Abstract
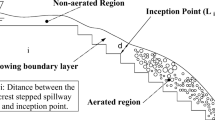
The location of the inception point of the air entrainment directly affects the energy dissipation ratio, the cavitation damage control, and the training wall height designs for a stepped spillway and a stilling basin. In this paper, the boundary layer theory of plates is used to predict the location of the inception point of the air entrainment over the stepped spillways by assuming the steps on the spillways as a kind of roughness. An empirical formula is presented based on the physical model experiments, with the maximum error less than 1% except at one point where the error is 1.6%, as compared to the experimental data. Meanwhile, it is shown that the location of the inception point of the air entrainment for the stepped spillway is much nearer to the top of the spillway than that for a smooth spillways, which explains why the high ratio of the energy dissipation is provided for the stepped spillway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
STEPHENSON D. Energy dissipation down stepped spillways[J]. International Water Power and Dam Construction, 1991, 43(9): 27–30.
ZHANG Zhi-chang, ZENG Dong-yang and ZHENG Aman et al. Experimental investigation on the pressure characteristics of skimming flow on stepped spill-ways[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2003, 18(5): 652–659(in Chinese).
CHANSON H. Hydraulics of stepped spillways: Current status[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Asce, 2000, 126(9): 636–637.
CHENG Xiang-ju, CHEN Yong-cai and LUO Lin. Numerical simulation of air-water two-phase flow over stepped spillways[J]. Science in China, Ser. E: Technological Sciences, 2006, 49(6): 674–684.
CHINNARASRI C., WONGWISES S. Flow patterns and energy dissipation over various stepped chutes[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 2006, 132(1): 70–76.
QIAN Zhong-dong, HU Xiao-qing and HUAI Wen-xin. Numerical simulation and analysis of water flow over stepped spillways[J]. Science in China, Ser. E: Technological Sciences, 2009, 52(7): 1958–1965.
FELDER S., CHANSON H. Energy dissipation down a stepped spillway with nonuniform step heights[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Asce, 2011, 137(11): 1543–1548.
PFISTER M., HAGER W. H. Self-entrainment of air on stepped spillways[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2011, 37(2): 99–107.
PFISTER M., HAGER W. H. and MINOR H.-E. Stepped chutes: Pre-aeration and spray reduction[J]. Inter-national Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2006, 32(2): 269–284.
CHEN Jian-gang, ZHANG Jian-min and XU Wei-lin. Practical engineering application and hydraulic characteristics of the flow in stepped spillway with pre-aerator slot[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Enginee-ring Science Edition), 2010, 42(6): 6–11(in Chinese).
MICHAELS V., LOVELY M. Some prototype observa-tions of air entrained flows[C]. Proceedings of Minnesota Conference, IAHR. Minnesota, USA, 1953, 403–414.
WOOD I. R., ACKERS P. and LOVELESS J. General method for critical point on spillways[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Asce, 1983, 109(2): 308–312.
CHANSON H. Hydraulics of skimming flows over stepped channels and spillways[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, IAHR, 1994, 32(3): 445–460.
HUNT S. L., KADAVY K. C. Inception point relationship for flat-sloped stepped spillways[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE, 2011, 137(2): 262–266.
BOES R. M., HAGER W. H. Two-phase flow characteristics of stepped spillways[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Asce, 2003, 129(9): 661–670.
RU Shu-xun, TANG Chao-yang and LIANG Chuan. Inception point location of air entrainment on curve-type spillways with steps[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 1996, 13(2): 7–16(in Chinese).
ZHANG Zhi-chang, ZENG Dong-yang and LIU Ya-fei. Experimental investigations of air entrainment for ste-pped spillway[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2003, 20(4): 97–100(in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foun- dation of China (Grant No. 51179114).
Biography: WU Jian-hua (1958-), Male, Ph. D., Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Jh., Zhang, B. & Ma, F. Inception point of air entrainment over stepped spillways. J Hydrodyn 25, 91–96 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(13)60342-X
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(13)60342-X