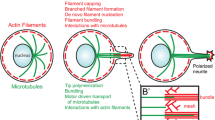
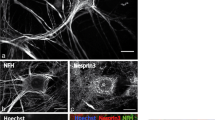
Abstract
Neurofilament proteins, a major intermediate filament component of the neuronal cytoskeleton, are organized as 10 nm thick filaments in axons and dendrites. They are large, abundantly phosphorylated proteins with numerous phosphate acceptor sites, up to 100 in some cases, organized as numerous repeat motifs. Together with other cytoskeletal components such as microtubules, MAPs, actin and plectin-like linking molecules, they make up a dynamic lattice that sustains neuronal function from neuronal “birthday” to apoptotic cell death. The activity of the neuronal cytoskeleton is regulated by phosphorylation, dephosphorylation reactions mediated by numerous associated kinases, phosphatases and their regulators. Factors regulating multisite phosphorylation of NFs are topographically localized, with maximum phosphorylation of NF proteins consigned to axons. Phosphorylation defines the nature of NF interactions with one another and with other cytoskeletal components such as microtubules, MAPs and actin. To understand how these functional interactions are regulated by phosphorylation we attempt to identify the relevant kinases and phosphatases, their specific targets and the factors modulating their activity. As an initial working model we propose that NF phosphorylation is regulated topographically in neurons by compartment-specific macromolecular complexes of substrates, kinases and phosphatases. This implies that axonal complexes differ structurally and functionally from those in cell bodies and dendrites. Such protein assemblies, by virtue of conformational changes within proteins, facilitate ordered, sequential multisite phosphorylations that modulate dynamic cytoskeletal interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ALBERTS, B. (1998) The cell as a collection of protein machines; preparing the next generation of molecular biologists. Cell 92, 291-294.
ANDRA, K., NIKOLIC, B., STOCHER, M., DRENCKHAHN, D. & WICHE, G. (1998) Not just scaffolding: plectin regulates actin dynamics in cultured cells. Genes Dev 12, 3442-3451.
ATHLAN, E. S., SACHER, M. G. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1997) Associations between intermediate filament proteins expressed in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Neurosci. Res 47, 300-310.
BEAUDET, L., CHARRON, G., HOULE, D., TRETJAKOFF, I., PETERSON, A. & JULIEN, J. P. (1992) Intragenic regulatory elements contribute to transcriptional control of the neurofilament light gene. Gene 116, 205-214.
BEAUDET, L., COTE, F., HOULE, D. & JULIEN, J. P. (1993) Different posttranscriptional controls for the human neurofilament light and heavy genes in transgenic mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 18, 23-31.
BEAULIEU, J. M., JACOMY, H. & JULIEN, J. P. (2000) Formation of intermediate filament protein aggregates with disparate effects in two transgenic mouse models lacking the neurofilament light subunit. J Neurosci 20, 5321-5328.
BEAULIEU, J. M., ROBERTSON, J. & JULIEN, J. P. (1999) Interactions between peripherin and neurofilaments in cultured cells: disruption of peripherin assembly by the NF-M and NF-H subunits. Biochem Cell Biol 77, 41-45.
BENNETT, G. S. (1987) Changes in intermediate filament composition during neurogenesis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 21, 151-183.
BENNETT, G. S. & DILULLO, C. (1985) Expression of a neurofilament protein by the precursors of a subpopulation of ventral spinal cord neurons. Dev Biol 107, 94-106.
BENNETT, G. S. & QUINTANA, R. (1997) Identification of Ser-Pro and Thr-Pro phosphorylation sites in chicken neurofilament-M tail domain. J Neurochem 68, 534-543.
BENSON, D. L., MANDELL, J. W., SHAW, G. & BANKER, G. (1996) Compartmentation of alpha-internexin and neurofilament triplet proteins in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurocytol 25, 181-196.
BLACK, J. A., WAXMAN, S. G., RANSOM, B. R. & FELICIANO, M. D. (1986) A quantitative study of developing axons and glia following altered gliogenesis in rat optic nerve. Brain Res 380, 122-135.
BOYNE, L. J., FISCHER, I. & SHEA, T. B. (1996) Role of vimentin in early stages of neuritogenesis in cultured hippocampal neurons. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 14, 739-748.
BRADY, S. T., W., A. S., KIRKPATRICK, L. L., DE WAEGH, S. M., READHEAD, C., TU, P-H & LEE, V. M.-Y. (1999) Formation of compact myelin is required for maturation of the axonal cytoskeleton. J Neurosci. 19, 7278-7288.
BREEN, K. C. & ANDERTON, B. H. (1991) Temporal expression of neurofilament polypeptides in differentiating neuroblastoma cells. Neuroreport 2, 21-24.
BROWN, A. & LASEK, R. J. (1990). The cytoskeleton of the squid giant axon. In Squid as experimental animals, edited by Gilbert, D. S. Adelman, W. J. J. & Arnold, J. M., pp. 235-302, New York: Plenum Press.
BROWNLEES, J., YATES, A., BAJAJ, N. P., DAVIS, D., ANDERTON, B. H., LEIGH, P. N., SHAW, C. E. & MILLER, C. C. (2000) Phosphorylation of neurofilament heavy chain side-arms by stress activated protein kinase-1b/Jun N-terminal kinase-3. J Cell Sci 113, 401-407.
BURKE, B. E. & DELORENZO, R. J. (1982) Ca2+ and calmodulin-regulated endogenous tubulin kinase activity in presynaptic nerve terminal preparations. Brain Res 236, 393-415.
CANETE-SOLER, R. & SCHLAEPFER, W. W. (2000) Similar poly(C)-sensitive RNA-binding complexes regulate the stability of the heavy and light neurofilament mRNAs. Brain Res 867, 265-279.
CARDEN, M. J., GOLDSTEIN, M. E., BRUCE, J., COOPER, H. S. & SCHLAEPFER, W. W. (1987a) Studies of neurofilaments that accumulate in proximal axons of rats intoxicated with beta,beta'-iminodipropionitrile (IDPN). Neurochem Pathol 7, 189-205.
CARDEN, M. J., SCHLAEPFER, W. W., LEE, V. M., TROJANOWSKI, J. Q. & LEE, V. M. (1985) The structure, biochemical properties, and immunogenicity of neurofilament peripheral regions are determined by phosphorylation state Expression of neurofilament antigens by normal and neoplastic human adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem 260, 101-104.
CARDEN, M. J., TROJANOWSKI, J. Q., SCHLAEPFER, W. W. & LEE, V. M. (1987b) Two-stage expression of neurofilament polypeptides during rat neurogenesis with early establishment of adult phosphorylation patterns. J Neurosci 7, 3489-3504.
CHAE, T., KWON, Y. T., BRONSON, R., DIKKES, P., LI, E. & TSAI, L. H. (1997) Mice lacking p35, a neuronal specific activator of Cdk5, display cortical lamination defects, seizures, and adult lethality. Neuron 18, 29-42.
CHARRON, G., GUY, L. G., BAZINET, M. & JULIEN, J. P. (1995a) Multiple neuron-specific enhancers in the gene coding for the human neurofilament light chain. J Biol Chem 270, 30604-30610.
CHARRON, G., JULIEN, J.-P. & BIBOR-HARDY, V. (1995b) Neuron specificity of the neurofilament light promoter in transgenic mice requires the presence of DNA unwinding elements. J. Biol. Chem 270, 25739-25745.
CHEN, J., NAKATA, T., ZHANG, Z. & HIROKAWA, N. (2000) The C-terminal tail domain of neurofilament protein-H (NF-H) forms the crossbridges and regulates neurofilament bundle formation. J Cell Sci 113, 3861-3869.
CHING, G. Y. & LIEM, R. K. (1993) Assembly of type IV neuronal intermediate filaments in nonneuronal cells in the absence of preexisting cytoplasmic intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol 122, 1323-1335.
CHING, G. Y. & LIEM, R. K. (1998) Roles of head and tail domains in alpha-internexin's self-assembly and coassembly with the neurofilament triplet proteins. J Cell Sci 111, 321-333.
