Abstract
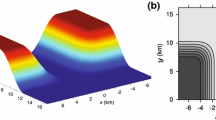
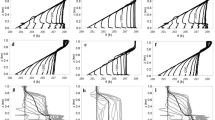
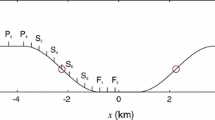
A three-dimensional, non-hydrostatic model was used to examine the dynamical characteristics of morning and evening transition periods in the atmosphere over four idealised valleys. The simulations provided detailed structure over full diurnal cycles of the valley-wind system. An essentially two-dimensional simulation (Case 1) clearly showed valley-side slope flows, driven by pressure gradients and modulated by vertical diffusion and Coriolis effects. The rotation of the wind was clockwise on both valley sides, contrary to most observations in nature. Three-dimensional simulations (Cases 2–4) rectified this feature and that for Case 4 satisfactorily modelled the valley-plain wind system throughout the diurnal cycle. Three types of transition were identified with the aid of different tools: hodographs; space-time evolution of the wind fields; and the evolution of the forcing terms in the momentum and temperature equations. Whichever type or Case was considered, the evening transition was longer than the morning one and the along-valley transition followed the along-slope one. In Cases 1 and 4 the evening transition started up to 2 h before sunset and the morning transition started up to 2.5 h after sunrise. In the three-dimensional cases the evening transition began at about 1700 and ended at about 2400, starting at the bottom of the valley and propagating up both valley sides, but at different speeds. It also started at the ground and propagated vertically. The morning transition began at about 0900 and ended at about 1100, also starting at the bottom of the valley and propagating both vertically and up the valley sides, albeit with different regimes on the two sides. The along-valley transition lagged that on the slopes by about 1.5 h. In Case 1 the forcing terms were dominated by the pressure gradient and the vertical diffusion, with the Coriolis effects introducing an along-valley component to the slope flows. The three dimensional cases were more complex, with not only the addition of the effects of advection and horizontal diffusion but also more temporal variation of more of the forcings than in Case 1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, B.W.: 1995, 'Orographic and Stability Effects on Valley-Side Drainage Flows', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 75, 403-428.
Atkinson, B. W. and Shabub, A. N.: 1994, 'Orographic and Stability Effects on Day-Time, Valley-Side Slope Flows', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 68, 275-300.
Bader, D. C. and McKee, T. B.: 1983, 'Dynamical Model Simulation of the Morning Boundary Layer Development in Deep Mountain Valleys', J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 22, 341-351.
Bader, D. C. and McKee, T. B.: 1985, 'Effects of Shear, Stability and Valley Characteristics on the Destruction of Temperature Inversions', J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 24, 822-832.
Bader, D. C. and Whiteman, C. D.: 1989, 'Numerical Simulation of Cross-Valley Plume Dispersion during the Morning Transition Period', J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 652-664.
Bader, D. C., McKee, T. B., and Tripoli, G. J.: 1987, 'Mesoscale Boundary Layer Evolution over Complex Terrain. Part 1: Numerical Simulation of the Diurnal Cycle', J. Atmos. Sci. 44, 2823-2838.
Ballard, S. P. and Golding, B. W.: 1991, 'Basic Model Formulation', Short Range Forecasting Research, Mesoscale Documentation Paper No. 4, Meteorological Office, Bracknell, 42 pp.
Banta, R. M.: 1984, 'Day-Time Boundary Layer Evolution over Mountainous Terrain. Part 1: Observations of the Dry Circulations', Mon. Wea. Rev. 112, 340-356.
Banta, R. M.: 1986, 'Day-Time Boundary Layer Evolution over Mountainous Terrain. Part 2: Numerical Studies of Upslope Flow Duration', Mon. Wea. Rev. 114, 1112-1130.
Banta, R. M. and Cotton, W. R.: 1981, An Analysis of the Structure of Local Wind Systems in a Broad Mountain Basin', J. Appl. Meteorol. 20, 1255-1266.
Banta, R. M., Olivier, L. D., Neff, W. D., Levinson, D. H., and Ruffieux, D.: 1995, 'Influence of Canyon-Induced Flows on Flow and Dispersion over Adjacent Plains', Theor. Appl. Climatol. 52, 27-42.
Blumen, W. (ed.): 1990, 'Atmospheric Processes over Complex Terrain', Meteorol. Monographs, Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 23,No. 45, 323 pp.
Bossert, J. E. and Poulos, G. S.: 1995, 'A Numerical Investigation of Mechanisms Affecting Drainage Flows in Highly Complex Terrain', Theor. Appl. Climatol. 52, 119-134.
Carpenter, K. M.: 1979, 'An Experimental Forecast Using a Non-Hydrostatic Mesoscale Model', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 105, 629-655.
Chen, Y. L. and Nash, A. J.: 1994, 'Diurnal Variation of Surface Airflow and Rainfall Frequencies on the Island of Hawai', Mon. Wea. Rev. 122, 34-56.
Clements, W. E., Archuleta, J. A., and Hoard, D. E.: 1989, 'Mean Structure of the Nocturnal Drainage Flow in a Deep Valley', J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 457-462.
Davidson, B.: 1961, 'Valley Wind Phenomena and Air Pollution Problems', Air Pollut. Control Assoc. J. 11, 364-386.
de Wekker, S. F., Zhong, S., Fast, J. D., and Whiteman, C. D.: 1998, 'A Numerical Study of the Thermally Driven Plain-to-Basin Wind over Idealized Basin Topographies', J. Appl. Meteorol. 37, 606-622.
