Article contents
Stability of wall bounded, shear flows of dense granular materials: the role of the Couette gap, the wall velocity and the initial concentration
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 February 2016
Abstract
In this paper, the stability of a plane, unidirectional Couette flow of a dense granular material is investigated via the means of a normal mode stability analysis. Our studies are based on a continuum mechanical model for the flows of interest coupled with the constitutive expressions for the normal and the shear stresses of the granular material induced by the 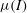 ${\it\mu}(I)$-rheology. According to our analysis, both the Couette gap and the wall velocity play a destabilizing role in the flows of interest as opposed to the initial concentration that acts as stabilizer. For sufficiently high Couette gaps and wall velocities, unstable modes are recovered. The predicted instability manifests itself through shear-induced dilatancy that, in turn, engenders particle migration and the formation of bulbs, similar to the ones that have been acquired through molecular dynamics simulations.
${\it\mu}(I)$-rheology. According to our analysis, both the Couette gap and the wall velocity play a destabilizing role in the flows of interest as opposed to the initial concentration that acts as stabilizer. For sufficiently high Couette gaps and wall velocities, unstable modes are recovered. The predicted instability manifests itself through shear-induced dilatancy that, in turn, engenders particle migration and the formation of bulbs, similar to the ones that have been acquired through molecular dynamics simulations.
JFM classification
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2016 Cambridge University Press
References
- 4
- Cited by





