Abstract
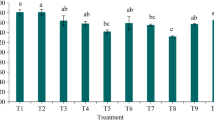
The use of organic waste materials such as milk sewage as an organic fertilizer could have the dual advantages of organic-waste disposal and reduced dependence on inorganic fertilizers. The effects of fertilization with (1) conventional mineral fertilization, (2) milk sewage sludge at 40 kg N ha−1 target rate and (3) no fertilization on pasture production and tree growth were examined in an experiment consisting of two pasture mixtures under a one-year-old Pinus radiata plantation with a density of 2500 trees ha−1. The two pasture mixtures were: (1) Dactylis glomerata L. var. saborto (25 kg ha−1) + Trifolium repens L. group Ladino (4 kg ha−1) + Trifolium pratense L. var. Marino (1 kg ha−1); (2) Lolium perenne L. var. Tove (25 kg ha−1) + Trifolium repens L. group Ladino (4 kg ha−1) + Trifolium pratense L. var. Marino (1 kg ha−1). The experiment began in the spring of 1995 using a randomized block design with three replicates in Castro Riberas de Lea (Lugo, Galicia, north-western Spain). Plot size was 12 × 8 m2, with a 1 m buffer strip between plots. Two-year data showed that fertilization with either material had a positive effect on pasture production, with no significant difference between the two fertilization treatments. Tree growth in the milk sewage sludge plot was significantly higher than in the control plots. Inorganic fertilization increased pasture production, but affected tree growth negatively. The results show that milk sewage sludge could be used as a fertilizer in silvo-pastoral systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bontoux L, Vega M and Papameletiou D (1998) Tratamiento de las aguas residuales urbanas en Europa: el problema de los lodos. Instituto de perspectiva technológica (eds) IPTS, abril, report no. 23. Comisión Europea
Commission of European Community (1986) Council directive on protection of the environment and in particular of the soil when sewage sludge is used in agriculture. Official Journal of the European Communities, No. L 181/6-12, 4 July
Gómez-Ibarlucea-Sempere C (1986) Valor fertilizante de los purines. In: Xunta de Galicia (eds) Memoria 1984-1985 del Centro de Investigaciones Agrarias de Mabengondo. Santiago de Compostela, Spain
González-Rodríguez A and Mosquera-Losada R (1991) Dinámica y fertilización de praderas. In: Xunta de Galicia (eds) Memoria del Centro de Investigaciones Agrarias de Mabegondo. Santiago de Compostela, Spain
Hopmans P and Clerehan S (1991) Growth and uptake of N, P, K and B by Pinus radiata D. Don in response to applications of borax. Plant and Soil 131: 115-127
Kellas JD, Bird PR, Cumming KN, Kearney GA and Ashton AK (1995) Pasture production under a series of Pinus radiata-Pasture agroforestry systems in South-west Victoria, Australia. Australian Journal Agricultural Research 46: 1285-1297
Mosquera-Losada MR and González-Rodríguez A (1992) Mixed sward response to nitrogen and potassium fertilizer in Galicia. 14th General Meeting of European Grassland Federation. Lathi. Finland, 511-512
Mosquera-Losada MR and González-Rodríguez A (1998) Effect of annual stocking rates on dairy systems. Pasture production, offered pasture and intake. Grass and Forage Science 53: 95-98
Piñeiro J and Pérez M (1989) Evaluación de variedades comerciales de gramíneas pratenses de interés para la España hÚmeda. In: Xunta de Galicia (eds) Memoria 1989 del Centro de Investigaciones Agrarias de Mabegondo
Pomares J (1982) Valor fertilizante de los lodos de las depuradoras de aguas residuales. Información técnia económica agraria 49: 47-67
Silva Pando FJ, González P, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A, Rozados-Lorenzo MJ and Prunell A (1998) Livestock grazing under pinewood and eucalypus forests: multiple use in Northwest Spain. Agroforestry Forum 9(1): 36-43
Smith SR (1996) Agricultural recycling of sewage sludge and the environment. Smith SR (eds) CAB International, WRC Marlow Buckinghamshire, UK
Waring HD and Snowdown P (1986) Early growth responses by Pinus radiata to three mixed fertilizers. Australian Forestry Research 16: 91-95
Wolstenholme R, Dutch J, Moffat AJ, Bayes CD and Taylor CMA (1992) A manual for good practice for the use of Sewage Sludge in Forestry. Forestry Commission Bulletin 107, UK
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rigueiro-Rodríguez, A., Mosquera-Losada, M.R. & Gatica-Trabanini, E. Pasture production and tree growth in a young pine plantation fertilized with inorganic fertilizers and milk sewage in northwestern Spain. Agroforestry Systems 48, 245–256 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006233204645
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006233204645