CHING, G. Y. & LIEM, R. K. (1999) Analysis of the roles of the head domains of type IV rat neuronal intermediate filament proteins in filament assembly using domainswapped chimeric proteins. J Cell Sci 112, 2233-2240.
COCHARD, P. & PAULIN, D. (1984) Initial expression of neurofilaments and vimentin in the central and peripheral nervous system of the mouse embryo in vivo. J. Neurosci. 4, 2080-2094.
COLE, J., MESSING, A., TROJANOWSKI, J. Q. & LEE V. M.-Y. (1994) Modulation of axon diameter and neurofilaments by hypomyelinating Schwann cells in transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 14, 6956-6966.
COTE, F., COLLARD, J. F. & JULIEN, J. P. (1993) Progressive neuronopathy in transgenic mice expressing the human neurofilament heavy gene: a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell 73, 35-46.
CRISPINO, M., CAPANO, C. P., KAPLAN, B. B. & GIUDITTA, A. (1993) Neurofilament proteins are synthesized in nerve endings from squid brain. J Neurochem 61, 1144-1146.
CRISPINO, M., KAPLAN, B. B., MARTIN, R., ALVAREZ, J., CHUN, J. T., BENECH, J. C. & GIUDITTA, A. (1997) Active polysomes are present in the large presynaptic endings of the synaptosomal fraction from squid brain. J Neurosci 17, 7694-7702.
CRUTE, B. E. & VAN BUSKIRK, R. G. (1992) A casein kinase-like kinase phosphorylates beta-tubulin and may be a microtubule-associated protein. J Neurochem 59, 2017-2023.
DE FREITAS, M. S., DE MATTOS, A. G., CAMARGO, M. M., WANNMACHER, C. & PESSOA-PUREUR, R. (1995) Cytoskeletal-associated protein kinase and phosphatase activities fromcerebral cortex of young rats. Neurochem Res 20, 951-956.
DE WAEGH, S. M., LEE, V. M. & BRADY, S. T. (1992) Local modulation of neurofilament phosphorylation, axonal caliber, and slow axonal transport by myelinating Schwann cells. Cell 68, 451-463.
DOBI, A., PALKOVITS, M., PALKOVITS, C. G., RING, M. A. & AGOSTON, D. V. (2000) Septamer elementbinding proteins in neuronal and glial differentiation. J. Neurosci. 20, 1073-1084.
DONG, D. L., XU, Z. S., CHEVRIER, M. R., COTTER, R. J., CLEVELAND, D. W. & HART, G. W. (1993) Glycosylation of mammalian neurofilaments. Localization of multiple O-linked N-acetylglucosamine moieties on neurofilament polypeptides L and M. J Biol Chem 268, 16679-16687.
DONG, D. L., XU, Z. S., HART, G. W. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1996) Cytoplasmic O-GlcNAc modification of the head domain and the KSP repeat motif of the neurofilament protein neurofilament-H. J Biol Chem 271, 20845-20852.
DOSEMECI, A., FLOYD, C. C. & PANT, H. C. (1990) Characterization of neurofilament-associated protein kinase activities from bovine spinal cord. Cell Mol Neurobiol 10, 369-382.
DOSEMECI, A. & PANT, H. C. (1992) Association of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase with neurofilaments. Biochem J 282, 477-481.
DREWES, G., EBNETH, A., PREUSS, U., MANDELKOW, E. M. & MANDELKOW, E. (1997) MARK, a novel family of protein kinases that phosphorylate microtubule-associated proteins and trigger microtubule disruption. Cell 89, 297-308.
EHLERS, M. D., FUNG, E. T., O'BRIEN, R. J. & HUGANIR, R. L. (1998) Splice variant-specific interaction of the NMDA receptor subunit NR1 with neuronal intermediate filaments. J Neurosci 18, 720-730.
ELDER, G. A., FRIEDRICH, V. L., JR., BOSCO, P., KANG, C., GOUROV, A., TU, P. H., LEE, V. M. & LAZZARINI, R. A. (1998a) Absence of the mid-sized neurofilament subunit decreases axonal calibers, levels of light neurofilament (NF-L), and neurofilament content. J Cell Biol 141, 727-739.
ELDER, G. A., FRIEDRICH, V. L., JR., KANG, C., BOSCO, P., GOUROV, A., TU, P. H., ZHANG, B., LEE, V. M. & LAZZARINI, R. A. (1998b) Requirement of heavy neurofilament subunit in the development of axons with large calibers [see comments]. J Cell Biol 143, 195-205.
ELDER, G. A., LIANG, Z., SNYDER, S. E. & LAZZARINI, R. A. (1992) Multiple nuclear factors interact with the promoter of the human neurofilament M gene. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 15, 99-107.
ELHANANY, E., JAFFE, H., LINK, W. T., SHEELEY, D. M., GAINER, H. & PANT, H. C. (1994) Identification of endogenously phosphorylated KSP sites in the high-molecular-weight rat neurofilament protein. J Neurochem 63, 2324-2335.
EYER, J., CLEVELAND, D. W., WONG, P. C. & PETERSON, A. C. (1998) Pathogenesis of two axonopathies does not require axonal neurofilaments. Nature 391, 584-587.
EYER, J. & PETERSON, A. (1994) Neurofilament-deficient axons and perikaryal aggregates in viable transgenic mice expressing a neurofilament-beta-galactosidase fusion protein. Neuron 12, 389-405.
FABRIZI, C., KELLY, B. M., GILLESPIE, C. S., SCHLAEPFER, W. W., SHERER, S. S. & BROPHY, P. J. (1997) Transient expression of the neurofilament proteins NF-L and NF-M by Schwann cells is regulated by axonal contact. J Neurosci Res 50, 291-299.
FEDTSOVA, N. G. & TURNER, E. E. (1995) Brn-3.0 expression identifies early post-mitotic CNS neurons and sensory neural precursors. Mech. Dev. 53, 291-304.
FISCHER, I. & ROMANO-CLARKE, G. (1990) Changes in microtubule-associated protein MAP1B phosphorylation during rat brain development. J Neurochem 55, 328-333.
FISCHER, I., ROMANO-CLARKE, G. & GRYNSPAN, F. (1991) Calpain-mediated proteolysis of microtubule associated proteins MAP1B and MAP2 in developing brain. Neurochem Res 16, 891-898.
FISCHER, I. & SHEA, T. B. (1991) Differential appearance of extensively phosphorylated forms of the high molecular weight neurofilament protein in regions of mouse brain during postnatal development. J. Neuroimm. 31, 73-81.
FLOYD, C. C., GRANT, P., GALLANT, P. E. & PANT, H. C. (1991) Principal neurofilament-associated protein kinase in squid axoplasm is related to casein kinase I. J Biol Chem 266, 4987-4994.
GARRINGTON, T. P. & JOHNSON, G. L. (1999) Organization and regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11, 211-218.
GIASSON, B. I., BRUENING, W., DURHAM, H. D. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1999) Activation of stressactivated protein kinases correlates with neurite outgrowth induced by protease inhibition in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 72, 1081-1087.
GIASSON, B. I., CROMLISH, J. A., ATHLAN, E. S. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1996a) Activation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in akadaic acid-treated neurons potentiates neurofilament fragmentation and stimulates phosphorylation of Ser2 in the low-molecular mass neurofilament subunit. J. Neurochem. 66, 1207-1213.
GIASSON, B. I. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1996b) Aberrant stress-induced phosphorylation of perikaryal neurofilaments. J Biol Chem 271, 30404-30409.
GIASSON, B. I. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1997) Okadaic acid reversibly inhibits neurite outgrowth in embryonic dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurobiol 32, 193-201.
GIASSON, B. I. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1997) Study of proline-directed protein kinases involved in phosphorylation of the heavy neurofilament subunit. J. Neuroscien 17, 9466-9472.
GIASSON, B. I. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1998) Intermediate filament disassembly in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons is associated with amino-terminal head domain phosphorylation of specific subunits. J Neurochem 70, 1869-1875.
