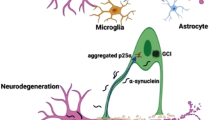
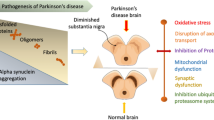
Abstract
Neurodegenerative diseases are often consideredincurable with no efficient therapies to modifyor halt the progress of disease, and ultimatelylead to reduced quality of life and to death.Our knowledge of the nervous system in healthand disease has, however, increasedconsiderably during the last fifty years andtoday, neuroscience reveals promising newstrategies to deal with disorders of thenervous system.Some of these results have been implementedwith success in the treatment of Parkinson'sdisease, a common neurodegenerative illnessaffecting approximately 1% of the populationaged seventy or more. Parkinson's disease ischaracterized by a massive loss of dopaminergicneurons in the substantia nigra, leading tosevere functional disturbance of the neuronalcircuitry in the basal ganglia. A thoroughdescription of basal ganglia circuitry inhealth and disease is presented. We describehow the functional disturbances seen inParkinson's disease may be corrected atspecific sites in this circuitry by medicaltreatment or, in advanced stages of Parkinson'sdisease, by neurosurgical methods. The latterinclude lesional surgery, neuraltransplantation and deep brain stimulation,together with future treatment strategies usingdirect or indirect implantation of geneticallymodified cell-lines capable of secretingneurotrophic factors or neurotransmitters.Advantages and disadvantages are brieflymentioned for each strategy and theimplications for the future and the possibleuse of these interventions in otherneurodegenerative diseases are discussed, withspecial emphasis on deep brain stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albin RL, Young AB and Penney B (1989) The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci 12: 366–375
Alexander GE (1994) Basal ganglia-Thalamocortical circuits: Their role in control of movements. J Clin Neurophysiol 11: 420–431
Alexander GE and Crutcher MD (1990) Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci 13: 266–271
Ballard PA, Tetrud JW and Langston JW (1985) Permanent human parkinsonism due to MPTP. Neurology 35: 949–956
Baron MS, Vitek JL, Bakey RA, Green J, Kaneoke Y, Hashimoto T, Turner RS, Woodard JL, Cole SA, McDonald WM and DeLong MR (1996) Treatment of advanced Parkinson's disease by posterior GPi pallidotomy: 1-year results of a pilot study. Ann Neurol 40: 355–366
Benabid AL, Pollak P, Louveau A, Henry S and de Rougemont J (1987) Combined (thalamotomy and stimulation) stereotactic surgery of the VIM thalamic nucleus for bilateral Parkinson's disease. Appl Neurophysiol 50: 344–346
Benabid AL, Pollak P, Gervason C, Hoffmann D, Gao DM, Hommel M, Perret JE and de Rougemont J (1991) Long-term suppression of tremor, by chronic stimulation of the ventral intermediate thalamic nucleus. Lancet 337: 403–406
Benabid AL, Pollak P, Gao D, Hoffman D, Limousin P, Gay E, Payen I and Benazzouz A (1996) Chronic electrical stimulation of the ventralis intermedius nucleus of the thalamus as a treatment of movement disorders. J Neurosurg 84: 203–214
Bergman H, Wichmann T and DeLong MR (1990) Reversal of experimental parkinsonism by lesions of the subthalamic nucleus. Science 249: 1436–1438
Bernheimer H, Birkmeyer W, Hornykiewicz O, Jellinger K and Seitelberger F (1973) Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. J Neurol Sci 20: 415–455
Bertler A and Rosengren E (1959) Occurence and distribution of catecholamines in brain. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 47: 350–361
Birkmayer W and Hornykiewicz O (1961) Der L-3,4-Dioxyphenylalanin (= DOPA)-Effekt bei der Parkinson-Akinesie. Wien Klin Wochenschr 73: 786–786
Björklund A and Stenevi U (1979) Reconstruction of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway by intracerebral nigral transplants. Brain Res 177: 555–560
Blond S, Caparros-Lefebvre D, Parker F, Assaker R, Petit H, Guieu JD and Christiaens JL (1992) Control of tremor and involuntary movement disorders by chronic stereotactic stimulation of the ventral intermediate thalamic nucleus. J Neurosurg 77: 62–68
Boer GJ (1994) Ethical guidelines for the use of human embryonic or fetal tissue for experimental and clinical neurotransplantation and research. J Neurol 242: 1–13
