Article contents
Hilbert boundary value problems—a distributional approach
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 February 2012
Synopsis
Hilbert boundary value problems for a half-space are considered for analytic representations of Schwartz distributions: given data g ∈D'(ℛ) and a coefficient x we seek functions F(z) analytic for Jmz≠0 whose limits 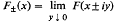 exist in D'(ℛ) and satisfy F+—XF– = g on an open subset U of the real line R. U is the complement of a finite set which contains the singular support and the zeros of X·X and its reciprocal satisfy certain growth conditions near the boundary points of U. Solutions F(z) are shown to exist, and their general form is determined by obtaining a suitable factorisation of x.
exist in D'(ℛ) and satisfy F+—XF– = g on an open subset U of the real line R. U is the complement of a finite set which contains the singular support and the zeros of X·X and its reciprocal satisfy certain growth conditions near the boundary points of U. Solutions F(z) are shown to exist, and their general form is determined by obtaining a suitable factorisation of x.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Section A: Mathematics , Volume 77 , Issue 3-4 , 1977 , pp. 193 - 208
- Copyright
- Copyright © Royal Society of Edinburgh 1977
References
- 10
- Cited by