GIBB, B. J., BRION, J. P., BROWNLEES, J., ANDERTON, B. H. & MILLER, C. C. (1998) Neuropathological abnormalities in transgenic mice harbouring a phosphorylation mutant neurofilament transgene. J Neurochem 70, 492-500.
GIBB, B. J. M., ROBERTSON, J. & MILLER, C. C. J. (1996) Assembly properties of neurofilament light chain Ser55 mutants in transfected mammalian cells. J. Neurochem. 66, 1306-1311.
GOEDERT, M. & (1998) Filamentous nerve cell inclusions in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 8, 619-632.
GOLDENRING, J. R., CASANOVA, J. E. & DELORENZO, R. J. (1984) Tubulin-associated calmodulin-dependent kinase: evidence for an endogenous complex of tubulin with a calcium-calmodulin-dependent kinase. J. Neurochem. 43, 1669-1679.
GOLDSTEIN, M. E., COOPER, H. S., BRUCE, J., CARDEN, M. J., LEE, V. M. & SCHLAEPFER, W. W. (1987) Phosphorylation of neurofilament proteins and chromatolysis following transection of rat sciatic nerve. J Neurosci 7, 1586-1594.
GONDA, Y., NISHIZAWA, K., ANDO, S., KITAMURA, S., MINOURA, Y., NISHI, Y. & INAGAKI, M. (1990) Involvement of protein kinase C in the regulation of assembly-disassembly of neurofilaments in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 167, 1316-1325.
GOU, J. P., GOTOW, T., JANMEY, P. A. & LETERRIER, J. F. (1998) Regulation of neurofilament interactions in vitro by natural and synthetic polypeptides sharing Lys-Ser-Pro sequences with the heavy neurofilament subunit NF-H: neurofilament crossbridging by antiparallel sidearm overlapping. Med Biol Eng Comput 36, 371-387.
GRANT, P., DIGGINS, M. & PANT, H. C. (1999) Topographic regulation of cytoskeletal protein phosphorylation by multimeric complexes in the squid giant fiber system. J Neurobiol 40, 89-102.
GRANT, P., TSENG, D., GOULD, R. M., GAINER, H. & PANT, H. C. (1995) Expression of neurofilament proteins during development of the nervous system in the squid Loligo pealei. J Comp Neurol 356, 311-326.
GUAN, R. J., HALL, F. L. & COHLBERG, J. A. (1992) Proline-directed protein kinase (p34cdc2/p58cyclin A) phosphorylates bovine neurofilaments. J Neurochem 58, 1365-1371.
GUAN, R. J., KHATRA, B. S. & COHLBERG, J. A. (1991) Phosphorylation of bovine neurofilament proteins by protein kinase FA (glycogen synthase kinase 3). J Biol Chem 266, 8262-8267.
GUIDATO, S., BAJAJ, N. P. & MILLER, C. C. (1996a) Cellular phosphorylation of neurofilament heavy-chain by cyclin-dependent kinase-5 masks the epitope for monoclonal antibody N52. Neurosci Lett 217, 157-160.
GUIDATO, S., TSAI, L. H., WOODGETT, J. & MILLER, C. C. (1996b) Differential cellular phosphorylation of neurofilament heavy side-arms by glycogen synthase kinase-3 and cyclin-dependent kinase-5. J Neurochem 66, 1698-1706.
HALL, G. F., CHU, B., LEE, S., LIU, Y. & YAO, J. (2000) The single neurofilament subunit of the lamprey forms filaments and regulates axonal caliber and neuronal size in vivo. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 46, 166-182.
HASHIMOTO, R., NAKAMURA, Y., GOTO, H., WADA, Y., SAKODA, S., KAIBUCHI, K., INAGAKI, M. & TAKEDA, M. (1998) Domain-and site-specific phosphorylation of bovine NF-L by Rho-associated kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 245, 407-411.
HASHIMOTO, R., NAKAMURA, Y., KOMAI, S., KASHIWAGI, Y., MATSUMOTO, N., SHIOSAKA, S. & TAKEDA, M. (2000a) Phosphorylation of neurofilament-L during LTD. Neuroreport 11, 2739-2742.
HASHIMOTO, R., NAKAMURA, Y., KOMAI, S., KASHIWAGI, Y., TAMURA, K., GOTO, T., AIMOTO, S., KAIBUCHI, K., SHIOSAKA, S. & TAKEDA, M. (2000b) Site-specific phosphorylation of neurofilament-L is mediated by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the apical dendrites during long-term potentiation. J Neurochem 75, 373-382.
HEINS, S., WONG, P. C., MULLER, S., GOLDIE, K., CLEVELAND, D. W. & AEBI, U. (1993) The rod domain of NF-L determines neurofilament architecture, whereas the end domains specify filament assembly and network formation. J Cell Biol 123, 1517-1533.
HERRMANN, H. & AEBI, U. (2000) Intermediate filaments and their associates: multi-talented structural elements specifying cytoarchitecture and cytodynamics. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12, 79-90.
HIROKAWA, N. (1991). Molecular architecture and dynamics of neuronal cytoskeleton. In The Neuronal Cytoskeleton, edited by R. D. BURGOYNE, pp. 5-74, NewYork: Wiley.
HIROKAWA, N. & TAKEDA, S. (1998) Gene targeting studies begin to reveal the function of neurofilament proteins. J Cell Biol 143, 1-4.
HISANAGA, S. & HIROKAWA, N. (1988) Structure of the peripheral domains of neurofilaments revealed by low angle rotary shadowing. J Mol Biol 202, 297-305.
HISANAGA, S. & HIROKAWA, N. (1989) The effects of dephosphorylation on the structure of the projections of neurofilament. J Neurosci 9, 959-966.
HISANAGA, S. & HIROKAWA, N. (1990) Molecular architecture of the neurofilament. II. Reassembly process of neurofilament L protein in vitro. J Mol Biol 211, 871-882.
HISANAGA, S., KUSUBATA, M., OKUMURA, E. & KISHIMOTO, T. (1991) Phosphorylation of neurofilament H subunit at the tail domain by CDC2 kinase dissociates the association to microtubules. J Biol Chem 266, 21798-21803.
HISANAGA, S., MATSUOKA, Y., NISHIZAWA, K., SAITO, T., INAGAKI, M., HIROKAWA, N., HISANAGA, S., YASUGAWA, S., YAMAKAWA, T., MIYAMOTO, E., IKEBE, M., UCHIYAMA, M. & KISHIMOTO, T. (1994) Phosphorylation of native and reassembled neurofilaments composed of NF-L, NF-M, and NF-H by the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Dephosphorylation of microtubulebinding sites at the neurofilament-H tail domain by alkaline, acid, and protein phosphatases. Mol Biol Cell 5, 705-709.
HISANAGA, S., UCHIYAMA, M., HOSOI, T., YAMADA, K., HONMA, N., ISHIGURO, K., UCHIDA, T., DAHL, D., OHSUMI, K. & KISHIMOTO, T. (1995) Porcine brain neurofilament-H tail domain kinase: its identification as cdk5/p26 complexandcomparison with cdc2/cyclin B kinase. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 31, 283-297.
HISANAGA, S., YASUGAWA, S., YAMAKAWA, T., MIYAMOTO, E., IKEBE, M., UCHIYAMA, M. & KISHIMOTO, T. (1993) Dephosphorylation of microtubule-binding sites at the neurofilament-H tail domain by alkaline, acid, and protein phosphatases. J Biochem (Tokyo) 113, 705-709.
HOFFMAN, P. N., CLEVELAND, D. W., GRIFFIN, J. W., LANDES, P. W., COWAN, N. J. & PRICE, D. L. (1987) Neurofilament gene expression: a major determinant of axonal caliber. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84, 3472-3476.
HOLLANDER, B. A., BENNETT, G. S. & SHAW, G. (1996) Localization of sites in the tail domain of the middle molecular mass neurofilament subunit phosphorylated by a neurofilament-associated kinase and by casein kinase I. J Neurochem 66, 412-420.
HOUSEWEART, M. K. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1998) Intermediate filaments and their associated proteins; multiple dynamic personalities. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 10, 93-101.