Bonifati V, Fabrizio E, Vanacore N, De Mari M and Meco G (1995) Familial Parkinson's disease: a clinical genetic analysis. Can J Neurol Sci 22: 272–279
Bredberg E, Tedroff J, Aquilonius S-M and Paalzow L (1990) Pharmacokinetics and effects of levodopa in advanced Parkinson's disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39: 385–389
Bredberg E, Nilsson D, Johansson K, Aquilonius S-M, Johnels B, Nyström C and Paalzow L (1993) Intraduodenal infusion of a water-based levodopa dispersion for optimisation of the therapeutic effect in severe Parkinson's disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 45: 117–122
Brundin P, Strecker RE, Widner H, Clarke DJ, Nilsson OG, Astedt B, Lindvall O and Björklund A (1988) Human fetal dopamine neurons grafted in a rat model of Parkinson's disease: immunological aspects, spontaneous and drug-induced behaviour, and dopamine release. Exp Brain Res 70: 192–208
Brundin P, Pogarell O, Hagell P, Piccini P, Widner H, Schrag A, Kupsch A, Crabb L, Odin P, Gustavii B, Björklund A, Brooks DJ, Marsden CD, Oertel WH, Quinn NP, Rehncrona S and Lindvall O (2000) Bilateral caudate and putamen grafts of embryonic mesencephalic tissue treated with lazaroids in Parkinson's disease. Brain 123: 1380–1390
Burns RS, Chiueh CC, Markey SP, Ebert MH, Jacobowitz DM and Kopin IJ (1983) A primate model of parkinsonism: selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons in pars compacta of the substantia nigra by N-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3,6-tetrahydropyrid ine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 4546–4550
Carlsson A (1959) The occurrence, distribution and physiological role of catecholamines in the nervous system. Pharmacol Rev 11: 490–493
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M, Magnuson T and Waldeck B (1958) On the presence of 3-hydroxythyramin in the brain. Science 127: 471–471
Ceballos-Baumann AO, Obeso JA, Vitek JL, DeLong MR, Bakay R, Linazasoro G and Brooks DJ (1994) Restoration of thalamocortical activity after posteroventral pallidotomy in Parkinson's disease. Lancet 344: 814
Chesselet M-F and Delfs JM (1996) Basal ganglia and movement disorders: an update. Trends Neurosci 19: 417–422
Colzi A, Turner K and Lees AJ (1998) Continuous subcutaneous waking day apomorphine in the long term treatment of levodopa induced interdose dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64: 573–576
Cooper IS (1965) Surgical treatment of parkinsonism. Ann RevMed 16: 309–330
Davis GC, Williams AC, Markey SP, Ebert MH, Caine ED, Reichert CM and Kopin IJ (1979) Chronic parkinsonism secondary to intravenous injection of meperidine analogues. Psychiatry Res 1: 249–254
Deacon T, Schumacher J, Dinsmore J, Thomas C, Palmer P, Kott S, Edge A, Penney D, Kassissieh S, Dempsey P and Isacson O (1997) Histopathological evidence of fetal pig neural cell survival after transplantation into a patient with Parkinson's disease. Nature Med 3: 350–353
DeLong MR (1990) Primate models of movement disorders of basal ganglia origin. Trends Neurosci 13: 281–285
Duda JE, Lee VM and Trojanowski JQ (2000) Neuropathology of synuclein aggregates. J Neurosci Res 61: 121–127
Dunnett SB (1991) Transplantation of embryonic dopamine neurons; what we know from rats. J Neurol 238: 65–74
Dunnett SB and Annett LE (1991) Nigral transplants in primate models of parkinsonism. In: Lindvall O, Björklund A and Widner H (eds) Intracerebral Transplantation in Movement Disorders. Experimental Basis and Clinical Experiences, pp 27–51. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam
Duvoisin RC (1999) Genetic and environmental factors in Parkinson's disease In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 161–163. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Duvoisin RC and Yahr MD (1965) Encephalities and Parkinsonism. Arch Neurol 12: 227
Fahn S and Cohen G (1992) The oxidant strees hypothesis in Parkinson's disease: evidence supporting it. Ann Neurol 32: 805–812
Fearnley J and Lees AJ (1997) Parkinson's disease: Neuropathology. In: Watts RL and Koller WC (eds) Movement Disorders: Neurologic Principles and Practice, pp 263–278. McGraw-Hill, New York
Fisher LJ and Ray J (1994) in vivo and ex vivo gene transfer to the brain. Curr Opin Neurobiol 4: 735–741
