Abstract
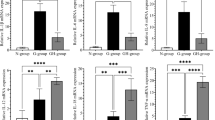
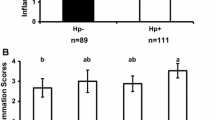
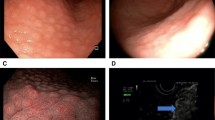
The cagA-positive Helicobacter pylori strains are thought to be able to induce interleukin-8 expression and to be associated with gastroduodenal diseases. Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) may be involved in inflammatory pathogenesis. Our aim was to investigate the interrelationships between cagA and the expression of interleukin-8 and iNOS messenger RNAs, and with the type and degree of inflammation in gastric mucosa. In biopsies from 108 Chinese patients, the cagA, 16S rRNA, interleukin-8, and iNOS mRNAs were analyzed using reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Specimens infected with cagA-positive strains had significantly more severe infiltration by mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leukocytes and more frequently expressed interleukin-8 and iNOS mRNAs than those infected with cagA-negative strains. iNOS and interleukin-8 mRNAs were significantly more frequently expressed together in the specimens with moderate or severe inflammation than in those with normal mucosa or mild inflammation. Our data suggest that interleukin-8 and excess nitric oxide play important roles in the pathogenesis of H. pylori-associated gastroduodenal diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Mobley HL: Helicobacter pylori factors associated with disease development. Gastroenterology 113:S21-S28, 1997
Nomura A, Stemmermann GN, Chyou PH, Kato I, Perez Perez GI, Blaser MJ: Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese Americans in Hawaii. N Engl J Med 325:1132-1136, 1991
Parsonnet J, Harris RA, Hack HM, Owens DK: Modelling cost-effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori screening to prevent gastric cancer: A mandate for clinical trials. Lancet 348:150-154, 1996
Tummuru MK, Cover TL, Blaser MJ: Cloning and expression of a high-molecular-mass major antigen of Helicobacter pylori: Evidence of linkage to cytotoxin production. Infect Immun 61:1799-1809, 1993
Crabtree JE, Taylor JD, Wyatt JI, Heatley RV, Shallcross TM, Tompkins DS, Rathbone BJ: Mucosal IgA recognition of Helicobacter pylori 120 kDa protein, peptic ulceration, and gastric pathology. Lancet 338:332-335, 1991
Blaser MJ, Perez PG, Kleanthous H, Cover TL, Peek RM, Chyou PH, Stemmermann GN, Nomura A: Infection with Helicobacter pylori strains possessing cagA is associated with an increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Cancer Res 55:2111-2115, 1995
Maeda S, Ogura K, Yoshida H, Kanai F, Ikenoue T, Kato N, Shiratori Y, Omata M: Major virulence factors, VacA and CagA, are commonly positive in Helicobacter pylori isolates in Japan. Gut 42:338-343, 1998
Larsen CG, Anderson AO, Appella E, Oppenheim JJ, Matsushima K: The neutrophil-activating protein (NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science 243:1464-1466, 1989
Kitadai Y, Haruma K, Sumii K, Yamamoto S, Ue T, Yokozaki H, Yasui W, Ohmoto Y, Kajiyama G, Fidler IJ, Tahara E: Expression of interleukin-8 correlates with vascularity in human gastric carcinomas. Am J Pathol 152:93-100, 1998
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, Sawai N, Tanahashi T, Kashima K, Imanishi J: Chemokines in the gastric mucosa in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 42:609-617, 1998
Ando T, Kusugami K, Ohsuga M, Shinoda M, Sakakibara M, Saito H, Fukatsu A, Ichiyama S, Ohta M: Interleukin-8 activity correlates with histological severity in Helicobacter pyloriassociated antral gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol 91:1150-1156, 1996
Crabtree JE, Farmery SM, Lindley IJ, Figura N, Peichl P, Tompkins DS: CagA/cytotoxic strains of Helicobacter pylori and interleukin-8 in gastric epithelial cell lines. J Clin Pathol 47:945-950, 1994
Crabtree JE, Covacci A, Farmery SM, Xiang Z, Tompkins DS, Perry S, Lindley IJ, Rappuoli R: Helicobacter pylori induced interleukin-8 expression in gastric epithelial cells is associated with CagA positive phenotype. J Clin Pathol 48:41-45, 1995
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, Sawai N, Kashima K, Imanishi J: Induction of various cytokines and development of severe mucosal inflammation by cagA gene positive Helicobacter pylori strains. Gut 41:442-451, 1997
Sharma SA, Tummuru MK, Miller GG, Blaser MJ: Interleukin-8 response of gastric epithelial cell lines to Helicobacter pylori stimulation in vitro. Infect Immun 63:1681-1687, 1995
Tummuru MK, Sharma SA, Blaser MJ: Helicobacter pylori picB, a homologue of the Bordetella pertussis toxin secretion protein, is required for induction of IL-8 in gastric epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol 18:867-876, 1995
Ohshima H, Bartsch H: Chronic infections and inflammatory processes as cancer risk factors: Possible role of nitric oxide in carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 305:253-264, 1994