HOUSEWEART, M. K. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1999) Cytoskeletal linkers: new MAPs for old destinations. Curr Biol 9, R864-866.
HSEIH, S. T., CRAWFORD, T. O. & GRIFFIN, J. W. (1994) Neurofilament distribution and organization in the myelinated axons of the peripheral nervous system. Brain Res 642, 316-326.
IKENAKA, K., NAKAHIRA, K., TAKAYAMA, C., WADA, K., HATANAKA, H. & MIKOSHIBA, K. (1990) Nerve growth factor rapidly induces expression of the 68-kDa neurofilament gene by posttranscriptional modification in PC12h-R cells. J Biol Chem 265, 19782-19785.
INAGAKI, M., INAGAKI, N., TAKAHASHI, T. & TAKAI Y. (1997) Phosphorylation-dependent control of structures of intermediate filaments: a novel approach using site-and phosphorylation state-specific antibodies. J. Biochem (Tokyo) 121, 407-414.
INAGAKI, M., MATSUOKA, Y., TSUJIMURA, K., ANDO, S., TOKUI, T., TAKAHASHI, T. & INAGAKI, N. (1996) Dynamic property of intermediate filaments: regulation by phosphorylation. BioEssays 18, 481-487.
ISHIGURO, K., IHARA, Y., UCHIDA, T. & IMAHORI, K. (1988) A novel tubulin-dependent protein kinase forming a paired helical filament epitope on tau. J Biochem (Tokyo) 104, 319-321.
ISHIGURO, K., KOBAYASHI, S., OMORI, A., TAKAMATSU, M., YONEKURA, S., ANZAI, K., IMAHORI, K. & UCHIDA, T. (1994) Identification of the 23 kDa subunit of tau protein kinase II as a putative activator of cdk5 in bovine brain. Febs Lett 342, 203-208.
JACOBS, A. J., KAMHOLZ, J. & SELZER, M. E. (1995) The single lamprey neurofilament subunit (NF-180) lacks multiphosphorylation repeats and is expressed selectively in projection neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 29, 43-52.
JACOMY, H., ZHU, Q., COUILLARD-DESPRES, S., BEAULIEU, J. M. & JULIEN, J. P. (1999) Disruption of type IV intermediate filament network in mice lacking the neurofilament medium and heavy subunits. J Neurochem 73, 972-984.
JAFFE, H., VEERANNA & PANT, H. C. (1998a) Characterization of serine and threonine phosphorylation sites Neurofilament protein 867 in beta-elimination/ethanethiol addition-modified proteins by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry and database searching. Biochemistry 37, 16211-16224.
JAFFE, H., VEERANNA, SHETTY, K. T. & PANT, H. C. (1998b) Characterization of the phosphorylation sites of human high molecular weight neurofilament protein by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry and database searching. Biochemistry 37, 3931-3940.
JAFFE, H., SHARMA, P., GRANT, P. & PANT, H. C. (2001) Characterization of the phosphorylation sites of the squid (holigs pealei) high-molecular-weight neurofilament protein from giant axon axoplasm. J. Neurochem. 76, 1022-1031.
JULIEN, J. P. (1999) Neurofilament functions in health and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9, 554-560.
JULIEN, J. P. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1983) The distribution of phosphorylation sites among identified proteolytic fragments of mammalian neurofilaments. J Biol Chem 258, 4019-4025.
JULIEN, J. P. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1998) Neurofilaments in health and disease. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 61, 1-23.
JULIEN, J. P., TRETJAKOFF, I., BEAUDET, L. & PETERSON, A. (1987) Expression and assembly of a human neurofilament protein in transgenic mice provide a novel neuronal marking system. Genes Dev 1, 1085-1095.
JUNG, C., YABE, J. T., LEE, S. & SHEA, T. B. (2000) Hypophosphorylated neurofilament subunits undergo axonal transport more rapidly than more extensively phosphorylated subunits in situ [In Process Citation]. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 47, 120-129.
KAPLAN, M. P., CHIN, S. S., FLIEGNER, K. H. & LIEM, R. K. (1990) Alpha-internexin, a novel neuronal intermediate filament protein, precedes the low molecular weight neurofilament protein (NF-L) in the developing rat brain. J Neurosci 10, 2735-2748.
KENNELLY, P. J. & KREBS, E. G. (1991) Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem 266, 15555-15558.
KOENIG, E. & GIUDITTA, A. (1999) Protein-synthesizing machinery in the axon compartment. Neuroscience 88, 5-15.
KOMIYA, Y., COOPER, N. A. & KIDMAN, A. D. (1986) The long-term effects of a single injection of beta,beta'-iminodipropionitrile on slow axonal transport in the rat. J Biochem 100, 1241-1246.
KWON, Y. T., TSAI, L. H. & CRANDALL, J. E. (1999) Callosal axon guidance defects in p35(—/—) mice. J Comp Neurol 415, 218-229.
LANDMESSER, L. & SWAIN, S. (1992) Temporal and spatial modulation of a cytoskeletal antigen during peripheral axonal pathfinding. Neuron 8, 291-305.
LEAPMAN, R. D., GALLANT, P. E., REESE, T. S. & ANDREWS, S. B. (1997) Phosphorylation and subunit organization of axonal neurofilaments determined by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 7820-7824.
LEE, K. Y. & JOHNSTON, R. N. (1997) Neurofilaments are part of the high-molecular weight complex containing neuronal cdc2-like kinase (NCLK). Brain Res. 773, 197-202.
LEE, V., TROJANOWSKI, J. Q. & SCHLAEPFER, W. W. (1982) Induction of neurofilament triplet proteins inPC12 cells by nerve growth factor. Brain Res 238, 169-180.
LEE, V., WU, H. L. & SCHLAEPFER, W. W. (1982) Monoclonal antibodies recognize individual neurofilament triplet proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79, 6089-6092.
LEE, V. M., CARDEN, M. J., SCHLAEPFER, W. W. & TROJANOWSKI, J. Q. (1987) Monoclonal antibodies distinguish several differentially phosphorylated states of the two largest rat neurofilament subunits (NF-H and NF-M) and demonstrate their existence in the normal nervous system of adult rats. J Neurosci 7, 3474-3488.
LEE, J. K., HWANG, W. S., LEE, Y. D. & HAN, P. L. (1999) Dynamic expression of SEK1 suggests multiple roles of the gene during embryogenesis and in adult brain of mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 66, 133-140.
LEE, M. K., XU, Z., WONG, P. C. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1993) Neurofilaments are obligate heteropolymers in vivo. J Cell Biol 122, 1337-1350.
LEE, V. M., OTVOS, L., JR., CARDEN, M. J., HOLLOSI, M., DIETZSCHOLD, B. & LAZZARINI, R. A. (1988) Identification of the major multiphosphorylation site in mammalian neurofilaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85, 1998-2002.
LENDHAL, U., ZIMMERMAN, L. & MCKAY, R. (1990) CNS stem cells express a new class of intermediate protein. Cell 60, 585-595.
LETERRIER, J. F., HARTWIG, J., KAS, J., VEGNERS, R. & JANMEY, P. (1996) Mechanical effects of neurofilament crossbridges:modulation by phosphorylation, lipids and interactions with F-actin. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 15687-15694.
LEVAVASSEUR, F., ZHU, Q. & JULIEN, J. P. (1999) No requirement of alpha-internexin for nervous system development and for radial growth of axons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 69, 104-112.
LEW, J., BEAUDETTE, K., LITWIN, C. M. & WANG, J. H. (1992a) Purification and characterization of a novel proline-directed protein kinase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem 267, 13383-13390.
LEW, J., HUANG, Q. Q., QI, Z., WINKFEIN, R. J., AEBERSOLD, R., HUNT, T. & WANG, J. H. (1994) A brain-specific activator of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371, 423-426.
LEW, J., WINKFEIN, R. J., PAUDEL, H. K. & WANG, J. H. (1992b) Brain proline-directed protein kinase is a neurofilament kinase which displays high sequence homology to p34cdc2. J Biol Chem 267, 25922-25926.