Forno LS (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55: 259–272
Freed CR, Breeze RE, Rosenberg NL, Schneck SA, Wells TH, Barrett JN, Grafton ST, Huang SC, Eidelberg D and Rottenberg DA (1990) Transplantation of human fetal dopamine cells for Parkinson's disease. Results at 1 year. Arch Neurol 47: 505–512
Freed WJ (1991) Substantia nigra grafts and Parkinson's disease: from animal experiments to human therapeutic trials. Restor Neurol Neurosci 3: 109–134
Freeman W (1925) The pathology of paralysis agitans. Ann Clin Med 4: 106–116
Galpern WG, Burns LH, Deacon TW, Dinsmore J and Isacson O (1996) Xeno-transplantation of porcine fetal ventral mesencephalon in a rat model of Parkinson's disease: functional recovery and graft morphology. Exp Neurol 140: 1–13
Galvez-Jimenez N, Lozano AM, Duff J, Trèpanier L, Saint-Cyr JA and Lang AE (1996) Bilateral pallidotomy: pronounced amelioration of incapacitating levodopa-induced dyskinesias but accompanying cognetive decline. Mov Disord 11: 242
Gassen M, Gross A and Youdim MBH (1998) Apomorphine enantiomers protect cultured pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells from oxidative stress induced by H2O2 and 6-Hydroxydopamine. Mov Disord 13(2): 242–248
Gasser T (1999) Is Parkinson's disease an inherited condition? In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 143–152. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Gerfen CR (1992) The neostriatal mosaic: multiple levels of compartmental organization in the basal ganglia. Ann Rev Neurosci 15: 285–320
Ghika J, Favre J, Frankhauser H and Regli F (1996) Neurological and neuropsychological complications of bilateral contemporanous pallidotomy in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 46: A417
Golbe LI, Miller D and Duvoisin RC (1990) Autosomal dominant Lewy-body Parkinson's disease. In: Strefler MR, Korczyn AD, Melamed E and Youdoim MGH (eds) Parkinson's Disease: Anatomy, Pathology, and Therapy. Advances in Neurology, Vol 53, pp 287–292. Raven Press, New York
Greenfield JG and Bosanquet FD (1953) The brain-stem lesions in parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 16: 213–226
Gross C, Rougier A, Guehl D, Boraud T, Julien J and Bioulac B (1997) High-frequency stimulation of the globus pallidus internalis in Parkinson's disease: a study of seven cases. J Neurosurg 87: 491–498
Grünblatt E, Mandel S, Berkuzki T and Youdim MBH (1999) Apomorphine protects against MPTP-Induced neurotoxicity in mice. Mov Disord 14(4): 612–618
Halloway R and the Parkinson study group (2000) Pramipexole versus levodopa in early Parkinson's disease: a randomized clinical trial. Neurology 54(3): S19. 003
Hariz MI (1999) Current controversies in pallidal surgery. In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 593–602. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Haas RH, Nasirian F, Nakano K, Ward D, Pay M, Hill R and Shults CW (1995) Low platelet mitochondrial complex I and complex II/III activity in early untreated Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 37: 714–722
Harder S, Baas H and Rietbrock S (1995) Concentration-effect relationship of levodopa in patients with Parkinson's disease. Clin Pharmacokinet 29: 243–256
Henderson BTH, Clough CG, Hughes RC et al. (1991) Implantation of human fetal ventral mesencephalon to the right caudate nucleus in advanced Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol 48: 822–827
Hirai T, Ryu H, Nagaseki Y, Gaur MS, Fujii M and Takizawa T (1999) Image-guided electrophysiologically controlled posteroventral pallidotomy for the treatment of Parkinson's disease: A 28-case analysis. In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 585–591. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Iacono RP, Carlson JD, Kuniyoshi SM, Li YJ, Mohamed AS and Maeda G (1997) Electrophysiological target localization in posteroventral pallidotomy. Acta Neurochir 139: 433–441
Jankovic J, Lai EC, Krauss J and Grossman R (1999) Surgical Treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesias. In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 603–609. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Jenkins IH, Fernandez W, Playford ED, Lees AJ, Frackowiak RS, Passingham RE and Brooks DJ (1992) Impaired activation of the supplementary motor area in Parkinson's disease is reversed when akinesia is treated with apomorphine. Ann Neurol 32: 749–757
