Abstract
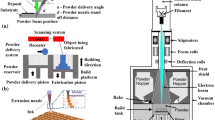
We introduce a scalable thermally activated solvent extraction based additive manufacturing process to produce lightweight, yet high-hardness, multicomponent alloys. The cost-effective process involves layer-wise curing a slurry composed of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy powder and a transparent ultraviolet-sensitive photopolymer, by stereolithography 3D printing followed by sintering. The alloy pellets assume a density of 4.3 g/cm3 and hardness of 400 HV with a BCC/FCC multiphase microstructure. A broad distribution in the particle sizes of the alloy powder augments the manufacturing process because the smaller particles operate as fillers to weld the larger ones. The relatively higher surface energy of the smaller particles limits the activation energy required for the onset of particulate diffusion that instigates the necking. Microscopic characterization reveals passivating surface oxides on the powder particles fabricating an alloy part suitable for harsh environments.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors will make available, upon request, the data used in the applications described in this work. It is understood that the data provided will not be for commercial use.
References
B. Cantor, I.T.H. Chang, P. Knight, A.J.B. Vincent, Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375–377, 213–218 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEA.2003.10.257
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299–303 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/ADEM.200300567
D.B. Miracle, O.N. Senkov, A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 122, 448–511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.08.081
P. Sharma, N. Naushin, S. Rohila, A. Tiwari, Magnesium containing high entropy alloys. in Magnesium Alloys Structure and Properties (IntechOpen, 2022). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.98557
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, Z.P. Lu, Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 61, 1–93 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001
Z. Ye, C. Li, J. Gu, Phase stability in high-entropy alloys: the role of configurational entropy. JOM 74, 4154–4161 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05307-y
X. Yan, Y. Zhang, Functional properties and promising applications of high entropy alloys. Scr. Mater. 187, 188–193 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCRIPTAMAT.2020.06.017
O. El-Atwani, N. Li, M. Li, A. Devaraj, J.K.S. Baldwin, M.M. Schneider, D. Sobieraj, J.S. Wróbel, D. Nguyen-Manh, S.A. Maloy, E. Martinez, Outstanding radiation resistance of tungsten-based high-entropy alloys. Sci Adv. 5, eaav2002 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIADV.AAV2002/SUPPL_FILE/AAV2002_SM.PDF
D. Zhang, H. Zhao, X. Wu, Y. Deng, Z. Wang, Y. Han, H. Li, Y. Shi, X. Chen, S. Li, J. Lai, B. Huang, L. Wang, D. Zhang, H. Zhao, X. Wu, Y. Deng, Z. Wang, Y. Han, H. Li, Y. Shi, J. Lai, L. Wang, X. Chen, S. Li, B. Huang, Multi-site electrocatalysts boost pH-universal nitrogen reduction by high-entropy alloys. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2006939 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/ADFM.202006939
X. Jin, J. Bi, L. Zhang, Y. Zhou, X. Du, Y. Liang, B. Li, A new CrFeNi2Al eutectic high entropy alloy system with excellent mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 770, 655–661 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2018.08.176
Y. Zhang, M. Liu, J. Sun, G. Li, R. Zheng, W. Xiao, C. Ma, Excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties of bulk nanostructured FeCoNiCu high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 835, 142670 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEA.2022.142670
K.V. Yusenko, S. Riva, P.A. Carvalho, M.V. Yusenko, S. Arnaboldi, A.S. Sukhikh, M. Hanfland, S.A. Gromilov, First hexagonal close packed high-entropy alloy with outstanding stability under extreme conditions and electrocatalytic activity for methanol oxidation. Scr. Mater. 138, 22–27 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCRIPTAMAT.2017.05.022
S. Dixit, S. Rodriguez, M.R. Jones, P. Buzby, R. Dixit, N. Argibay, F.W. DelRio, H.H. Lim, D. Fleming, Refractory high-entropy alloy coatings for high-temperature aerospace and energy applications. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 31, 1021–1031 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11666-022-01324-0/FIGURES/8
K.R. Lim, K.S. Lee, J.S. Lee, J.Y. Kim, H.J. Chang, Y.S. Na, Dual-phase high-entropy alloys for high-temperature structural applications. J. Alloys Compd. 728, 1235–1238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2017.09.089
A.E. Afolabi, A.P.I. Popoola, O.M. Popoola, High entropy alloys: advance material for landing gear aerospace applications, in Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications (Springer, Cham, 2020), pp. 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11155-7_179-1
C.L.P. Pavithra, S.R. Dey, Advances on multi-dimensional high-entropy alloy nanoarchitectures: unconventional strategies and prospects. Nano Select. 4, 48–78 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/nano.202200081
I. Gibson, D. Rosen, B. Stucker, M. Khorasani, Development of additive manufacturing technology. in Additive Manufacturing Technologies (Springer, Cham, 2021), pp. 23–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56127-7_2
W.E. Frazier, Metal additive manufacturing: a review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23, 1917–1928 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-0958-z
W. Tao, M.C. Leu, Design of lattice structure for additive manufacturing. in 2016 International Symposium on Flexible Automation (ISFA), IEEE, 2016, pp. 325–332. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISFA.2016.7790182
