Abstract
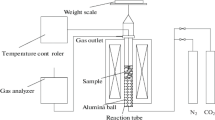
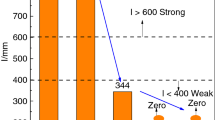
The interaction mechanism between the combustion products of pulverized coal injected and coke in the raceway of blast furnace was studied through thermodynamic calculation and experiments. The results indicated that additives significantly affected the melting property of coal ash in high temperature zone. Although the unburnt char, raw coal ash, and catalyzed coal ash failed to wet the coke surface, the wettability of the catalyzed coal ash on the coke was greater than that of the raw coal ash. Since the unburnt char had weak reaction with the coke surface, it showed little influence on the surface morphology of the coke. The interaction between the raw coal ash and the coke gave rise to the increase in the pore size on the coke surface. However, the raw coal ash only affected the coke surface and the entrances of the pores owing to its poor fluidity. After being melted, the catalyzed coal ash was expected to immerge into the inside part of the coke and then react with the coke, resulting in an expansion and increase of coke cavities. The raw coal ash and the unburnt char reduced the coke reactivity, while the catalyzed coal ash improved the coke reactivity. Thereinto, the coal ash containing Fe2O3 exhibited a larger influence on the reactivity than that containing CaO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Jiang, J. Zhang, J. Fu, J. Chang, J. Li, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18 (2011) No. 3, 6–12.
K. Nozawa, A. Kasai, Y. Matsui, S. Kitayama, S. Kitano, K. Shibata, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) No. 8, 1336–1343.
S. Du, W. Chen, Int. Commun. Heat and Mass Transfer 33 (2006) No. 3, 327–334.
H. Nogami, S. Pintowantoro, J. Yagi, ISIJ Int. 45 (2005) No. 10, 1489–1495.
W. Xu, X. Wu, J. Chen, H. Qian, J. Lin, Iron and Steel 38 (2003) No. 3, 4–7 (in Chinese).
K. Yamaguchi, T. Uno, T. Yammoto, H. Ueno, N. Kon-no, S. Matsuzki, Tetsu-to-Hagane 82 (1996) No. 8, 641–646 (in Japanese).
H. Ueno, K. Yamaguchi, K. Tamura, ISIJ Int. 33 (1993) No. 6, 640–645.
K. Khairil, D. Kamihashira, I. Narus, Proc. Combust. Inst. 29 (2002) No. 1, 805–810.
W. Lu, in: Proceedings of the McMaster Iron and Steelmaking Symposium, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, 1991, pp. 14–16.
H. W. Gudenau, D. Senk, K. Fukada, A. Babich, C. Froehling, L. L. Garcia, A. Formoso, F. J. Alguacil, A. Cores, Revista de Metalurgia 39 (2003) No. 5, 367–377.
Q. Y. Yu, J. Cao, F. M. Shen, Baosteel Technol. (2006) Suppl. 1, 31–34 (in Chinese).
B. Zhang, Z. Zhu, D. Zou, Iron and Steel 29 (1994) No. 3, 22–26 (in Chinese).
I. Naruse, K. Nakayama, A. Higuchi, ISIJ Int. 40 (2000) No. 8, 744–748.
C. Zou, L. Wen, S. Zhang, C. Bai, G. Yin, Fuel Process. Technol. 119 (2014) No. 1, 136–145.
A. Babich, S. Yaroshevskii, A. Formoso, A. Isidro, S. Ferreira, A. Cores, L. Garcia, ISIJ Int. 36 (1996) No. 10, 1250–1258.
X. Gong, Z. Guo, Z. Wang, Combust. Flame 157 (2010) No. 2, 351–356.
X. Gong, Z. Guo, Z. Wang, Energy 35 (2010) No. 2, 506–511.
D. Senk, H. Gudenau, S. Geimer, ISIJ Int. 46 (2006) No. 46, 1745–1751.
A. Wijayanta, M. Alam, K. Nakaso, J. Fukai, K. Kunitom, Fuel Process. Technol. 117 (2014) No. 1, 53–59.
J. A. Castro, G. Mattos Araújo, I. Oliveira da Mota, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2 (2013) No. 4, 308–314.
S. Du, W. Chen, J. Lucas, Energy Convers. Manage. 48 (2007) No. 1, 2069–2076.
J. Zhang, S. Ren, B. Su, Y. Lin, S. Long, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 19 (2012) No. 2, 12–16.
C. Goni, S. Hell, X. Garcia, Fuel 82 (2003) No. 15–17, 2087–2095.
S. Ren, J. Zhang, W. Liu, C. Tian, Y. Yuan, J. Liu, J. Iron Steel Res. 24 (2012) No. 10, 11–15 (in Chinese).
B. Gao, J. Zhang, H. Zuo, C. Qi, Y. Rong, Z. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21 (2014) No. 8, 723–728.
S. Zhang, L. Wen, K. Wang, C. Zou, J. Xu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22 (2015) No. 10, 897–904.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, C., Wen, Ly., Zhao, Jx. et al. Interaction mechanism between coal combustion products and coke in raceway of blast furnaces. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 24, 8–17 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(17)30003-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(17)30003-1