Jenner P and Olanow CW 1996) Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Neurology 47: 161–170
Kelly PJ (1988) Contempory stereotactic ventralis lateral thalamotomy in the treatment of parkinsonian tremor and other movement disorders. In: Heilbrun MP (ed) Stereotactic Neurosurgery, Vol 2, pp 133–147. William and Wilkins, Baltimore
Kelly PJ and Gillingham FJ (1980) The long-term results of stereotaxic surgery and L-dopa therapy in patients with Parkinson's disease. A 10-year follow-up study. J Neurosurg 53: 332–337
Kish SJ, Shannak HK and Hornykiewicz O (1988) Uneven pattern of dopamine loss in the striatum of patients with Parkinson's disease-pathophysiologic and clinical implications. N Engl J Med 318: 876–880
Kondziolka D, Dempsey PK, Lunsford LD, Kestle JR, Dolan EJ, Kanal E and Tasker RR (1992) A comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography for stereotactic coordinate determination. Neurosurgery 30: 402–407
Kordower JH, Freeman TB, Snow BJ, Vingerhoets FJ, Mufson EJ, Sanberg PR, Hauser RA, Smith DA, Nauert GM, Perl DP et al. (1995) Neuropathological evidence of graft survival and striatal reinnervation after the transplantation of fetal mesencephalon in a patient with Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 332: 1118–1124
Kordower JH, Emborg ME, Bloch J, Ma SY, Chu Y, Leventhal L, McBride J, Chen E-Y, Palfi S, Roitberg BZ, Brown WD, Holden JE, Pyzalski R, Taylor MD, Carvey P, Ling Z, Trono D, Hantraye P, Déglon N and Aebischer P (2000) Neurodegeneration prevented by lentiviral vector delivery of GDNF in primate models of Parkinson's disease. Science 290: 767–772
Kostic V, Przedborski S, Flaster E and Sternic N (1991) Early development of levodopa-induced dyskinesias and response fluctuations in young-onset Parkinson's disease. Neurology 41: 202–205
Krack P, Pollak P, Limousin P, Hoffmann D, Benazzouz A, Le Bas JF, Koudsie A and Benabid AL (1998a) Opposite motor effect of pallidal stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 43: 180–192
Krack P, Pollak P, Limousin P, Hoffmann D, Xie J, Benazzouz A and Benabid AL (1998b) Subthalamic nucleus or internal pallidal stimulation in young onset Parkinson's disease. Brain 121: 451–457
Laitinen LV, Bergenheim AT and Hariz MI (1992) Leksell's posteroventral pallidotomy in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosurg 76: 53–61
Lang AE and Lozano AM (1998) Parkinson's disease: Second of two parts. N Engl J Med 339: 1130–1143
Lang AE, Lozano A, Montgomery EB, Tasker RR and Hutchison WD (1999) Posteroventral medial Pallidotomy in advanced Parkinson's disease. In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 575–583. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Langston JW (1995) MPTP as it relates to the etiology of Parkinson's disease. In: Ellenberg JH, Koller WH and Langston JW (eds) Etiology of Parkinson's Disease, pp 367–399. Marcel Dekker, New York
Langston JW, Ballard P, Tetrud J and Irwin I (1983) Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-Analog synthesis. Science 219: 979–980
Langston JW, Forno LS, Rebert CS and Irwin I (1984) Selective nigral toxicity after systemic administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in the squirrel monkey. Brain Res 292: 390–394
Larsen JP, Boas J and Erdal J (1999) Does selegiline modify progression of early Parkinson's disease? Results from a five year study. The Norwegian-Danish Study Group. Eur J Neurol 6: 539–547
Lazzarini AM, Myers RH, Zimmerman TR Jr, Mark MH, Golbe LI, Sage JI, Johnson WG and Duvoisin RC (1994) A clinical genetic study of Parkinson's disease: evidence for dominant transmission. Neurology 44(31): 499–506
Lees AJ (1995) Comparison of therapeutic effects and mortality data of levodopa and levodopa combined with selegiline in patients with early, mild Parkinson's disease. BMJ 311: 1602–1607
Lilienfeld DE and Perl DP (1993) Projected neurodegenerative disease mortality in the United States, 1990–2040. Neuroepidemiology 12: 219–228
