Abstract
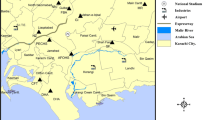
In order to quantify the role of industries on atmospheric depositions, wet depositions were collected at different sites in Singrauli area of Sonbhadra district, U.P., India. Rainwater samples were collected on event basis and were analyzed for pH and concentration of H+ ion, cations and anions. The monthly variations in rainwater pH clearly indicate that early rainfall is more alkaline and as rainy season proceeds rainwater showed lower pH. The pH of rain from June to September varied from 6.6 to 4.8 at most polluted locality. Among different cations, Ca2+ showed maximum concentration followed by NH4 +,Na+, Mg2+ and then K+, whereas among anions sulphate concentration was maximum followed by nitrate and then chloride.
A significant positive correlation observed between sulphate and accumulated rainfall suggests that the source of sulphate is mainly the industrial activities. While the negative correlations of other cations with accumulated rain suggest their additional sources in the area. The study clearly indicates that the abundance of alkaline substances reduces the acidity of wet depositions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, M., and Singh, J.: 2000, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 60, 261.
Chandrawanshi, C. K., Patel, V. K. and Patel, K. S.: 1997, Indian Journal of Environmental Protection 17, 656.
Florence, T. M. and Farrar, Y. J.: 1971, Analytical Chemistry Acta 54, 373.
Jackson, M. L.: 1958, Soil Chemical Analysis. Asia Publishing House, Bombay, India.
Khemani, L. T., Momin, G. A., Rao, P. S. P., Pillai, A. G., Safai, P. D., Mohan, K. and Rao, M. G.: 1994, Atmospheric Environment 28, 3145.
Khemani, L. T., Tiwari, S., Singh, G., Momin, G. A., Naik, M. S., Rao, P. S. P., Safai, P. D. and Pillai, A. G.: 1995, TAO 6, 453.
Li, T. Y. and Landsberg, H. E.: 1975, Atmospheric Environment 9, 1.
Likens, G. E. and Bormann, F. H.: 1974, Science 184, 1176.
Matzner, E. and Meiwes, K. J.: 1994, Journal of Environmental Quality 3, 87.
Moore, P. D. and Chapman, S. B.: 1986, Methods in Plant Ecology. Blackwell Scientific Publications, London.
Sequeira, R.: 1976, Tellus 28, 275.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J. J.: 1970, Aquatic Chemistry. Wiley Inter Science, London.
Subramanian, V. and Saxena, K. K.: 1980, Tellus 32, 558.
Wetzel, R. G., Likens, G. E.: 1979, Lymnological analysis. W. B. Savder, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agrawal, M., Singh, R.K. Effect of Industrial Emission on Atmospheric Wet Deposition. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 130, 481–486 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013814108347
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013814108347