Abstract
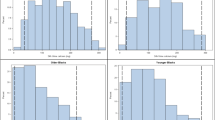
The purpose of the present investigation was to determine the effect of chronic aspirin administration on the serum concentration and renal clearance of inorganic sulfate in healthy volunteers. In a randomized crossover study, eight male subjects received either no treatment or 975 mg of enteric-coated aspirin three times daily for 8 days. Blood and urine samples were collected on the eighth day over a 7-hr period. Midpoint salicylic acid concentrations in serum varied between 55 and 182 µg/ml (mean concentration of 109 µg/ml). Serum inorganic sulfate concentrations demonstrated a small but significant decrease on the eighth day of aspirin administration but there was no apparent change in the renal clearance of sulfate. There were significant correlations between the renal clearances, urinary excretion rates, and serum concentrations of creatinine and sulfate, reflecting the dependence of sulfate homeostasis on renal function. The serum concentration and renal clearance of creatinine, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus were unaffected by aspirin treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. H. Demeio. In D. M. Greenway (ed.), Metabolic Pathways, 3rd ed., Academic Press, New York, 1975, pp. 287–357.
A. A. Farooqui and L. A. Horrocks. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 66:87–95 (1985).
F. A. Ofusu, G. J. Modi, and M. A. Blajchman. Biochem. J. 248:889–896 (1987).
J. M. Walenga, M. Petitou, M. Samama, J. Fareed, and J. Choay. Thromb. Res. 52:553–563 (1988).
W. B. Huttner. Topics Biol. Sci. 12:361–363 (1987).
G. J. Mulder. In G. J. Mulder (ed.), Sulfation of Drugs and Related Compounds, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1981, pp. 131–186.
F. Berglund. Acta Physiol. Scand. 49 (Suppl. 172):1–37 (1960).
E. L. Becker, H. O. Heinemann, K. Igarashi, J. E. Hodler, and H. Gershberg. J. Clin. Invest. 39:1909–1913 (1960).
M. E. Morris, O. Kwon, and I. L. Mansfield. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 244:945–949 (1988).
L. T. Wong, G. Solomanraj, and B. H. Thomas. Xenobiotica. 6:574–584 (1976).
B. H. Thomas, W. Zeitz, and B. B. Coldwell. J. Pharm. Sci. 9:1367–1370 (1974).
B. J. de Vries, W. B. van den Berg, and L. B. A. van de Putte Arth. Rheum. 28:922–929 (1985).
M. J. Palmoski and K. D. Brandt. Arth. Rheum. 26:994–1001 (1983).
B. J. de Vries, W. B. van den Berg, E. Vitters, and L. B. A. Van de Putte. J. Rheumatol. 13:686–693 (1986).
J. C. Lukas, T. S. Rosenkrantz, J. R. Raye, P. J. Porte, and A. F. Phillips. Am. J. Obstet. 156:245–249 (1987).
G. Turner and E. Collins. Lancet 2:338–339 (1975).
M. E. Morris and I. L. Mansfield. J. Pharm. Sci. 77:814–815 (1988).
H. Greiling and B. Schuler. Z. Rheumaforsch. 22:47–56 (1963).
G. Levy. J. Pharm. Sci. 54:959–967 (1965).
M. E. Morris and G. Levy. Anal. Biochem. 172:16–21 (1988).
K. R. Krijgsheld, E. Scholtens, and G. J. Mulder. Biochem. Pharmacol. 30:1973–1979 (1981).
Z. I. Sabry, S. B. Shadarevian, J. W. Cowan, and J. A. Campbell. Nature (Lond.) 206:931–933 (1965).
I. Smith and P. D. Mitchell. Biochem. J. 142:189–191 (1974).
M. E. Morris and G. Levy. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 20:107–114 (1983).
M. Walser, D. W. Seldin, and A. Grollman. J. Clin. Invest. 32:299–311 (1953).
P. Lundquist, J. Mårtensson, B. Sörbo, and S. Öhman. Clin. Chem. 26:1178–1181 (1980).
M. E. Morris and G. Levy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 33:529–536 (1983).
J. R. Leonards and G. Levy. JAMA 193:99–104 (1965).
J. H. Lin and G. Levy. J. Pharm. Sci. 72:213–217 (1983).
M. S. Meier and W. Schmidt-Kessen. Munch. med. Wschr. 120:357–362 (1978).
M. E. Morris, S. LeRoy, and S. C. Sutton. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 25:371–382 (1987).
R. M. Freeman and C. J. Richards. Kidney Int. 15:167–175 (1979).
P. Kincaid-Smith. Drugs 32(Suppl. 4):109–128 (1986).
G. Levy. Drug Metab. Rev. 9:3–19 (1979).
E. J. Zambraski, D. C. Atkinson, and J. Diamond. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 247:96–103 (1988).
E. J. Zambraski, S. M. Guidotti, D. C. Atkinson, and J. Diamond. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 247:983–988 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morris, M.E., Benincosa, L.J. Sulfate Homeostasis. II. Influence of Chronic Aspirin Administration on Inorganic Sulfate in Humans. Pharm Res 7, 719–722 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015811504674
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015811504674