LI, B. S., VEERANNA, GRANT, P. & PANT, H. C. (1999a) Calcium influx and membrane depolarization induce phosphorylation of neurofilament (NF-M) KSP repeats in PC12 cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 70, 84-91.
LI, B. S., VEERANNA, GU, J., GRANT, P. & PANT, H. C. (1999b) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (Erk1 and Erk2) cascade results in phosphorylation of NF-M tail domains in transfected NIH 3T3 cells. Eur J Biochem 262, 211-217.
LI, B. S., ZHANG, L., GU, J., AMIN, N. D. & PANT, H. C. (2000) Integrin alpha(1) beta(1)-mediated activation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity is involved in neurite outgrowth and human neurofilament protein H Lys-Ser-Pro tail domain phosphorylation. J Neurosci 20, 6055-6062.
LIEM, R. K. A. H., S.B. (1982) Purification of individual components of the neurofilament triplet: filament assembly from the 70000-dalton subunit. Biochemistry 21, 3221-3226.
LIN, W. & SZARO, B. G. (1995) Neurofilaments help maintain normal morphologies and support elongation of neurites in Xenopus laevis cultured embryonic spinal cord neurons. J Neurosci 15, 8331-8344.
LINDENBAUM, M. H., CARBONETTO, S., GROSVELD, F., FLAVELL, D. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1988) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional effects of nerve growth factor on expression of the three neurofilament subunits in PC-12 cells. J Biol Chem 263, 5662-5667.
LINK, W. T., DOSEMECI, A., FLOYD, C. C. & PANT, H. C. (1993) Bovine neurofilament-enriched preparations contain kinase activity similar to casein kinase I— neurofilament phosphorylation by casein kinase I (CKI). Neurosci Lett 151, 89-93.
LINK, W. T., GRANT, P., HIDAKA, H. & PANT, H. C. (1992) Casein kinase I and II from squid brain exhibit selective neurofilament phosphorylation. Mol Cell Neurosci 3, 548-558.
MALECZ, N., FOISNER, R., STADLER, C. & WICHE, G. (1996) Identification of plectin as asubstrate of p34cdc2 kinase and mapping of a single phosphorylation site. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 8203-8208.
MARSZALEK, J. R., WILLIAMSON, T. L., LEE, M. K., XU, Z., HOFFMAN, P. N., BECHER, M. W., CRAWFORD, T. O. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1996) Neurofilament subunit NF-H modulates axonal diameter by selectively slowing neurofilament transport. J Cell Biol 135, 711-724.
MARTIN, J. H., MOHIT, A. A. & MILLER, C. A. (1996) Developmental expression in the mouse nervous system of the p493F12 SAP kinase. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 35, 47-57.
MATA, M., KUPINA, N. & FINK, D. J. (1992) Phosphorylation-dependent neurofilament epitopes are reduced at the node of Ranvier. J Neurocytol 21, 199-210.
MATHIEU, J. F., MA, D., DESCARRIES, L., VALLEE, A., PARENT, A., JULIEN, J. P. & DOUCET, G. (1995) CNS distribution and overexpression of neurofilament light proteins (NF-L) in mice transgenic for the human NF-L: aberrant accumulation in thalamic perikarya. Exp Neurol 132, 134-146.
MEIER, J., COUILLARD-DESPRES, S., JACOMY, H., GRAVEL, C. & JULIEN, J. P. (1999) Extra neurofilament NF-L subunits rescue motor neuron disease caused by overexpression of the human NF-H gene in mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58, 1099-1110.
MERRICK, S. E., TROJANOWSKI, J. Q. & LEE, V. M.-Y. (1997) Selective destruction of stable microtubules and axons by inhibitors of protein serine/threonine phosphatases in cultured human neurons. J Neurosci. 17, 5726-5737.
METUZALS, J., HODGE, A. J., LASEK, R. J. & KAISERMAN-ABRAMOF, I. R. (1983) Neurofilamentous network and filamentous matrix preserved and isolated by different techniques from squid giant axon. Cell Tissue Res 228, 415-432.
MIYASAKA, H., OKABE, S., ISHIGURO, K., UCHIDA, T. & HIROKAWA, N. (1993) Interaction of the tail domain of high molecular weight subunits of neurofilaments with the COOH-terminal region of tubulin and its regulation by tau protein kinase II. J Biol Chem 268, 22695-22702.
MORGAN, D. O. (1997) Cyclin-dependent kinases: Engines, clocks and microprocessors. Annu Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13, 261-291.
MORRIS, J. R. & LASEK, R. J. (1982) Stable polymers of the axonal cytoskeleton: the axoplasmic ghost. J Cell Biol 92, 192-198.
MORRIS, J. R. & LASEK, R. J. (1984) Monomer-polymer equilibria in the axon: direct measurement of tubulin and actin as polymer and monomer in axoplasm. J Cell Biol 98, 2064-2076.
MOSKOWITZ, P. F. & OBLINGER, M. M. (1995) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms regulating neurofilament and tubulin gene expression during normal development of the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 30, 211-222.
MULLIGAN, L., BALIN, B. J., LEE, V. M. & IP, W. (1991) Antibody labeling of bovine neurofilaments: implications on the structure of neurofilament sidearms. J Struct Biol 106, 145-160.
NAIR, A. P., HAHN, S., BANHOLZER, R., HIRSCH, H. H. & MORONI, C. (1994) Cyclosporin A inhibits growth of autocrine tumour cell lines by destabilizing interleukin-3 mRNA. Nature 369, 239-242.
NAKAGAWA, T., CHEN, J., ZHANG, Z., KANAI, Y. & HIROKAWA, N. (1995) Two distinct functions of the carboxyl-terminal tail domain of NF-M upon neurofilament assembly: cross-bridge formation and longitudinal elongation of filaments. J Cell Biol 129, 411-429.
NAKAMURA, Y., HASHIMOTO, R., KASHIWAGI, Y., WADA, Y., SAKODA, S., MIYAMAE, Y., KUDO, T. & TAKEDA, M. (1999) Casein kinase II is responsible for phosphorylation of NF-L at Ser-473. FEBS Lett 455, 83-86.
NAKAMURA, Y., SAKAKIBARA, S., MIYATA, T., OGAWA, M., SHIMAZAKI, T., WEISS, S., KAGEYAMA, R. & OKANO, H. (2000) The bHLH gene hes1 as a repressor of the neuronal commitment of CNS stem cells. J Neurosci 20, 283-293.
NAKAMURA Y., H., R., KASHIWAGI, Y., AIMOTO, S., FUKUSHO, E., MATSUMOTO, N., KUDO, T. & TAKEDA, M. (2000) Major phosphoylation site (Ser55) of neurofilament L by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in rat primary neuronal culture. J Neurochem. 74, 949-959.
NIKOLIC, M., DUDEK, H., KWON, Y. T., RAMOS, Y. F. & TSAI, L. H. (1996) The cdk5/p35 kinase is essential for neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation. Genes Dev 10, 816-825.
NIXON, R. A. (1993) The regulation of neurofilament protein dynamics by phosphorylation: clues to neurofibrillary pathobiology. Brain Pathol 3, 29-38.
NIXON, R. A. (1998) Dynamic behavior and organization of cytoskeletal proteins in neurons: reconciling old and new findings. Bioessays 20, 798-807.
NIXON, R. A., LEWIS, S. E. & MAROTTA, C. A. (1987) Posttranslational modification of neurofilament proteins by phosphate during axoplasmic transport in retinal ganglion cell neurons. J Neurosci 7, 1145-1158.
NIXON, R. A., PASKEVICH, P. A., SIHAG, R. K. & THAYER, C. Y. (1994) Phosphorylation on carboxyl terminus domains of neurofilament proteins in retinal ganglion cell neurons in vivo: influences on regional neurofilament accumulation, interneurofilament spacing, and axon caliber. J Cell Biol 126, 1031-1046.
NIXON, R. A. & SHEA, T. B. (1992) Dynamics of neuronal intermediate filaments: a developmental perspective. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 22, 81-91.
NIXON, R. A. & SIHAG, R. K. (1991) Neurofilament phosphorylation: anewlook at regulation and function. Trends Neurosci 14, 501-506.
