Abstract
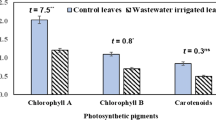
For productive utilisation of effluent–contaminated agricultural land, mobilisation and statistical analysis of potentially toxic elements in soil and plants of fields irrigated with mixedindustrial effluent have been undertaken. Total Fe,Mn, Zn, Cu, Pb, Ni and Cr have been estimated in soiland plant species of contaminated and noncontaminatedsites. 18 plants species and 18 root adjacent soilsamples from contaminated Kalipur area and 11 plantsspecies and 11 root adjacent soil samples fromuncontaminated Madhabpur area comprising majorcrops, vegetables and weeds have been included in thestudy. It is revealed that Hibiscusesculentus, Lycopersicon esculentum and Luffa acutangula growing in effluent–contaminated field show mobilisation ratio <0.5 for most of the PTE (Potentially Toxic Elements) likeCu, Pb, Ni, Cr and Cd and normal morphology.Surprisingly, weeds in particular, show highmobilization ratio >0.5 and simultaneously exhibithealthy gigantic morphology at the early floweringstage. Coriandrum sativum, Raphhanussativus, Solanum melongena, Spinaceaoleracea, Oryza sativum, Brassica oleraceashowed mobilization ratio >0.5 butmaintained normal growth. Based on mobilization ratioand external morphology, we suggest the cultivation ofplants H. esculentus, L. acutangula, L. esculentum in land irrigated with industrial effluent. The highest andsecond highest enrichment factor (EFpp)was found for Cd and Pb, respectively. Pearson'scorrelation coefficient indicated that the metal levelin soil is not the main factor governing metaluptake. This study will help in selecting plantspecies for cultivation in contaminated fields.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, P. J.: 1914,‘The effect of dust from cement mills in the setting of fruit’ Plant World 17, 57.
Barman, S. C. and Lal, M. M.: 1994,‘Accumulation of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Cd, and Pb) in soil and cultivated vegetables and weeds grown in industrially polluted fields’ Indian J. Environ. Biol. 15(2), 107.
Buchaure, M. J.: 1973,‘Contamination of soil and vegetation near a zinc smelter by Zn, Cd, Cu and Pb’ Environ. Sci. and Technol. 7(2), 131.
Cataldo, D. A. and Wildung, R. E.: 1978,‘Soil and plant factors influencing the accumulation of heavy metals by plants’ Environ. Hlth. Perspectives 27, 149.
Chambers, J. C. and Siddle, R. C.: 1991,‘Fate of heavy metals in abandoned lead zinc tailing ponds: I Vegetation’ J. Environ. Qual. 20, 745.
Chaney, R. L.: 1973,‘Crop and food chain effects of toxic elements in sludge and effluents: Recycling municipal sludges and effects on land’ U.S. EPA, Washington, D.C., 129–141.
Chang, A. C., Page, A. L., Foster, K. W. and Jones, T. E.: 1982,‘Comparison of cadmium and zinc accumulation by four cultivars of barley grown in sludge amended soils’ J. Environ. Qual. 11, 409.
Clijsters, H. and Van Assche, F.: 1985,‘Inhibition of photosynthesis by heavy metals’ Photosyn. Res. 7, 31.
Czaja, A. T.: 1962,‘Uber Das Problem Der Zementstaubwirk-Ungen and Pflanzen’ Staub 22, 228.
Eepstein, E. and Jefferies, R. L.: 1964,‘The genetic basis of selective ion transport in plants’ Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 29, 511.
Faucherre, J., Pinart, A. M. and Dutof, A.: 1985, Mecanisme biogeochemique de contamination des vegetaux par le plomb, le cadmium et le zinc C.R. contract C. Comm. Europe, January.
Gestring, W. D. and Jarnell, W. M.: 1982,‘Plant availability of phosphorus and heavy metals in soils amended with chemically treated sewage sludge’ J. Environ Qual. 11, 669.
Kabata-Pendias, A. and Pendias, H.: 1992, Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 2nd edn., CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fla.
Leita, L., Nobili, M. D., Pardini, G., Ferari, F. and Sequi, P.: 1989,‘Anomalous contents of heavy metals in soils and vegetation of mine area in south west Sardinia’ Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 48, 423.
Mc Nichol, R. D. and Beckett, P. H. T.: 1985,‘Critical tissue concentrations of potentially toxic elements’ Plant Soil 85, 107.
Mitchell, R. L., Reith, J. W. S. and Johnston, I. M.: 1957,‘Trace element uptake inrelation to soil content’ J. Sci. Food Agric. 8(Suppl. Issue), 51.
Olaniya, M. S., Bhoyar, R. V. and Bhide, A. D.: 1991,‘Effect of solid waste disposal on land, Indian’ J. Environ. Hlth. 34(2), 143.
Rao, D. N. and Singh, S. N.: 1978,‘Effect of cement dust pollution on soil properties and on wheat plants’ Indian J. Environ. Hlth. 20(3), 258.
Ray, M.: 1990,‘Accumulation of heavy metals in plants grown in industrial areas’ Indian Biologist, Vol. XXII, No.2.
Roberts, R. D. and Johnson, M. S.: 1978,‘Dispersal of heavy metals from abandoned mine workings and their transference through terrestrial food chains’ Environ. Poll. 16, 293.
Villanueva, V. R. and Santerre, A.: 1989,‘On the mechanism of adaptive metabolism of healthyresistant trees from forest polluted areas’ Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 48, 59.
Xian, X.: 1989,‘Response of kidney bean to concentration and chemical form of cadmium, zinc and lead in polluted soils’ Environ. Poll. 57, 127.
Yassoglou, N., Kosmas, C. Asimakopoulos, J. and Kallinou, C.: 1987,‘Heavy metal contamination of roadside soils in the greater Athens area’ Environ. Poll. 47, 293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kisku, G.C., Barman, S.C. & Bhargava, S.K. Contamination of Soil and Plants with Potentially Toxic Elements Irrigated with Mixed Industrial Effluent and its Impact on the Environment. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 120, 121–137 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005202304584
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005202304584