Doran, J. C. and Horst, T. W.: 1983, 'Observations and Models of Simple Nocturnal Slope Flows', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 18, 495-527.
Fast, J. D., Zhong, S., and Whiteman, C. D.: 1996, 'Boundary-Layer Evolution within a Canyonland Basin. Part 2: Numerical Simulations of Nocturnal Flows and Heat Budgets', J. Appl. Meteorol. 35, 2162-2178.
Gudiksen, P. H. and Shearer, D. L.: 1989, 'The Dispersion of Atmospheric Tracers in Nocturnal Drainage Flow', J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 602-608.
Hawkes, H. B.: 1947, Mountain and Valley Winds with Special Reference to the Diurnal Mountain Winds of the Great Salt Lake Region, Ph.D. Dissertation, Ohio State University, 312 pp.
Helmis, C. G., Asimacopoulos, D. N., Deligiorgi, D. G., and Petrakis, M. C.: 1990, 'Some Observations on the Destruction of the Morning Temperature Inversions in a Large and Broad Mountain Valley', J. Appl. Meteorol. 29, 396-400.
Horst, T. W. and Doran, J. C.: 1986, 'Nocturnal Drainage Flow on Simple Slopes', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 34, 263-286.
Kelly, R. D.: 1988, 'Asymmetric Removal of Temperature Inversions in a High Mountain Valley', J. Appl. Meteorol. 27, 664-673.
Kondo, H.: 1995, 'The Thermally Induced Local Wind and Surface Inversion over the Kanto Plain on Calm Winter Nights', J. Appl. Meteorol. 34, 1439-1448.
Kuwagata, T. and Kimura, F.: 1995, 'Day-Time Boundary Layer Evolution in a Deep Valley. Part 1: Observations in the Ina Valley', J. Appl. Meteorol. 34, 1082-1091.
Mellor, G. L. and Yamada, T.: 1982, 'Development of a Turbulence Closure Model for Geophysical Fluid Problems', Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 20, 851-875.
Mursch-Radlgruber, E.: 1995, 'Observations of Flow Structure in a Small Forested Valley System', Theor. Appl. Climatol. 52, 3-17.
Orgill, M. M.: 1989, 'Early Morning Transition of a Gaseous Tracer from a Mountain Valley', J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 636-651.
Papadopoulos, K. H., Helmis, C. G., Soilemes, A. T., Kalogiros, J., Papageorgias, P. G., and Asimakopoulos, D. N.: 1997, 'The Structure of Katabatic Flows Down a Simple Slope', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 123, 1581-1602.
Poulos, G. S. and Bossert, J. E.: 1995, 'An Observational and Prognostic Numerical Investigation of Complex Terrain Dispersion', J Appl. Meteorol. 34, 650-669.
Ramanathan, N. and Srinivasan, K.: 1998, 'Simulation of Airflow in Kashmir Valley for a Summer Day', J. Appl. Meteorol. 37, 497-508.
Roach, W. T. and Slingo, A.: 1979, 'A High Resolution Infrared Radiative Transfer Scheme to Study the Interaction of Radiation with Cloud', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 105, 603-614.
Ruffieux, D.: 1995, 'Climatology and Meteorology in Complex Terrain', Theor. Appl. Climatol. 52, 1-134.
Slingo, A. and Schrecker, H. M.: 1982, 'On the ShortWave Radiation Properties of Stratiform Water Clouds', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 108, 407-426.
Tapp, M. C. and White, P.W.: 1976, 'A Non-Hydrostatic Mesoscale Model', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 102, 277-296.
Triantafyllou, A. G., Helmis, C. G., Asimakopoulos, D. N., and Soilemes, A. T.: 1995, 'Boundary-Layer Evolution over a Large and Broad Mountain Basin', Theor. Appl. Climatol. 52, 19-25.
Whiteman, C. D.: 1982, 'Breakup of Temperature Inversions in Deep Mountain Valleys. Part 1: Observations', J. Appl. Meteorol. 21, 270-289.
Whiteman, C. D.: 1989, 'Morning Transition Tracer Experiments in a Deep Narrow Valley', J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 626-635.
Whiteman, C. D.: 1990, 'Observations of Thermally Developed Wind Systems in Mountainous Terrain', in W. Blumen (ed.), Meteorol. Monographs, Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 23,No. 45, 5-42.
Whiteman, C. D. and McKee, T. B.: 1982, 'Breakup of Temperature Inversions in Deep Mountain Valleys: Part 2. Thermodynamic Model', J. Appl. Meteorol. 21, 290-302.
Whiteman, C. D., Allwine, K. J., Fritschen, L. J., Orgill, M. M., and Simpson, J. R.: 1989, 'Deep Valley Radiation and Surface Energy Budget Microclimates', J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 414-437.
Whiteman, C. D., McKee, T. B., and Doran, J. C.: 1996, 'Boundary-Layer Evolution within a Canyon Land Basin. Part 1: Mass, Heat and Moisture Budgets from Observations', J. Appl. Meteorol. 35, 2145-2161.
Yamada, T. and Bunker, S.: 1989, 'A Numerical Study of Nocturnal Drainage Flows with Strong Wind and Temperature Gradients', J. Appl. Meteorol. 28, 545-554.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, JG., Atkinson, B.W. Transition Regimes in Valley Airflows. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 91, 385–411 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001846005338
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001846005338