OBLINGER, M. M., BRADY, S. T., MCQUARRIE, I. G. & LASEK, R. J. (1987) Cytotypic differences in the protein composition of the axonally transported cytoskeleton in mammalian neurons. J Neurosci 7, 453-462.
OHSHIMA, T., WARD, J. M., HUH, C. G., LONGENECKER, G., VEERANNA, PANT, H. C., BRADY, R. O., MARTIN, L. J. & KULKARNI, A. B. (1996) Targeted disruption of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 gene results in abnormal corticogenesis, neuronal pathology and perinatal death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93, 11173-11178.
PAGLINI, G., PIGINO, G., KUNDA, P., MORFINI, G., MACCIONI, R., QUIROGA, S., FERREIRA, A. & CACERES, A. (1998) Evidence for the participation of the neuron-specific CDK5 activator P35 during lamininenhanced axonal growth. J Neurosci 18, 9858-9869.
PANG, L., SAWADA, T., DECKER, S. J. & SALTIEL, A. R. (1995) Inhibition of MAP kinase kinase blocks the differentiation of PC-12 cells induced by nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem 270, 13585-13588.
PANT, H. C. (1988) Dephosphorylation of neurofilament proteins enhances their susceptibility to degradation by calpain. Biochem J 256, 665-668.
PANT, H., & VEERANNA. (1995) Neurofilament phosphorylation. Biochem Cell Biol 73, 575-592.
PANT, H. C., GALLANT, P. E. & GAINER, H. (1986) Characterization of a cyclic nucleotide-and calciumindependent neurofilament protein kinase activity in axoplasm from the squid giant axon. J Biol Chem 261, 2968-2977.
PANT, H. C., VEERANNA & GRANT, P. (2000) Regulation of axonal neurofilament phosphorylation. Curr. Top. Cell. Reg. 36, 133-150.
PANT, H. C., SHECKET, G., GAINER, H. & LASEK, R. J. (1978) Neurofilament protein is phosphorylated in the squid giant axon. J Cell Biol 78, R23-27.
PANT, A. C., VEERANNA, PANT, H. C. & AMIN, N. (1997) Phosphorylation of human high molecular weight neurofilament protein (hNF-H) by neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5). Brain Res 765, 259-266.
PANT, H. C., KRINKS, M. H., KLEE, C. B., PANT, H. C. & GAINER, H. (1988) Dephosphorylation of neurofilament proteins enhances their susceptibility to degradation by calpain. Identification and quantification of calcium-binding proteins in squid axoplasm. Biochem J 256, 2172-2182.
PARYSEK, L. M. & GOLDMAN, R. D. (1988) Distribution of a novel 57 kDa intermediate filament (IF) protein in the nervous system. J Neurosci 8, 555-563.
PATERNO, G. D., GILLESPIE, L. L., JULIEN, J. P. & SKUP, D. (1997) Regulation of neurofilament L, M and H gene expression during retinoic acid-induced neural differentiation of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Brain Res Mol BrainRes 49, 247-254.
PHILPOTT, A., PORRO, E. B., KIRSCHNER, M. W. & TSAI, L. H. (1997) The role of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and a novel regulatory subunit in regulating muscle differentiation and patterning. Genes Dev 11, 1409-1421.
PHILPOTT, A., TSAI, L. & KIRSCHNER, M. W. (1999) Neuronal differentiation and patterning in Xenopus: the role of cdk5 and a novel activator xp35.2. Dev Biol 207, 119-132.
PIGINO, G., PAGLINI, G., ULLOA, L., AVILA, J. & CACERES, A. (1997) Analysis of the expression, distribution and function of cyclin dependent kinase 5 (cdk5) in developing cerebellar macroneurons. J Cell Sci 110, 257-270.
QI, Z., TANG, D., ZHU, X., FUJITA, D. J. & WANG, J. H. (1998) Association of neurofilament proteins with neuronal Cdk5 activator. J Biol Chem 273, 2329-2335.
RAO, M. V., HOUSEWEART, M. K., WILLIAMSON, T. L., CRAWFORD, T. O., FOLMER, J. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1998) Neurofilament-dependent radial growth of motor axons and axonal organization of neurofilaments does not require the neurofilament heavy subunit (NFH) or its phosphorylation [see comments]. J Cell Biol 143, 171-181.
ROACH, P. J. (1991) Multisite and hierarchal protein phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem 266, 14139-14142.
ROBERSON, M. D., TOEWS, A. D., GOODRUM, J. F. & MORELL, P. (1992) Neurofilament and tubulin mRNA expression in Schwann cells. J Neurosci Res 33, 156-162.
RODER, H. M., EDEN, P. A. & INGRAM, V. M. (1993) Brain protein kinase PK40erk converts TAU into a PHFlike form as found in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 193, 639-647.
ROOSA, J. R., GERVASI, C. & SZARO, B. G. (2000) Structure, biological activity of the upstream regulatory sequence, and conserved domains of a middle molecular mass neurofilament gene of Xenopus laevis. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 82, 35-51.
ROSALES, J. L., NODWELL, M. J., JOHNSTON, R. N. & LEE, K. Y. (2000) Cdk5/p25(nck5a) interaction with synaptic proteins in bovine brain. J Cell Biochem 78, 151-159.
SACHER, M. G., ATHLAN, E. S. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1992) Okadaic acid induces the rapid and reversible disruption of the neurofilament network in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 186, 524-530.
SACHER, M. G., ATHLAN, E. S. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1994) Increased phosphorylation of the amino-terminal domain of the low molecular weight neurofilament subunit in okadaic acid-treated neurons. J Biol Chem 269, 18480-18484.
SAITO, T., SHIMA, H., OSAWA, Y., NAGAO, M., HEMMINGS, B. A., KISHIMOTO, T. & HISANAGA, S. (1995) Neurofilament-associated protein phosphatase 2A: its possible role in preserving neurofilaments in filamentous states. Biochemistry 34, 7376-7384.
SAKAGUCHI, T., OKADA, M., KITAMURA, T. & KAWASAKI, K. (1993) Reduced diameter and conduction velocity of myelinated fibers in the sciatic nerve of a neurofilament-deficient mutant quail. Neurosci Lett 153, 65-68.
SASAHARA, Y., KOBAYASHI, T., ONODERA, H., ONODA, M., OHNISHI, M., KATO, S., KUSUDA, K., SHIMA, H., NAGAO, M., ABE, H., YANAGAWA, Y., HIRAGA, A. & TAMURA, S. (1996) Okadaic acid suppresses neural differentiation-dependent expression of the neurofilament-L gene in P19 embryonal carcinoma cells by post-transcriptional modification. J BiolChem 271, 25950-25957.
SCHWARTZ, M. L., BRUCE, J., SHNEIDMAN, P.S. & SCHLAEPFER, W. W. (1995) Deletion of 3'-untranslated region alters the level of mRNA expression of a neurofilament light subunit transgene. J.Biol.Chem. 270, 26364-26369.
SCHWARTZ, M. L., SHNEIDMAN, P. S., BRUCE, J. & SCHLAEPFER, W. W. (1994) Stabilization of neurofilament transcripts during postnatal development. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 27, 215-220.
SENGUPTA, A., WU, Q., GRUNDKE-IQBAL, I., IQBAL, K. & SINGH, T. J. (1997) Potentiation of GSK-3-catalyzed Alzheimer-like phosphorylation of human tau by cdk5. Mol Cell Biochem 167, 99-105.
SERRANO, L., DIAZ-NIDO, J., WANDOSELL, F. & AVILA, J. (1987) Tubulin phosphorylation by casein kinase II is similar to that found in vivo. J Cell Biol 105, 1731-1739.
SERRANO, L., HERNANDEZ, M. A., DIAZ-NIDO, J. & AVILA, J. (1989) Association of casein kinase II with microtubules. Exp Cell Res 181, 263-272.
SHARMA, M., SHARMA, P. & PANT, H. C. (1999a) CDK-5-mediated neurofilament phosphorylation in SHSY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 73, 79-86.
