Abstract
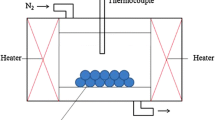
The selective HCl leaching method was used to remove phosphorus from high phosphorus iron ores. The hydroxyapatite in high phosphorus iron ores was converted into soluble phosphate during the process of HCl leaching. The effects of reaction time, particle size, hydrochloric acid concentration, reaction temperature, liquid-solid ratio and stirring strength on the dephosphorization ratio were studied. The results showed that the dephosphorization ratio can exceed 98% under the conditions of reaction time 30–45 min, particle size <0. 147 mm, hydrochloric acid concentration 2. 5 mol/L, reaction temperature 25 °C, liquid-solid ratio 5: 1 and stirring strength 5. 02–12. 76 s−1. After dephosphorization reaction, the content of phosphorus in iron ore complied completely with the requirements of steel production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CHEN Hong. Scenario of World Iron Resources and Its Production Situation [J]. Iron and Steel, 2001, 36(11): 69 (in Chinese).
CUI Ji-rang, FANG Qi-xue, HUANG Guo-zhi, et al. The Present Status and Trends of Dephosphorising of High Phosphorus Iron Ore [J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 1998(6): 20 (in Chinese).
Peixoto G. Improvement of the Reduction Process in P Content and Other Gangues in Iron Ore and Its Agglomerates: WO, W01993010271 A2 [P]. 1993-05-27.
Mamoun Muhammed, YU Zhang. A Hydrometallurgical Process for the Dephosphorization of Iron ore [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1989, 21(3): 277.
JIN Yong-shi, JIANG Tao, YANG Yong-bin, et al. Removal of Phosphorus From Iron Ores by Chemical Leaching [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2006, 13(6): 673 (in Chinese).
HE Liang-ju, ZHOU Jian-min, HU Fang-ren, et al. Characteristics of Meishan Iron Ore With High Phosphorous-Bearing and Feasibility of Biodephosphorization [J]. Gold Journal, 2000, 2(1): 26 (in Chinese).
Forssberg R, Asolfsson G. Dephosphorisation of High Phosphorus Iron Ores by Means of Acid Leaching [J]. Erzmetal, 1981(34): 316.
YU Zhang, Mamoun Muhammed. An Integrated Process for the Treatment of Apatite Obtained From Dephosphorization of Iron Ore [J]. Journal of Chemical Technology Biotechnology, 1990, 47(1): 47 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ CSTC of China (2009BA7071)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Wt., Ren, Zd. & Gao, Yf. Removal of Phosphorus From High Phosphorus Iron Ores by Selective HCl Leaching Method. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18, 1–4 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(11)60055-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(11)60055-1