Abstract
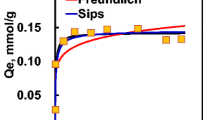
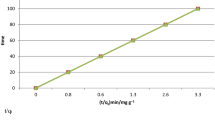
Biosorption, the passive accumulation of metal ions by biomass, can be used for purifying metal bearing wastewater. Seaweeds represent a readily available source of biosorbent material that possesses a high metal binding capacity. For example, Sargassum can accumulate 2 mequiv of Cd per gram of biomass i.e. 10% of its dry weight. Binding of Cd and Cu by Sargassum is an ion exchange process involving both covalent and ionic bonds. The amount of cations bound covalently or by complexation can be predicted using multi-component sorption isotherms involving 2 types of binding sites, carboxyl and sulphate. A Donnan model was used to account for the effect of ionic strength and electrostatic attraction. The use of a multi-component isotherm that included one term for Na binding was less appropriate than the Donnan model for modelling ionic strength effects. It was possible to predict metal and proton binding as a function of the pH value, metal concentration and ionic strength of the solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartschat BM, Cabaniss SE, Morel FMM (1992) Oligoelectrolyte model for cation binding by humic substances. Envir. Sci. Technol. 26: 284–294.
Buffle J (1988) Complexation Reactions in Aquatic Systems: An Analytical Approach. Ellis Horwood Ltd., Chichester, UK: 156–329.
Crist RH, Martin JR, Carr D,Watson JR, Clarke HJ, Crist DR (1994) Interactions of metals and protons with algae. 4. Ion exchange vs. adsorption models and a reassessment of Scatchard plots; ionexchange rates and equilibria compared with calcium alginate. Envir. Sci. Technol. 28: 1859–1866
Crist RH, Oberholser K, Schwartz D, Marzoff J, Ryder D, Crist DR (1988) Interactions of metals and protons with algae. Envir. Sci. Technol. 22: 755–760.
Ferguson J, Bubela B (1974) The concentration of Cu (II), Pb (II), and Zn (II) from aqueous solutions by particulate algal matter. Chem. Geol. 13: 163–186.
Fourest E, Volesky B (1996) Contribution of sulphonate groups and alginate to heavy metal biosorption by the dry biomass of Sargassum fluitans. Envir. Sci. Technol. 30: 277–282.
Greene B, McPherson R, Darnall D (1987) Algal sorbents for selective metal ion recovery. In: Patterson JW, Pasino R (eds), Metals Speciation, Separation and Recovery, Lewis, Chelsea, MI: 315–338.
Haug A (1961) Dissociation of alginic acid. Acta Chem. Scand. 15: 950–952.
Holan ZR, Volesky B, Prasetyo I (1993) Biosorption of cadmium by biomass of marine algae. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 41: 819–825.
Katchalsky A, Michaeli I (1955) Polyelectrolyte gels in salt solutions. J. Polym. Sci. 15: 69–86.
Kinniburgh DG, Milne CJ, Benedetti MF, Pinheiro JP, Filius J, Koopal LK, Van Riemsdijk WH (1996) Metal ion binding by humic acid: Application of the NICA-Donnan model. Envir. Sci. Technol. 30: 1687–1698.
Kuyucak N, Volesky B (1989) Themechanism of cobalt biosorption. Biotechnol. Bioengng 33: 823–831.
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40: 1361–1403.
Lee RE (1980) Phycology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK: 224–225.
Lin FG, Marinsky JA (1993) A Gibbs-Donnan-based interpretation of the effect of medium counterion concentration levels on the acid dissociation properties of alginic acid and chondroitin sulfate. React. Polym. 19: 27–45.
Marinsky JA (1987) A two-phase model for the interpretation of proton and metal ion interaction with charged polyelectrolyte gels and their linear analogs. In Stumm W (ed.), Aquatic Surface Chemistry, Wiley Interscience, John Wiley and Sons, NY: 49–81.
Ramelow GJ, Fralick D, Zhao Y (1992) Factors affecting the uptake of aqueous metal ions by dried seaweed biomass. Microbios 72: 81–93.
Schiewer S, Volesky B (1995) Modelling of the proton-metal ion exchange in biosorption. Envir. Sci. Technol. 29: 3049–3058.
Schiewer S, Volesky B (1997a) Ionic strength and electrostatic effects in biosorption of protons. Envir. Sci. Technol. 30: 1863–1871.
Schiewer S, Volesky B (1997b) Ionic strength and electrostatic effects in biosorption of divalent metal ions and protons. Envir. Sci. Technol. 30: 2478–2485.
South GR, Whittick A (1987) Introduction to Phycology. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, UK: 61–62.
Tipping E (1993) Modelling the competition between alkaline earth cations and trace metal species for binding by humic substances. Envir. Sci. Technol. 27: 520–529.
Tsezos M, Volesky B (1981) Biosorption of uranium and thorium. Biotechnol. Bioengng 23: 583–604.
Volesky B, Holan ZR (1995) Biosorption of heavy metals. Biotechnol. Progr. 11: 235–250.
Westall JC, Jones JD, Turner GD, Zachara JM (1995) Models for association of metal ions with heterogeneous environmental sorbents: I. Complexation of Co(II) by leonardite humic acid as a function of pH and NaClO4 concentration. Envir. Sci. Technol. 29: 951–959.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schiewer, S. Modelling complexation and electrostatic attraction in heavy metal biosorption by Sargassum biomass. Journal of Applied Phycology 11, 79–87 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008025411634
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008025411634