Abstract
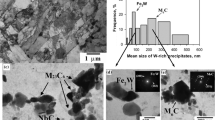
Standardarized creep and rupture strength tests were conducted for commercial T91 martensitic heat-resistant steel at 650 °C and corresponding microstructure was characterized by BSED, TEM and EDS. The martensitic microstructure degenerated seriously during creep exposure, including martensitic substructure recovering, carbides coarsening, dissolving and precipitating. EDS analysis shows that the M23C6 carbides in different morphologies have dissimilar compositions. The rod/sheet like M23C6 particles within the matrix contain more additions, which might precipitate in situ while fine MX particles were re-solving. The high content of silicon in these rod/sheet like M23C6 carbides is probably related to self diffusion coefficient increasing for the exposed condition at 650 °C close to Curie temperature Tc. For those reasons, martensite substructure becomes unstable, and microstructure evolution is accelerated and leads to creep strength deteriorating severely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masuyama F. History of Power Plant and Progress in Heat Resistant Steels [J]. ISIJ International, 2001, 41: 612.
Ennis P J, Czyrska F A. Recent Advances in Creep-Resistant Steels for Power Plant Applications [J]. Sadhana, 2003, 28(3/4): 709.
Abe F, Horiuchi T, Taneike M, et al. Stabilization of Marten-sitic Microstructure in Advanced 9Cr Steel During Creep at High Temperature [J]. Mater Sei and Eng, 2004, 378A: 299.
Hald J. Microstructure and Long-Term Creep Properties of 9-13Cr Steels [J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2008, 85: 30.
Abe F. Analysis of Creep Rates of Tempered Martensitic 9%Cr Steel Based on Microstructure Evolution [J]. Mater Sei and Eng, 2009, 510A: 64.
Ennis P, Quadakkers W J. The Steam Oxidation Resistance 9–12%Cr Steels [C]//Schubert F. Proceedings of the Seventh Liege Conference on Materials for Advanced Power Engineering. Liege: [s. n. ], 2002: 1131.
Kutsumi H, Itagaki T, Abe F. Improvement of Steam Oxidation Resistance for Ferritic Heat-Resistant Steels [C]// Schubert F. Proceedings of the Seventh Liege Conference on Materials for Advanced Power Engineering. Liege: [s. n.], 2002: 1629.
HU Zheng-fei, WU Xing-fang, LI Xiu-qiu, et al. M2C Precipitate in Isothermal Tempering of High Co-Ni Alloy Steel [J]. J Iron and Steel Res Int, 2001, 8(2): 56.
Hattestrand M, Andren H O. Evaluation of Particle Size Distributions of Precipitates in a 9% Cr Steel Using Energy Filtered Transmission Electron Microscopy [J]. Micron, 2001, 22: 789.
Abe F. Coarsening Behavior of Lath and Its Effect on Creep Rates in Tempered Martensitic 9Cr-W Steels [J]. Mater Sei and Eng, 2004, 387A: 565.
Cerjak H, Hofer P, Schaffernak B. Microstructural Aspects on Creep Behaviour of Advanced Power Plant Steels [J]. Key Eng Mater, 2000, 171-174: 453.
Maruyama K, Sawada K, Koike J. Strengthening Mechanisms of Creep Resistant Tempered Martensitic Steel [J]. ISIJ International, 2001, 41(6): 641.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (50871076)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Zf., Wang, Qj. & Zhang, B. Microstructure Evolution in 9Cr Martensitic Steel During Long-Term Creep at 650 °C. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 19, 55–59 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(12)60113-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(12)60113-7