Limousin P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, Hoffman D, Le Bas J-F, Broussolle E, Perret JE and Benabid A-L (1995) Effect on parkinsonian signs and symptoms of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Lancet 345: 91–95
Limousin P, Greene J, Pollak P, Rothwell J, Benanid A-L and Frackowiak R (1997) Changes in cerebral activity pattern due to subthalamic nucleus or internal pallidum stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 42: 283–291
Lindvall O (1994) Clinical application of neuronal grafts in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol 241: S54-S56
Lindvall O (1999) Neural transplantation: can we improve the symptomatic relief? In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 635–640. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Lindvall O, Rehncrona S, Brundin P, Gustavii B, Astedt B, Widner H, Lindholm T, Björklund A, Leenders KL, Rothwell JC et al. (1989) Human fetal dopamine neurons grafted into the striatum in two patients with severe Parkinson's disease: a detailed account of methodology and a 6-month follow-up. Arch Neurol 46: 615–631
Lindvall O, Sawle G, Widner H, Rothwell JC, Björklund A, Brooks D, Brundin P, Frackowiak R, Marsden CD, Odin P and Rehncrona S (1994) Evidence for long-term survival and function of dopaminergic grafts in progressive Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 35: 172–180
Lozano A, Lang AE, Galvez-Jimenez N, Miyasaki J, Duff J, Hutchinson WD and Dostrovsky JO (1995) Effect of GPi pallidotomy on motor function in Parkinson's disease. Lancet 346: 1383–1387
Lozano A, Hutchison W, Kiss Z, Tasker R, Davis K and Dostrovsky J (1996) Methods for microelectrode-guided posteroventral pallidotomy. J Neurosurg 84: 194–202
Lundberg C, Horellou P, Mallet J and Björklund A (1996) Generation of DOPA-producing astrocytes by retroviral transduction of the human tyrosine hydroxylase gene: in vitro characterization and in vivo effects in the rat Parkinson model. Exp Neurol 139: 39–53
Luquin MR, Scipioni O, Vaamonde J, Gershanik O and Obeso JA (1992) Levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease: clinical and pharmacological classification. Mov Disord 7: 117–124
Maraganore DM, Harding AE and Marsden CD (1991) A clinical and genetic study of familial Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 6(3): 205–211
Martinez-Serrano A and Björklund A (1997) Immortalized neural progenitor cells for CNS gene transfer and repair. Trends Neurosci 20: 530–538
Marsden CD (1994) Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 57: 672–681
Mendez I, Dagher A, Hong M, Hebb A, Gaudet P, Law A, Weerasinghe S, King D, Desrosiers J, Darvesh S, Acorn T and Robertson H (2000) Enhancement of survival of stored dopaminergic cells and promotion of graft survival by exposure of human fetal nigral tissue to glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with Parkinson's disease. J Neurosurg 92: 863–869
Merello M, Piran Arce G, Nouzeilles M and Leiguarda R (2000) Antidyskinetic effect of long-term waking day continuous infusion of apomorphine compared to posteroventral pallidotomy. Mov Disord 15(3): 54
Metman LV, Del Dotto P, Lepoole K, Konitsiotis S, Fang J and Chase TN (1999) Amantadine for levodopa induced dyskinesias: a 1-year follow up study. Arch Neurol 56: 1383–1386
Meyers R (1942) Surgical interruption of the pallidofugal fibers. Its effect on the syndrome of paralysis agitans and technical considerations in its application. N Y St J Med 42: 317–325
Mirra SS, Schneider JA and Gearing M (1997) Neuropathology of movement disorders: an overview. In: Watts RL and Koller WC (eds) Movement Disorders: Neurologic Principles and Practice, pp 263–278. McGraw-Hill, New York
Mjönes H (1949) Paralysis agitans: a clinical genetic study. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand 54: 1–195
Mutch WJ, Dingwall-Fordyce I, Downie AW, Paterson JG and Roy SK (1986) Parkinson's disease in a Scottish city. BMJ 292: 534–536
Nakagawa-Hattori Y, Yoshino H and Kondo T (1992) Is Parkinson's disease a mitochondrial disorder? J Neurol Sci 107: 29–33
Nakao N, Frodl EM, Duan WM, Widner H and Brundin P (1994) Lazaroids improve the survival of grafted rat embryonic dopamine neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 12408–12412
