Abstract
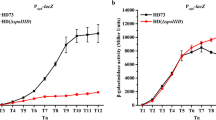
For the development of Bacillus subtilis as a host for foreign protein synthesis, three types of sigma factor deleted mutants (spoIIAC, spoIIIG and spoIIIC) were constructed by antibiotic marker insertion using plasmid vector-mediated method or LFH (Long Flanking Homology)-PCR. Mother cell specific sigma factor mutants of B. subtilis (σK), B. subtilis DB104 ΔspoIIIC (km r)::pMK101, had two to three times higher subtilisin activity than the wild type DB104::pMK101. Subtilisin expression by the other two mutants, B. subtilis DB104 ΔspoIIAC (km r)::pMK101 and DB104 ΔspoIIIG (km r)::pMK101, which are pre-spore specific sigma factor (σF and σG) deleted strains, was similar to, or less than that of the wild type.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bron S, Bosma P, Van Belkum M, Luxen E (1987) Stability function in Bacillus subtilis plasmid pTA1060. Plasmid 18: 8-15.
Cotinen VP, Sarvas M (1993) The prsA lipoprotein is essential for the protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis and sets a limit for high level secretion. Mol. Microbiol. 8: 727-737.
Errington J, Rong MS (1988) Transcriptional regulation and structure of the Bacillus subtilis sporulation locus spoIIIC. J. Bacteriol. 170: 1162-1167.
Ferrari E, Howard SM, Hoch JA (1986) Effect of stage 0 sporulation mutations on subtilisin expression. J. Bacteriol. 166: 173-179.
Fleming AB, Tangney M, Jorgensen PL, Diderichsen B, Priest FG (1995) Extracellular enzyme synthesis in a sporulation-deficient strain of Bacillus licheniformis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 3775-3780.
Fujita M (2000) Temporal and selective association of multiple sigma factors with RNA polymerase during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Cells 5: 79-88.
Hicks KA, Grossman AD (1996) Altering the level and regulation of the major sigma subunit of RNA polymerase affects gene expression and development in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 20: 201-212.
Ju J, Mitchell T, Peters H, Haldenwang WG (1999) Sigma factor displacement from RNA polymerase during Bacillus subtilis sporulation. J. Bacteriol. 181: 4969-4977.
Kerovuo J, von Weymarn N, Povelainen M, Auer S, Miasnikov A (2000) A new efficient expression system for Bacillus and its application to production of recombinant phytase. Biotechnol. Lett. 22: 1311-1317.
Lee JW, Parulekar SJ (1993) Enhanced production of α-amylase in the fed batch culture of Bacillus subtilis TN106[pAT5]. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 42: 1142-1150.
Nagarajan V, Ramaley R, Albertson H, Cheu M (1993) Secretion of streptividine from Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 3894-3898.
Oh MK, Kim BG, Park SH (1995a) Importance of spore mutants for fed-batch and continuous fermentation of Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 47: 696-702.
Oh MK, Park SH, Kim BG (1995b) Enhanced subtilisin production with spore mutants of Bacillus subtilis and their characterization. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 750: 444-451.
Oh MK, Park SH, Kim BG (1994) Development and characterization of sporulation mutants for overexpression of recombinant protein of Bacillus subtilis. Korean J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 9: 16-25.
Olmos J, de Anda R, Ferrari E, Bolivar F, Valle F (1997) Effects of the sinR and degU32 (Hy) mutations on the regulation of the aprE gene in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Gen. Genet. 20: 562-567.
Pierce JA, Robertson CR, Leighton TJ (1992) Physiological and genetic strategies for enhanced subtilisin production by Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Prog. 8: 211-218.
Schaeffer P, Millet J, Aubert J (1965) Catabolite repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 54: 704-711.
Wach A (1996) PCR-synthesis of marker cassette with long flanking homology regions for gene disruption in S. cerevisiae. Yeast 12: 259-265.
Wu XC, Lee W, Tran L, Wong SL (1991) Engineering a Bacillus subtilis expression-secretion system with a strain deficient in six extracellular protease. J. Bacteriol. 173: 4952-4958.
Yudkin MD (1987) Structure and function in a Bacillus subtilis sporulation-specific sigma factor: molecular nature of mutations in spoIIAC. J. Gen. Microbiol. 133: 475-481.
Zhang B, Struffi P, Kroos L (1999) Sigma K can negatively regulate sigE expression by two different mechanisms during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 181: 4081-4088.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JH., Kim, BG. Construction of spore mutants of Bacillus subtilis for the development as a host for foreign protein production. Biotechnology Letters 23, 999–1004 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010515632509
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010515632509