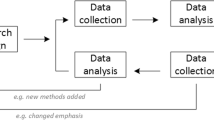
Abstract
Online data collection is becoming an essential and efficient tool for evaluators, researchers, and other educators. This paper touches on elements of the rather short, but eventful history of online data collection. A brief review of the current literature is presented, followed by a list of pros and cons to be considered when stepping into online surveying. Finally there is a brief look at what makes the online survey run—a database connected to the Internet. For those who would prefer, alternatives to creating or hosting your own online surveys are offered. The paper closes with contemplation toward the future of online data gathering.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abdouch, R., Grandgenett, N., Topp, N., Ostler, E., Pawloski, B., Timms, M., and Peterson, J. (1998). The Community Discovered: The Search for Meaning Through the Integration of Art and Technology in K-12 Education. Evaluation Progress Report No. 4. (ED436470)
Bowers, D. K. (1999,Winter98/Spring99). FAQ on online research. Marketing Research 10: 45-49.
Gaddis, S. E. (1998, June). How to design online surveys. Training and Development 52: 67-72.
Garrison, S., and Fenton, R. (1999, July-August). Database driven web systems for education. Educational Technology 39: 31-37.
urveys/survey-1997-10/
Hays, R. (1998, April 13). Internet-based surveys provide fast results. Marketing News 32: 13.
Lake, M. (1998). Surveying the scene: Take the sting out of information gathering. Computer Currents. Retrieved August 9, 1999, from http://www.currents.net/magazine/national/1609/ cprc1609.html
Meehan, M. L., and Burns, R. C. (1997, March 24-28). E-mail survey of a listserv discussion group: Lessons learned from surveying an electronic network of learners. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Chicago, IL. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED 411 292)
Read, W. H. (1991, January). Gathering opinion online. HRMagazine 36: 51.
Sheehan, K. B., and Hoy, M. G. (1999, March). Using e-mail to survey Internet users in the United States: Methodology and assessment. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication 4: RetrievedAugust 29, 2001, from http://www.ascusc.org/ jcmc/vol4/issue3/sheehan.html
Smith, C. B. (1997, June). Casting the Net: Surveying an Internet population. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication 3: Retrieved August 29, 2001, from http://jcmc.huji. ac.il/vol3/issue1/smith.html
Stanton, J. M. (1998, Fall). An empirical assessment of data collection using the Internet. Personnel Psychology 51: 709-726.
Trochim,W. (1999). The Research Methods Knowledge Base, 1st ed., Atomic Dog Publishing, Cincinnati, OH. Retrieved August 29, 2001, from http://trochim.human.cornell.edu/kb/
WebSM. (2001). WebSM: Web Survey Methodology Study. Research on Internet in Slovenia Project website. Retrieved August 30, 2001, from http://wsm.org
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topp, N.W., Pawloski, B. Online Data Collection. Journal of Science Education and Technology 11, 173–178 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014669514367
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014669514367