Nicklas WJ, Vyas I and Heikkila RE (1985) Inhibition of NADH-linked oxidation in brain mitochondria by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine, a metabolite of the neurotoxin, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Life Sci 36: 2503–2508
Nilsson D, Hansson L-E, Johansson K, Nyström C, Paalzow L and Aquilonius S-M (1998) Long-term intraduodenal infusion of a water based levodopa-carbidopa dispersion in very advanced Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol Scand 97: 175–183
Nisipeanu P, Paleacu D and Korczyn AD (1997) Infectious and postinfectious parkinsonism. In: Watts RL and Koller WC (eds) Movement Disorders: Neurologic Principles and Practice, pp 307–313. McGraw-Hill, New York
Nutt JG (1987) 'On-off’ phenomenon: relation to levodopa pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Ann Neurol 22: 535–540
Offen D, Hochman A, Gorodin S, Ziv I, Shirvan A, Barzilai A and Melamed E (1999) Oxidative stress and neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease: Implications from studies on dopamine-induced apoptosis. In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 265–269. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Olanow CW, Fahn S, Langston JW and Godbold J (1996) Selegiline and mortality in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 40: 841–845
Olanow CW, Myllyla VV, Sotaniemi KA, Larsen JP, Palhagen S, Przuntek H, Heinonen EH, Kilkku O, Lammintausta R, Maki-Ikola O and Rinne UK (1998) Effects of selegiline on mortality in patients with Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis. Neurology 51: 825–830
Pahwa R (1997) Toxin-induced parkinsonian syndromes. In: Watts RL and Koller WC (eds) Movement Disorders: Neurologic Principles and Practice, pp 315–323. McGraw-Hill, New York
Parent A and Hazrati L-N (1995a) Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. I. The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Brain Res Rev 20: 91–127
Parent A and Hazrati L-N (1995b) Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. II. The place of subthalamic nucleus and external pallidum in basal ganglia circuitry. Brain Res Rev 20: 128–154
Parkinson J (1817) An essay on the shaking palsy. Whittingham and Rowland, London
Payami H, Larsen K, Bernard S and Nutt J (1994) Increased risk of Parkinson's disease in parents and siblings of patients. Ann Neurol 36 (4): 659–661
Piccini P, Brooks DJ, Björklund A, Gunn RN, Grasby PM, Rimoldi O, Brundin P, Hagell P, Rehncrona S, Widner H and Lindvall O (1999) Dopamine release from nigral transplants visualized in vivo in a Parkinson's patient. Nat Neurosci 2(12): 1137–1140
Playford ED, Jenkins IH, Passingham RE, Nutt J, Frackowiak RS and Brooks DJ (1992) Impaired mesial frontal and putamen activation in Parkinson's disease: a positron emission tomography study. Ann Neurol 32: 151–161
Poewe W and Wenning GK (2000) Apomorphine: an underutilized theraphy for Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 15(5): 789–794
Rascol O, Brooks DJ, Korczyn AD, De Deyn PP, Clarke CE and Lang AE (2000) A five year study of the incidence of dyskinesia in patients with early Parkinson's disease who were treated with ropinirole or levodopa. N Engl J Med 342: 1484–1491
Rinne UK, Bracco F, Chouza C, Dupont E, Gershanik O, Masso JFM, Montastruc J-L and Marsden CD (1999) Early treatment of Parkinson's disease with cabergoline delays the onset of motor complications: results of a double-blind levodopa controlled trial. Eur J Neurol 6(5): S17-S23
Rodriguez MC, Obeso JA and Olanaw CW (1998) Subthalamic nucleus-mediated excitotoxicity in Parkinson's disease: A target for neuroprotection. Ann Neurol 44(1): S175-S188
Rosenblad C, Martinez-Serrano A and Björklund A (1996) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor increases survival, growth and function of intrastriatal fetal nigral dopaminergic grafts. Neurosci 75: 979–985
Rybecki BA, Johnson CC, Uman J and Gorell JM (1993) Parkinson's disease mortality and the industrial use of heavy metals in Michigan. Mov Disord 8: 87–92
Schurman PR, Speelman DJ and Bosch DA (1998) Thalamic stimulation versus thalamotomy in a prospective randomized trial. Acta Neurochir 140: 838
Selby G (1967) Stereotactic surgery for the relief of Parkinson's disease. Part 1. A critical review. J Neurol Sci 5: 315–342
