Article contents
Morphological and molecular study of Didymodiclinus marginati n. sp. (Trematoda: Didymozoidae) gill parasite of Epinephelus marginatus from the central and western Mediterranean Sea
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 May 2022
Abstract
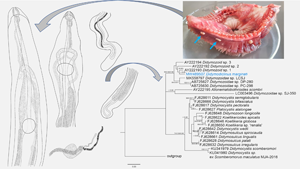
The current study provides a morphological and molecular characterization of a new species of Didymodiclinus (Trematoda: Didymozoidae) infecting the dusky grouper, Epinephelus marginatus (Teleostei: Serranidae) from the Mediterranean Sea. A total of 279 dusky grouper specimens were examined for didymozoid gill parasites from the Mediterranean Sea between 1998 and 2020. New species differs from the most similar congeneric species by the rudiments of female reproductive organs in functional male specimens, and the seminal receptacle, Mehlis gland and accessory gland cells in functional female specimens, not observed in Didymodiclinus branchialis (Yamaguti, 1970), Didymodiclinus epinepheli (Abdul-Salam, Sreelatha and Farah, 1990) and Didymodiclinus pacificus (Yamaguti, 1938), respectively. These species are also characterized by their different hosts and location within the host tissues, being from other geographical localities. Moreover, this is the first species reported in E. marginatus from the central and western Mediterranean Sea. Genetic analyses were performed on partial 28S and partial internal transcribed spacer-2 ribosomal RNA regions and the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase 1 (cox1) gene by polymerase chain reaction. Comparison of genetic sequences of Didymodiclinus marginati n. sp. with the available deposited sequences of 28S revealed that the new isolates cluster with several unidentified didymozoids and groups as a sister clade of the Nematobothrinae subfamily. Moreover, 28S and cox1 phylogenetic trees evidenced that Didymodiclinae is well separated from Didymozoinae and other gonochoric didymozoids. Following both morphological and genetic results, a key of identification for the genus Didymodiclinus is proposed.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press
Footnotes
Both authors contributed equally and share the first position.
References
- 1
- Cited by





