Abstract
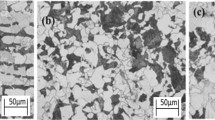
A three-step cooling pattern on the runout table (ROT) was conducted for the hot rolled TRIP steel. Microstructural evolution during thermomechanical controlled processing (TMCP) was investigated. Processing condition of controlled cooling on a ROT in the laboratory rolling mill was discussed. The results indicated that the microstructure containing polygonal ferrite, granular bainite and a significant amount of the stable retained austenite can be obtained through three-step cooling on the ROT after hot rolling. TMCP led to ferrite grain refinement. Controlled cooling after hot rolling resulted in the stability of the remaining austenite and a satisfactory TRIP effect. Excellent mechanical properties were obtained through TMCP for the hot rolled TRIP steel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zackay V F, Parker E R, Fahr D. The Enhancement of Ductility on High-Strength Steels [J]. Trans ASM, 1967, 60: 252.
Sakuma Y, Matsumura O, Takechi H. Mechanical Properties and Retained Austenite in Intercritically Heat-Treated Bainite-Transformed Steel and Their Variation With Si and Mn Additions [J]. Metall Trans, 1991, 22A(2): 489.
Srivastava A K, Jha G, Gope N. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cold Rolled C-Mn-Si TRIP-Aided Steel [J]. Materials Characterization, 2006, 57(2): 127.
Srivastava A K, Bhattacharjee D, Jha G, et al. Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of C-MnAl-Si Cold-Rolled TRIP-Aided Steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2007, 445-446A(15): 549.
Li Z, Wu D, Hu R. Effects of Silicon and Manganese on the Mechanical Properties of Low Plain Carbon TRIP Steel [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2005, 12(3): 51.
Hanzaki A Z, Hodgson P D, Yue S. Hot Deformation Characteristics of Si-Mn TRIP Steels With and Without Nb Microalloy Additions [J]. ISIJ International, 1995, 35(3): 324.
Li Z, Wu D, Hu R. Austempering of Hot Rolled Si-Mn TRIP Steels [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2006, 13(5): 41.
Li Z, Wu D. Effects of Hot Deformation and Subsequent Aus-tempering on the Mechanical Properties of Si-Mn TRIP Steels [J]. ISIJ International, 2006, 46(1): 121.
Meyer M D, Vanderschueren D, Cooman B C D, et al. The Influence of the Substitution of Si by Al on the Properties of Cold Rolled C-Mn-Si TRIP Steels [J]. ISIJ International, 1999, 39: 813.
Ryu H B, Speer J G. Effect of Thermomechanical Processing on the Retained Austenite Content in a Si-Mn Transformation-Induced-Plasticity [J]. Metall Trans, 2002, 33A(9): 2811.
Yue S, Dichiro A, Hanzaki A Z. Thermomechanieal Processing Effects on C-Mn-Si TRIP Steels [J]. JOM, 1997, (49): 59.
Timokhina I B, Hodgson P D. Effect of Deformation Schedule on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Thermo-mechanically Processed C-Mn-Si Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steel [J]. Metall Trans, 2003, 34A(8): 1599.
Matsumura O, Sakuma Y, Ishii Y, et al. Effect of Retained Austenite on Formability of High Strength Sheet Steels [J]. ISIJ International, 1992, 32(10): 1110.
Timokhina I B, Pereloma E V. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of C-Si-Mn(Nb) TRIP Steels After Simulated Thermomechanieal Processing [J]. Mater Sci Technol, 2001, 17(2): 135.
Stéphane G, Philippe H, Francis D. Effect of Hot-Rolling Conditions on the Tensile Properties of Multiphase Steels Exhibiting a TRIP Effect [J]. Steel Res, 2002, 73(6-7): 280.
Verhoeven J D. Fundamentals of Physical Metallurgy [M]. New York: John Wiley, 1975.
Guimaraes J R C. The Deformation-Induced Martensitic Reaction in Polycrystalline Fe-30. 7Ni-0. 06C [J]. Scripta Metal, 1972, 6(9): 795.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (50334010)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, D., Li, Z. & Lü, Hs. Effect of Controlled Cooling After Hot Rolling on Mechanical Properties of Hot Rolled TRIP Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 15, 65–70 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60034-5
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60034-5