SHARMA, P., SHARMA, M., AMIN, N. D., ALBERS, R. W. & PANT, H. C. (1999b) Regulation of cyclindependent kinase 5 catalytic activity by phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96, 11156-11160. [Record as supplied by publisher].
SHAW, G. & WEBER, K. (1982) Differential expression of neurofilament triplet proteins in brain development. Nature 298, 277-279.
SHAW, G., MILLER, R., WANG, D. S., TANG, D., HOLLANDER, B. A. & BENNETT, G. S. (1997) Characterization of additional casein kinase I sites in the Cterminal “tail” region of chicken and rat neurofilament-M. J Neurochem 69, 1729-1737.
SHEA, T. B. (1995) Differential synthesis and cytoskeletal deposition of neurofilament subunits before and during axonal outgrowth in NB2a/d1 cells: evidence that segregation of phosphorylated subunits within the axonal cytoskeleton involves selective deposition. J Neurosci Res 40, 225-232.
SHETTY, K. T., LINK, W. T. & PANT, H. C. (1993) cdc2-like kinase from rat spinal cord specifically phosphorylates KSPXK motifs in neurofilament proteins: isolation and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90, 6844-6848.
SHNEIDMAN, P. S., B., J., SCHWARTZ, M. L. & SCHLAEPFER, W. W. (1992) Negative regulatory regions are present upstream in the three mouse neurofilament genes. Brain Res Mol. Brain Res. 13, 127-138.
SIHAG, R. K. & NIXON, R. A. (1989) In vivo phosphorylation of distinct domains of the 70-kilodalton neurofilament subunit involves different protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 264, 457-464.
SIHAG, R. K. & NIXON, R. A. (1990) Phosphorylation of the amino-terminal head domain of the middle molecular mass 145-kDa subunit of neurofilaments. Evidence for regulation by second messenger-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 265, 4166-4171.
SIHAG, R. K. & NIXON, R. A. (1991) Identification of Ser-55 as a major protein kinase A phosphorylation site on the 70-kDa subunit of neurofilaments. Early turnover during axonal transport. J Biol Chem 266, 18861-18867.
SINGH, T. J. & (1995) Phosphorylation of tau protein by casein kinase-1 converts it to an abnormal Alzheimerlike state. J Neurochem. 64, 1420-1423.
SMITH, M. D., MORRIS, P. J., DAWSON, S. J., SCHWARTZ, M. L., SCHLAEPFER, W. W. & LATCHMAN, D. S. (1997) Coordinate induction of the three neurofilament genes by the Brn-3a transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 21325-21333.
SOBUE, K., AGARWAL-MAWAL, A., LI, W., SUN, W., MIURA, Y. & PAUDEL, H. K. (2000) Interaction of neuronal Cdc2-like protein kinase with microtubule-associated protein tau. J Biol Chem 275, 16673-16680.
SONSKA, A. & ENTLICHER, G. (1997) Phosphorylation of 68 kDa neurofilament proteins has no significant effect on their assembly. Acta Neurobiol Exp 57, 333-338.
SOTELO, J. R., KUN, A., BENECH, J. C., GIUDITTA, A., MORILLAS, J. & BENECH, C. R. (1999) Ribosomes and polyribosomes are present in the squid giant axon: an immunocytochemical study. Neuroscience 90, 705-715.
SOTELO-SILVEIRA, J. R., CALLIARI, A., KUN, A., BENECH, J. C., SANGUINETTI, C., CHALAR, C. & SOTELO, J. R. (2000) NeurofilamentmRNAsare present and translated in the normal and severed sciatic nerve. J Neurosci Res 62, 65-74.
STARR, R., ATTEMA, B., DEVRIES, G. H. & MONTEIRO, M. J. (1996a) Neurofilament phosphorylation is modulated by myelination. J Neurosci Res 44, 328-337.
STARR, R., HALL, F. L. & MONTEIRO, M. J. (1996b) A cdc2-like kinase distinct from cdk5 is associated with neurofilaments. J Cell Sci 109, 1565-1573.
STERNBERGER, L. A. & STERNBERGER, N. H. (1983) Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phosphorylated and non phosphorylated forms of neurofilaments in situ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 6126-6130.
STRACK, S., WESTPHAL, R. S., COLBRAN, R. J., EBNER, F. F. & WADZINSKI, B. E. (1997) Protein serine/ threonine phosphatase 1 and 2A associate with and dephosphorylate neurofilaments. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 49, 15-28.
STRONG, M. J., STRONG, W. L., JAFFE, H., TRAGERT, B., SOPPER, M. M. & PANT, H. C. (2001) Phosphorylation state of native high molecular weight human neurofilament sub-unit protein (NF-H) from cervical spinal cord in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis J. Neurochem. 76, 1315-1325.
SUN, D., LEUNG, C. L. & LIEM, R. (1996) Phosphorylation Neurofilament protein 871 of the high molecular weight neurofilament protein (NF-H) by Cdk5 and p35. J Biol Chem 271, 14245-14251.
SVITKINA, T. M., VERKHOVSKY, A. B. & BORISY, G. B. (1998) Plectin sidearms mediate interactions of intermediate filaments with microtubules and other components of the cytoskeleton. Biol Bull 194, 409-410.
SZARO, B. G., GRANT, P., LEE, V. M. & GAINER, H. (1991a) Inhibition of axonal development after injection of neurofilament antibodies into a Xenopus laevis embryo. J Comp Neurol 308, 576-585.
SZARO, B. G., LEE, V. M. & GAINER, H. (1989) Spatial and temporal expression of phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of neurofilament proteins in the developing nervous system of Xenopus laevis. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 48, 87-103.
SZARO, B. G., PANT, H. C., WAY, J. & BATTEY, J. (1991b) Squid low molecular weight neurofilament proteins are a novel class of neurofilament protein. A nuclear laminlike core and multiple distinct proteins formed by alternative RNA processing. J Biol Chem 266, 15035-15041.
TAKAHASHI, M., AMIN, N., GRANT, P. & PANT, H. C. (1995) P13suc1 associates with a cdc2-like kinase in a multimeric cytoskeletal complex in squid axoplasm. J Neurosci 15, 6222-6229.
TAPSCOTT, S. J., BENNETT, G. S. & HOLTZER, H. (1981) Neuronal precursor cells in the chick neural tube express neurofilament proteins. Nature 292, 836-838.
TERRY-LORENZO, R. T., INOUE, M., CONNOR, J. H., HAYSTEAD, T. A., ARMBRUSTER, B. N., GUPTA, R. P., OLIVER, C. J. & SHENOLIKAR, S. (2000) Neurofilament-L is aprotein phosphatase-1-binding protein associated with neuronal plasma membrane and post-synaptic density. J Biol Chem 275, 2439-2446.
TOKUOKA, H., SAITO, T., YORIFUJI, H., WEI, F., KISHIMOTO, T. & HISANAGA, S. (2000) Brainderived neurotrophic factor-induced phosphorylation of neurofilament-H subunit in primary cultures of embryo rat cortical neurons. J Cell Sci 113, 1059-1068.
TRAVERSE, S., GOMEZ, N., PATERSON, H., MARSHALL, C. & COHEN, P. (1992) Sustained activation of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade may be required for differentiation of PC12 cells. Comparison of the effects of nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor. Biochem J 288, 351-355.
TROY, C. M., MUMA, N. A., GREENE, L. A., PRICE, D. L. & SHELANSKI, M. L. (1990) Regulation of peripherin and neurofilament expression in regenerating rat motor neurons. Brain Res 529, 232-238.
TSAI, L. H., DELALLE, I., CAVINESS, V., JR., CHAE, T. & HARLOW, E. (1994) p35 is a neural-specific regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371, 419-423.
TSAI, L. H., TAKAHASHI, T., CAVINESS, V., JR. & HARLOW, E. (1993) Activity and expression pattern of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in the embryonic mouse nervous system. Development 119, 1029-1040.
TU, P. H., GURNEY, M. E., JULIEN, J. P., LEE, V. M. & TROJANOWSKI, J. Q. (1997) Oxidative stress, mutant SOD1, and neurofilament pathology in transgenic mouse models of human motor neuron disease [published erratum appears in Lab Invest 1997 Jun, 76 (6): following table of contents]. Lab Invest 76, 441-456.