Semchuk K, Love EJ and Lee RG (1992) Parkinson's disease and exposure to agricultural work and pesticide chemicals. Neurology 42: 1328–1335
Siegfried J and Lippitz B (1994) Bilateral chronic electrostimulation of ventroposterolateral pallidum: a new therapeutic approach for alleviating all Parkinsonian symptoms. Neurosurgery 35: 1126–1130
Siegfried J, Taub E and Wellis GN (1999) Long-term electrostimulation of the ventroposterolateral pallidum in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 623–626. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Smith Y and Parent A (1988) Neurons of the subthalamic nucleus in primates display glutamate but not GABA immunoreactivity. Brain Res 453: 353–356
Smith Y, Parent A, Séguéla P and Descarries L (1987) Distribution of GABA immunoreactive neurons in the basal ganglia of the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). J Comp Neurol 259: 50–65
Snow BJ, MacDonald L, Mcauley D and Wallis W 2000) The effect of amantadine on levo-dopa induced dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Pharmacol 23: 82–85
Spencer DD, Robbins RJ, Naftolin F et al. (1992) Unilateral transplantation of human fetal mesencephalic tissue into the caudate nucleus of patients with Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 327: 1541–1548
Spiegel EA and Wycis HT (1954) Ansotomy in paralysis agitans. Arch Neurol Psychiat (Chic.) 71: 598–614
Spiegelmann R and Chasin S (1996) Posteroventral pallidotomy: experience with 100 cases. Acta Neurochir 138: 644
Svennilson E, Torvik A, Lowe R and Leksell L (1960) Treatment of parkinsonism by stereotactic thermolesions in the pallidal region. A clinical evaluation of 81 cases. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand 35: 358–377
Tanner CM (1989) The role of environmental toxins in the etiology of Parkinson's disease. Trends Neurosci 12: 49–54
Tanner CM and Ben-Shlomo Y (1999) Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease. In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 265–269. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Tanner CM, Hubble JP and Chan P (1997) Epidemiology and genetics of Parkinson's disease. In: Watts RL and Koller WC (eds) Movement Disorders: Neurologic Principles and Practice, pp 137–152. McGraw-Hill, New York
Tasker RR, Yamashiro K and Lenz F (1988) Thalamotomy for Parkinson's disease: microelectrode technique. In: Lunsford LD (ed.) Modern Stereotactic Neurosurgery, pp 297–314. Nijhoff, The Hague
Tasker RR, Munz M, Junn FSCK et al. (1997) Deep brain stimulation and thalamotomy for tremor compared. Acta Neurochir 68 (Suppl): 49–53
Tretiakoff C (1919) Contribution a l'etude de l'anatomie pathologique du locus niger de Soemmering avec quelques deductions relatives a la pathogenie des troubles du tonus musculaires et de la maladie de Parkinson. Thesis. University of Paris
Tronnier VM, Krause M, Heck A, Kronenbürger M, Bonsanto MM, Tronnier J and Fogel W (1999) Deep brain stimulation for the treatment of movement disorders. Neurol Psychiatry Brain Res 6: 199–212
Von Economo C (1917) Encephalitis lethargica. Wien Klin Wochnschr 30: 581
Widner H (1999) The case for neural tissue transplantation as a treatment for Parkinson's disease. In: Stern GM (ed) Parkinson's Disease: Advances in Neurology, Vol 80, pp 641–649. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Widner H and Brundin P (1988) Immunological aspects of grafting in the mammalian central nervous system: a review and speculative synthesis. Brain Res Rev 13: 287–324
Wooten GF, Currie LJ, Bennett JP, Harrison MB, Trugman JM and Parker WD Jr (1997) Maternal inheritance in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 41: 265–268
Yurek D, Lu W, Hipkens S and Wiegand SJ (1996) BDNF enhances the functional reinnervation of the striatum by grafted fetal dopamine neurons. Exp Neurol 137: 105–118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bjarkam, C.R., Sørensen, J.C., Sunde, N.Å. et al. New strategies for the treatment of Parkinson's disease hold considerable promise for the future management of neurodegenerative disorders. Biogerontology 2, 193–207 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011565207964
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011565207964