Abstract
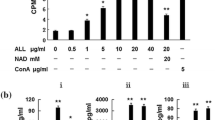
Lectins are powerful stimulants of quiescent peripheral blood lymphocytes. They can induce blast transformation leading to mitosis of these cells in vitro. We report here the dose-dependent proliferative curve for human peripheral blood monouclear cells (PBMC) stimulated by the lectin amansin, from Amansia multifida. Amansin stimulated proliferation of (PBMC) at relatively low concentrations (3.12 to 12.5 µg mL-1). We observed also a gradual reduction in mitogenic capacity with progressive increase in the lectin concentration above 12.5 µg mL-1. This decrease in the mitogenic potential did not result from a toxic effect on the cells, and was predominant at a lectin concentration above 50 µg mL-1. This decrease in lymphocyte proliferation could be blocked by avidin and could not be overcome by IL-2 or another lectin (Con Br) at stimulatory concentrations. Additionally, we observed that cells incubated at stimulatory concentrations of amansin produced IFN-γ. Analysis of the culture supernatants established a direct correlation between the IFN-γ and the mitogenic and anti-mitogenic capacity of amansin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borrebaeck C, Etzler M (1982) Mitogenic properties of two carbohydrate binding proteins from the Dolichos biflorus plant. FEBS Letts 145: 8–10.
Costa FHF (1995) Purificacāo e caracterizacāo parcial de una lectina mitogênica presente na alga marinha vermelha Amansia multifida Lamouroux. Ms. Thesis, in Departamento de Bioquímica e Biologia Molecular, Universidade Federal do Ceará, Brazil. 125 pp.
Ding L, Shevach EM (1992) IL-10 inhibits mitogen-induced T cell proliferation by selectively inhibiting macrophage costimulatory function. J. Immunol. 148: 3133–3139.
Dutton R (1972) Inhibitory and stimulatory effects of concanavalin A on the response of mouse spleen cell suspensions to antigen-I. Characterization of the inhibitory cell activity. J. exp. Med. 136: 1445–1460.
Gollob JA, Li J, Reinherz EL, Ritz J (1995) CD2 regulates responsiveness of activated T cells to interleukin 12. J. exp. Med. 182: 721–731.
Greene WC, Parker CM, Parker CW (1976) Opposing effects of mitogenic and non-mitogenic lectins on lymphocyte activation: evidence that wheat germ agglutinin produces a negative signal. J. biol. Chem. 254: 4017–4025.
Hori K, Ikegami S, Miyazawa K, Ito K (1988) Mitogenic and antineoplastic isoagglutinins from the red alga Solieria robusta. Phytochemistry 27: 2063–2067.
Kilpatrick DC (1988) Accessory cell paradox: monocytes enhance or inhibit lectin-mediated human T lymphocyte proliferation depending on the choice of mitogen. Scand. J. Immunol. 28: 247–249.
Kilpatrick DC, Graham C, Urbaniak SJ (1986) Inhibition of human lymphocyte transformation by tomato lectin. Scand. J. Immunol. 24: 11–19.
Kilpatrick DC, McCurrach PM (1987) Wheat germ agglutinin is mitogenic, non-mitogenic and anti-mitogenic for human lymphocytes. Scand. J. Immunol. 25: 343–348.
Moreira RA, Cavada BS (1984) Lectin from Canavalia brasiliensis (Mart). Isolation, characterization and behaviour during germination. Biologia Plantarum 26: 113–120.
Nowell PL (1960) Phytohaemagglutinin: an indicator of mitosis in cultures of normal human leucocytes. Cancer Res. 20: 462–466.
Pertile TL, Sharma JM, Walser MM (1995) Retrovirus infection in chickens primes splenic adherent macrophages to produce nitric oxide in response to T cell-produced factors. Cellular Immunol. 164: 207–216.
Pusztai A (1991) Plant Lectins. Cambridge U.P., Cambridge. 263 pp.
Reed JC, McCurrach PM, Kilpatrick DC (1985) Effect of wheat-germ agglutinin on the interleukin pathway of human T lymphocyte activation. J. Immunol. 134: 314–323.
Rogers DJ, Hori K (1993) Marine algal lectins: new developments. Hydrobiologia 260/261: 589–593.
Weiss A (1993) T Lymphocyte activation. In Paul WE (ed.), Fundamental Immunology. Raven Press, New York, 467–504.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, H.C., Costa, F.H.F., Sampaio, A.H. et al. Induction and inhibition of human lymphocyte transformation by the lectin from the red marine alga Amansia multifida. Journal of Applied Phycology 10, 153–162 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008016731752
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008016731752