TYTELL, M., ZACKROFF, R. V. & HILL, W. D. (1988) Axonal neurofilaments differ in composition and morphology from those in the soma of the squid stellate ganglion. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 9, 349-360.
TYTELL, M., PANT, H. C., GAINER, H. & HILL, W. D. (1990) Characterization of the distinctive neurofilament subunits of the soma and axon initial segments in the squid stellate ganglion. J Neurosci Res 25, 153-161.
VALLANO, M. L., GOLDENRING, J. R., LASHER, R. S. & DELORENZO, R. J. (1986) Association of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase withcytoskeletal preparations: phosphorylation of tubulin, neurofilament, and microtubule associated proteins. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 466, 357-374.
VEERANNA, AMIN, N. D., AHN, N. G., JAFFE, H., WINTERS, C. A., GRANT, P. & PANT, H. C. (1998) Mitogen-activated protein kinases (Erk1,2) phosphorylate Lys-Ser-Pro (KSP) repeats in neurofilament proteins NF-H and NF-M. J Neurosci 18, 4008-4021.
VEERANNA, SHETTY, K. T., LINK, W. T., JAFFE, H., WANG, J. & PANT, H. C. (1995) Neuronal cyclindependent kinase-5 phosphorylation sites in neurofilament protein (NF-H) are dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A. J Neurochem 64, 2681-2690.
VEERANNA, G. J., SHETTY, K. T., TAKAHASHI, M., GRANT, P. & PANT, H. C. (2000) Cdk5 and MAPK are associated with complexes of cytoskeletal proteins in rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 76, 229-236.
VICKERS, J. C., MORRISON, J. H., FRIEDRICH, V. L., JR., ELDER, G. A., PERL, D. P., KATZ, R. N. & LAZZARINI, R. A. (1994) Age-associated and cell-typespecific neurofibrillary pathology in transgenic mice expressing the human midsized neurofilament subunit. J Neurosci 14, 5603-5612.
WANG, S., LEES, G. J., ROSENGREN, L. E., KARLSSON, J. E., HAMBERGER, A. & HAGLID, K. G. (1992) Proteolysis of filament proteins in glial and neuronal cells after in vivo stimulation of hippocampal NMDA receptors. Neurochem Res 17, 1005-1009.
WAY, J., HELLMICH, M. R., JAFFE, H., SZARO, B., PANT, H. C., GAINER, H. & BATTEY, J. (1992) A high-molecular-weight squid neurofilament protein contains a lamin-like rod domain and a tail domain with Lys-Ser-Pro repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89, 6963-6967.
WICHE, G. (1998) Role of plectin in cytoskeleton organization and dynamics. J. Cell Sci. 111, 2477-2486.
WILLARD, M. & SIMON, C. (1983) Modulations of neurofilament axonal transport during the development of rabbit retinal ganglion cells. Cell 35, 551-559.
WILLIAMSON, T. L. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1999) Slowing of axonal transport is a very early event in the toxicity of ALS-linked SOD1 mutants to motor neurons. Nat Neurosci 2, 50-56.
WONG, J. & OBLINGER, M. M. (1990) Differential regulation of peripherin and neurofilament gene expression in regenerating rat DRG neurons. J Neurosci Res 27, 332-341.
WONG, P. C., MARSZALEK, J., CRAWFORD, T. O., XU, Z., HSIEH, S. T., GRIFFIN, J. W. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1995) Increasing neurofilament subunit NF-M expression reduces axonal NF-H, inhibits radial growth, and results in neurofilamentous accumulation in motor neurons. J Cell Biol 130, 1413-1422.
XIAO, J. & MONTEIRO, M. J. (1994) Identification and characterization of a novel (115 kDa) neurofilamentassociated kinase. J Neurosci 14, 1820-1833.
XU, Z. & TUNG, V. W. (2000) Overexpression of neurofilament subunitMaccelerates axonal transport of neurofilaments. Brain Res 866, 326-332.
XU, Z., CORK, L. C., GRIFFIN, J. W. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1993) Increased expression of neurofilament subunit NF-L produces morphological alterations that resemble the pathology of human motor neuron disease. Cell 73, 23-33.
XU, Z., MARSZALEK, J. R., LEE, M. K., WONG, P. C., FOLMER, J., CRAWFORD, T. O., HSIEH, S. T., GRIFFIN, J. W. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1996) Subunit composition of neurofilaments specifies axonal diameter. J Cell Biol 133, 1061-1069.
YAMASAKI, H., IKATURA, C. & MIZUTANI, M. (1991) Hereditary hypotrophic axonopathy with neurofilament deficiency in amutant strain of the Japanese quail. Acta Neuropathol. 82, 427-434.
YANG, Y., BAUER, C., STRASSER, G., WOLLMAN, R., JULIEN, J. P. & FUCHS, E. (1999) Integrators of the cytoskeleton that stabilize microtubules. Cell 98, 229-238.
YANG, Y., DOWLING, J., YU, Q.-C., KOUKLIS, P., CLEVELAND, W. W. & FUCHS, E. (1996) An essential cytoskeletal linker protein connecting actin microfilaments to intermediate filaments. Cell 86, 655-665.
YAWORSKY, P. J., GARDNER, D. P. & KAPPEN, C. (1997) Transgenic analyses reveal developmentally regulated neuron-and muscle-specific elements in the murine neurofilament light chain gene promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 25112-25120.
YAZDANBAKHSH, K., FRASER, P., KIOUSSIS, D., VIDAL, M., GROSVELD, F. & LINDENBAUM, M. (1993) Functional analysis of the human neurofilament light chain gene promoter. Nucleic Acid Res. 21, 455-461.
YIN, X., CRAWFORD, T. O., GRIFFIN, J. W., TU, P., LEE, V. M., LI, C., RODER, J. & TRAPP, B. D. (1998) Myelin-associated glycoprotein is a myelin signal that modulates the caliber of myelinated axons. J Neurosci 18, 1953-1962.
YOSHIMURA, Y., AOI, C. & YAMAUCHI, T. (2000) Investigation of protein substrates of Ca(2+)/calmodulindependent protein kinase II translocated to the postsynaptic density [In Process Citation]. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 81, 118-128.
YOSHIMURA, Y., SOGAWA, Y. & YAMAUCHI, T. (1999) Protein phosphatase 1 is involved in the dissociation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II from postsynaptic densities. FEBS Lett 446, 239-242.
ZHANG, Q., AHUJA, H. S., ZAKERI, Z. F. & WOLGEMUTH, D. J. (1997) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is associated with apoptotic cell death during development and tissue remodeling. Dev Biol 183, 222-233.
ZHAO, Y. & SZARO, B. G. (1995) The optic tract and tectal ablation influence the composition of neurofilaments in regenerating optic axons of Xenopus laevis. J Neurosci 15, 4629-4640.
ZHENG, M., LEUNG, C. L. & LIEM, R. K. (1998) Regionspecific expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5) and its activators, p35 and p39, in the developing and adult rat central nervous system. J Neurobiol 35, 141-159.
ZHU, Q., COUILLARD-DESPRES, S. & JULIEN, J. P. (1997) Delayed maturation of regenerating myelinated axons in mice lacking neurofilaments. Exp Neurol 148, 299-316.
ZHU, Q., LINDENBAUM, M., LEVAVASSEUR, F., JACOMY, H. & JULIEN, J. P. (1998) Disruption of the NF-H gene increases axonal microtubule content and velocity of neurofilament transport: relief of axonopathy resulting from the toxin beta,beta'-iminodipropionitrile [see comments]. J Cell Biol 143, 183-193.
ZOPF, D., DINEVA, B., BETZ, H. & GUNDELFINGER, E. D. (1990) Isolation of the chicken middle-molecular weight neurofilament (NF-M) gene and characterization of its promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 18, 521-529.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grant, P., Pant, H.C. Neurofilament protein synthesis and phosphorylation. J Neurocytol 29, 843–872 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010999509251
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010999509251