62–lead QRST subtraction algorithm. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2001;12:780–790.
DuFault R, Wilcox A. Automatic P-wave detection in surface ECGs. Proc Annu Int Conf IEEE EMBS, Chicago, IL, 1986.
Vasquez C, Hernandez A, Mora F, Carrault G, Passariello G. Atrial activity enhancement by Wiener filtering using an artificial neural network. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2001;48:940–944.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dilaveris, P.E., Gialafos, J.E. Future Concepts in P Wave Morphological Analyses. Card Electrophysiol Rev 6, 221–224 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016320807103
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016320807103