Abstract
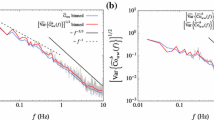
The correlations in turbulent wind speed data from the open ocean are studied. They are calculated as Fourier transforms of the spectraldensities, which are computed from Fourier transforms of the measured windspeed components. All correlations are found to decay within a few seconds.It is shown that the spectra are most efficiently calculated using data sections whose length does not exceed the observed correlation decay time.Longer runs include more random noise without containing more information.The ratio of the along-wind to transverse spectral levels is investigatedand found to be in excellent agreement with the assumption of isotropy inthe inertial wave number range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brigham, E. O.: 1974, The Fast Fourier Transform, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 252 pp.
Dobson, F. W., Smith, S. D., and Anderson, R. J.: 1994, 'Measuring the Relationship between Wind Stress and Sea State in the Open Ocean in the Presence of Swell',Atmosphere-Ocean 32, 237–256.
Dunckel, M., Hasse, L, Krügermeyer, L., Schriever, D., and Wucknitz, J.: 1974, 'Turbulent Fluxes of Momentum, Heat and Water Vapour in the Atmospheric Surface Layer at Sea during ATEX', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 6, 81–106.
Dupuis, H., Taylor, P. K., Weill, A., and Katsaros, K.: 1996, 'The Inertial Dissipation Method Applied toDerive Turbulent Fluxes over the Ocean during the SOFIA/ASTEXand SEMAPHORE Experiments in Low to Moderate Wind Speeds', J. Geophys. Res., in press.
Edson, J. B., Fairall, C. W., Mestayer, P. G., and Larsen, S. E.: 1991, 'A Study of the Inertial-Dissipation Method for Computing Air-Sea Fluxes', J. Geophys. Res. 96(C6), 10689–10711.
Fairall, C. W. and Larsen, S. E.: 1986, 'Inertial-Dissipation Methods and Turbulent Fluxes at the Air-Ocean Interface', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 34, 287–301.
Frenzen, P. and Vogel, C. A.: 1992, 'The TurbulentKinetic Energy Budget in the Atmospheric Surface Layer: A Review and an Experimental Reexamination in the Field', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 60, 49–76.
Henjes, K.: 1996, 'Justification of the Inertial Dissipation Technique in Anisotropic Mean Flow', Boundary-Layer Meteorology, submitted.
Hinze, J. O.: 1975, Turbulence, McGraw-Hill, New York, 790 pp.
Högström, U.: 1996, 'Review of Some Basic Characteristics of the Atmospheric Surface Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 78, 215–246.
Katul, G. G., Parlange, M. B., Albertson, J. D., and Chu, C. R.: 1995, 'Local Isotropy and Anisotropy in the Sheared and Heated Atmospheric Surface Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 72, 123–148.
Kolmogorov, A. N.: 1941, 'The Local Structure of Turbulence in Incompressible Viscous Fluid for Very Large Reynolds Numbers', Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 30. Reprinted in English in Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A (1991) 434, 9–13.
Landau, L. D. and Lifshitz, E.M.: 1987, Fluid Mechanics, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, pp. 539.
Large, W. G., Morzel, J., and Crawford, G. B.: 1995, 'Accounting for Surface Wave Distortion of the Marine Wind Profile in Low-Level Ocean Storms Wind Measurements', J. Phys. Oceanogr. 25, 2959–2971.
Large, W. G. and Pond, S.: 1981, 'Open Ocean Momentum Flux Measurements in Moderate to Strong Winds', J. Phys. Oceanogr. 11, 324–336.
Large, W. G. and Pond, S.: 1982, 'Sensible and Latent Heat Flux Measurements over the Ocean', J. Phys. Oceanogr. 12, 464–482.
Lumley, J. L. and Panofsky, H. A.: 1964, The Structure of Atmospheric Turbulence, JohnWiley, New York, 239 pp.
Marsden, R. F., McBean, G. A., and Proctor, B. A.: 1993, 'Momentum and Sensible Heat Fluxes Calculated by the Dissipation Technique during the Ocean Storms Project', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 63, 23–38.
Praskovsky, A. A., Gledzer, E. B., Karyakin, M. Yu., and Zhou, Ye: 1993, 'The Sweeping Decorrelation Hypothesis and Energy-Inertial Scale Interaction in High Reynolds Number Flows', J. Fluid Mech. 248, 493–511.
Schmitt, K. F., Friehe, C. A., and Gibson, C. H.: 1978, 'Sea Surface StressMeasurements',Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 15, 215–228.
Smith, S. D., Anderson, R. J., Oost, W. A., Kraan, C., Maat, N., DeCosmo, J., Katsaros, K. B., Davidson, K. L., Bumke, K., Hasse, L., and Chadwick, H. M.: 1992, 'Sea Surface Wind Stress and Drag Coefficients: The HEXOS Results', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 60, 109–142.
van Duin, C. A. and Janssen, P. A. E. M.: 1992, 'An Analytical Model of the Generation of Surface Gravity Waves by Turbulent Air Flow', J. Fluid Mech. 236, 197–215.
Yelland, M. and Taylor, P. K.: 1996, 'Wind Stress Measurements from the Open Ocean', J. Phys. Oceanogr. 26, 541–558.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henjes, K. Isotropic and anisotropic correlations in turbulent wind speed data. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 84, 149–167 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000386716341
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000386716341