Abstract
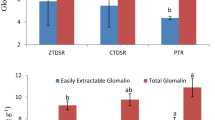
Declines in soil organic mailer (SOM) have occurred in most rainfed rice cropping systems in the world. Such declines threaten the sustainability of these systems and steps need to be taken to reverse the decline. Paired soil samples collected from forest and cropped areas in Northeast Thailand revealed an approximately 70% decline in both labile carbon (C L ) and total carbon (C T ) in the surface 10 cm as a result of cropping. C L was found to be higher in the 20–40 cm soil layer in the cropped than the forest soil indicating C leaching or soil mixing.
In a field experiment it was found that C L , and a calculated Carbon Management Index (CMI), increased with annual applications of low rates (1500 kg/ha dry matter) of leaf litter from Cajanus cajan, Phyllanthus taxodifolius, Acacia auriculiformis and Samanae saman. Five seasons of leaf litter application increased the C T pool by 24–37% and more than doubled C L and soil C lability. The retention of rice straw improved C T in the first year of the trial but led to no significant increases in subsequent years. Higher rates of fertilisers did not result in increased soil C, despite increased yields.
Crop residues, leaf litters and green manures with slow breakdown rates are needed to rehabilitate soil C. C L and the CMI can be used effectively to monitor the rate of change in soil C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberto M C R, Neue, H U, Capati A, Castro R U, Bernardo L M, Aduna J and Lantin R S 1996 Effect of different straw management practices on soil fertility, rice yields and the environment. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Maximising Sustainable Rice Yields Through Improved Soil and Environmental Management. Volume 1. Eds T Attanandana, I Kheoruenromne, P Pongsakul, and T Vearasilp. Khon Kaen, Thailand, 11–17 November, 1996. pp 197–206. Paddy Soil Working Group, ISSS.
Becker M, Ladha J K and Ottow J C G 1994 Nitrogen losses and lowland rice yield as affected by residue nitrogen release. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 58, 1660–1635.
Blair G J, Lefroy R D B and Lisle L 1995 Soil carbon fractions, based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 46, 1459–1466.
Cerri C, Bernoux M and Blair G J 1994 Carbon pools and fluxes in Brazilian natural and agricultural systems and the implications for the global CO2 balance. Transactions of the 15th World Congress of Soil Science. Volume 5a. Acapulco, Mexico, 10–16 July 1994. pp 399–406. ISSSC. and Mexican Society of Soil Science.
Chan K Y, Roberts W P and Heenan D P 1992 Organic carbon and associated soil properties of a red earth after 10 years of rotation under different stubble and tillage practices. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 30, 71–83.
Chantanaparb N, W Cholitkul and S Suwanawong 1976 Fertility of Thai Paddy soils. (In Thai). Report on soil chemistry and fertility No. 2, Department of Agriculture, Bangkok. 113 p.
Clément A, Ladha J K, and Chalifour, F P 1998 Nitrogen dynamics of various green manure species and the relationship to lowland rice production. Agron. J. 90, 149–154.
Dalal R C and Mayer R J 1986 Long-term trends in fertility of soils under continuous cultivation and cereal cropping in southern Queensland. II. Total organic carbon and its rate of loss from the soil profile. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 24, 281–292.
Doughton J A and Mackenzie J 1984 Comparative effects of black and green gram (mung beans) and grain sorghum on soil mineral nitrogen and subsequent grain sorghum yields on the Eastern Darling Downs. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb. 24, 244–249.
Gupta V V S R, Roper M M, Kirkgaard J A and Angus J F 1994 Changes in microbial biomass and organic matter levels during the first year of modified tillage and stubble management practices on a red earth. Aust. J. Soil Res. 32, 1339–1354.
Herrera W T, Vejpas C, Garrity D D, Sompaew V and N Thongpan 1989 Development of green manure technology for rainfed lowland rice on acid infertile soils in Northeast Thailand. Paper presented at the Saturday IRRI seminar, April 15, 1989
Jenkinson D S and Ayanaba A 1977 Decomposition of carbon-14 labelled plant material under tropical conditions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 41, 912–925.
Lefroy R D B, Konboon Y and Blair G J 1995 An in vitro Perfusion method to estimate rates of plant residue breakdown and associated nutrient release. Aust. J. Soil Res. 46, 1467–1476.
Ragland J L, Craig I and Choungchan P 1986 Northeast Rainfed Agricultural Development Project Final Quarterly Report No. 17. Univ. of Kentucky Technical Assistance Team. 48 p.
Strong W M, Harbison J, Nielson R G H, Hall B D and Best E K 1986 Nitrogen availability in a Darling Downs soil following cereal, oilseed and grain legume crops. 2. Effects of residual soil nitrogen and fertiliser nitrogen on subsequent wheat crops Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 26, 353–359.
Tian G, Kang B T and Brussaard L 1993 Mulching effect of plant residues with chemically contrasting compositions on maize growth and nutrient accumulation. Plant Soil 153, 179–187.
Tiessen H, Stewart J W B and Bettany J R 1982 Cultivation effects on the amounts and concentration of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in grassland soils. Agron. J. 74, 831–815.
Whitbread A M, Lefroy R D B and Blair G J (1996). Changes in soil physical properties and soil organic carbon fractions with cropping on a red brown earth soil. Proceedings of the 8th Australian Agronomy Conference. Toowoomba, Queensland, 30 Jan.-2 Feb., 1996. 582–585. (M. Ashgar) (The Australian Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Carlton, Vic.).
Whitbread A, Blair, G J, Naklang K, Lefroy R D B, Wonprasaid S, Konboon Y and Suriyaarunroj D 1998 The management of rice straw, fertilisers and leaf litters in rice cropping systems in Northeast Thailand. 2. Rice yields and nutrient balances. Plant Soil 209, 29–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naklang, K., Whitbread, A., Lefroy, R. et al. The management of rice straw, fertilisers and leaf litters in rice cropping systems in Northeast Thailand. Plant and Soil 209, 21–28 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004571015620
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004571015620