Pignatelli B, Bancel B, Estève J, Malaveille C, Calmels S, Correa P, Patricot LM, Laval M, Lyandrat N, Ohshima H: Inducible nitric oxide synthase, anti-oxidant enzymes and Helicobacter pylori infection in gastritis and gastric precancerous lesions in humans. Eur J Cancer Prev 7:439-447, 1998
Pignatelli B, Bancel B, Malaveille C, Calmels S, Correa PM, Patricot LM, Laval M, Lyandrat N, Ohshima H: Helicobacter pylori infection oxidative stress and stomach cancer. In International Agency for Research on Cancer Biennial Report 1994/1995, Lyon, IARC, 1995, pp 101-102
Mannick EE, Bravo LE, Zarama G, Realpe JL, Zhang XJ, Ruiz B, Fontham ET, Mera R, Miller MJ, Correa P: Inducible nitric oxide synthase, nitrotyrosine, and apoptosis in Helicobacter pylori gastritis: Effect of antibiotics and antioxidants. Cancer Res 56:3238-3243, 1996
Bruch Gerharz D, Fehsel K, Suschek C, Michel G, Ruzicka T, Kolb Bachofen V: A proinflammatory activity of interleukin 8 in human skin: Expression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase in psoriatic lesions and cultured keratinocytes. J Exp Med 184:2007-2012, 1996
Villarete LH, Remick DG: Nitric oxide regulation of interleukin-8 gene expression. Shock 7:29-35, 1997
Andrew PJ, Harant H, Lindley IJ: Nitric oxide regulates IL-8 expression in melanoma cells at the transcriptional level. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 214:949-956, 1995
McCall TB, Palmer RM, Moncada S: Interleukin-8 inhibits the induction of nitric oxide synthase in rat peritoneal neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 186:680-685, 1992
Peek RM Jr, Miller GG, Tham KT, Perez Perez GI, Cover TL, Atherton JC, Dunn GD, Blaser MJ: Detection of Helicobacter pylori gene expression in human gastric mucosa. J Clin Microbiol 33:28-32, 1995
Gray SF, Wyatt JI, Rathbone BJ: Simplified techniques for identifying Campylobacter pyloridis. J Clin Pathol 39:1279, 1986
Price AB: The Sydney System: Histological division. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:209-222, 1991
Peek-RM J, Moss SF, Tham KT, Perez PG, Wang S, Miller GG, Atherton JC, Holt PR, Blaser MJ: Helicobacter pylori cagA1 strains and dissociation of gastric epithelial cell proliferation from apoptosis. J Natl Cancer Inst 89:863-868, 1997
Peek-RM J, Miller GG, Tham KT, Perez PG, Zhao X, Atherton JC, Blaser MJ: Heightened inflammatory response and cytokine expression in vivo to cagA1 Helicobacter pylori strains. Lab Invest 73:760-770, 1995
Ambs S, Merriam WG, Bennett WP, Felley BE, Ogunfusika MO, Oser SM, Klein S, Shields PG, Billiar TR, Harris CC: Frequent nitric oxide synthase-2 expression in human colon adenomas: Implication for tumor angiogenesis and colon cancer progression. Cancer Res 58:334-341, 1998
Weel JF, van der Hulst RW, Gerrits Y, Roorda P, Feller M, Dankert J, Tytgat GN, van der Ende A: The interrelationship between cytotoxin-associated gene A, vacuolating cytotoxin, and Helicobacter pylori-related diseases. J Infect Dis 173:1171-1175, 1996
Pan ZJ, van der Hulst RW, Feller M, Xiao SD, Tytgat GN, Dankert J, van der Ende A: Equally high prevalences of infection with cagA-positive Helicobacter pylori in Chinese patients with peptic ulcer disease and those with chronic gastritis-associated dyspepsia. J Clin Microbiol 35:1344-1347, 1997
Miehlke S, Kibler K, Kim JG, Figura N, Small SM, Graham DY, Go MF: Allelic variation in the cagA gene of Helicobacter pylori obtained from Korea compared to the United States. Am J Gastroenterol 91:1322-1325, 1996
Shimoyama T, Fukuda S, Tanaka M, Mikami T, Saito Y, Munakata A: High prevalence of the CagA-positive Helicobacter pylori strains in Japanese asymptomatic patients and gastric cancer patients. Scand J Gastroenterol 32:465-468, 1997
Censini S, Lange C, Xiang Z, Crabtree JE, Ghiara P, Borodovsky M, Rappuoli R, Covacci A: cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14648-14653, 1996
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, Sawai N, Imanishi J: Helicobacter pylori cagA gene and expression of cytokine messenger RNA in gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 110:1744-1752, 1996
Maeda S, Yoshida H, Ikenoue T, Ogura K, Kanai F, Kato N, Shiratori Y, Omata M: Structure of cag pathogenicity island in Japanese Helicobacter pylori isolates. Gut 44:336-341, 1999
Rachmilewitz D, Karmeli F, Eliakim R, Stalnikowicz R, Ackerman Z, Amir G, Stamler JS: Enhanced gastric nitric oxide synthase activity in duodenal ulcer patients. Gut 35:1394-1397, 1994
Shapiro KB, Hotchkiss JH: Induction of nitric oxide synthesis in murine macrophages by Helicobacter pylori. Cancer Lett 102:49-56, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, CQ., Pignatelli, B. & Ohshima, H. Coexpression of Interleukin-8 and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Gastric Mucosa Infected with cagA+ Helicobacter pylori. Dig Dis Sci 45, 55–62 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005453125433
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005453125433