A. Kumar, L. Collini, A. Daurel, J.-Y. Jeng, Design and additive manufacturing of closed cells from supportless lattice structure. Addit. Manuf. 33, 101168 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101168
Z.U. Arif, M.Y. Khalid, E. ur Rehman, Laser-aided additive manufacturing of high entropy alloys: processes, properties, and emerging applications. J. Manuf. Process. 78, 131–171 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.04.014
C. Kenel, N.P.M. Casati, D.C. Dunand, 3D ink-extrusion additive manufacturing of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy micro-lattices. Nat. Commun. 10, 904 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08763-4
S.Y. Ahn, F. Haftlang, E.S. Kim, J.S. Lee, S.G. Jeong, J.B. Seol, H. Choi, H.S. Kim, Cellular structure engineering of additive manufactured CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy composite: the role of hard ceramic reinforcements in elemental segregation of constitutive elements. Addit. Manuf. Lett. 7, 100172 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addlet.2023.100172
W. Li, Y. Huang, Z. Xie, H. Chen, W. Li, B. Liu, B. Wang, Mechanical property and cellular structure of an additive manufactured FeCoNiCrMo0.2 high-entropy alloy at high-velocity deformation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 139, 156–166 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.08.013
S. Peng, S. Mooraj, R. Feng, L. Liu, J. Ren, Y. Liu, F. Kong, Z. Xiao, C. Zhu, P.K. Liaw, W. Chen, Additive manufacturing of three-dimensional (3D)-architected CoCrFeNiMn high- entropy alloy with great energy absorption. Scr. Mater. 190, 46–51 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.028
C. Han, Q. Fang, Y. Shi, S. Beng Tor, C. Kai Chua, K. Zhou, C. Han, S.B. Tor, K. Zhou, Q. Fang, Y. Shi, C.K. Chua, Recent advances on high-entropy alloys for 3D printing. Adv. Mater. 32, 1903855 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/ADMA.201903855
S. Chen, Y. Tong, P.K. Liaw, Additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys: a review. Entropy 20, 937 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/E20120937
A. Ostovari Moghaddam, N.A. Shaburova, M.N. Samodurova, A. Abdollahzadeh, E.A. Trofimov, Additive manufacturing of high entropy alloys: a practical review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 77, 131–162 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMST.2020.11.029
S. Guan, J. Ren, S. Mooraj, Y. Liu, S. Feng, S. Zhang, J. Liu, X. Fan, P.K. Liaw, W. Chen, Additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys: microstructural metastability and mechanical behavior. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 42, 748–771 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-021-00913-w
C. Kenel, N.P.M. Casati, D.C. Dunand, 3D ink-extrusion additive manufacturing of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy micro-lattices. Nat. Commun. 10, 1–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08763-4
Y. Zhang, T. Bian, X. Shen, Z. Wang, S. Ye, S. Feng, K. Yu, C. Ding, P. Yu, Sintering mechanism and microstructure evolution of a CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy fabricated by metal injection molding. J. Alloys Compd. 868, 158711 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2021.158711
N.E. Putra, M.A. Leeflang, M. Minneboo, P. Taheri, L.E. Fratila-Apachitei, J.M.C. Mol, J. Zhou, A.A. Zadpoor, Extrusion-based 3D printed biodegradable porous iron. Acta Biomater. 121, 741–756 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTBIO.2020.11.022
N.E. Putra, M.A. Leeflang, P. Taheri, L.E. Fratila-Apachitei, J.M.C. Mol, J. Zhou, A.A. Zadpoor, Extrusion-based 3D printing of ex situ-alloyed highly biodegradable MRI-friendly porous iron-manganese scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 134, 774–790 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTBIO.2021.07.042
G.K. Meenashisundaram, Z. Xu, M.L.S. Nai, S. Lu, J.S. Ten, J. Wei, Binder jetting additive manufacturing of high porosity 316L stainless steel metal foams. Materials 13, 3744 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/MA13173744
P. Mondal, A. Das, A. Wazeer, A. Karmakar, Biomedical porous scaffold fabrication using additive manufacturing technique: porosity, surface roughness and process parameters optimization. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 5, 384–396 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijlmm.2022.04.005
R. Otto, C. Kiener, Y. Küsters, K. Sørby, Additive manufacturing of open porous functional structures: roadmap from manufacturing to the application. Procedia CIRP. 112, 334–339 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2022.09.102
D. Ren, X. Ba, Z. Zhang, Z. Zhang, K. Zhao, L. Liu, Wire arc additive manufacturing of porous metal using welding pore defects. Mater. Des. 233, 112213 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2023.112213
Y.C. Wu, C.N. Kuo, M.Y. Shie, Y.L. Su, L.J. Wei, S.Y. Chen, J.C. Huang, Structural design and mechanical response of gradient porous Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by electron beam additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 158, 256–265 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.08.027
K. Kusada, H. Kobayashi, R. Ikeda, Y. Kubota, M. Takata, S. Toh, T. Yamamoto, S. Matsumura, N. Sumi, K. Sato, K. Nagaoka, H. Kitagawa, Solid solution alloy nanoparticles of immiscible Pd and Ru elements neighboring on Rh: changeover of the thermodynamic behavior for hydrogen storage and enhanced CO-oxidizing ability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 1864–1871 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja409464g
W. Ji, W. Qi, S. Tang, H. Peng, S. Li, Hydrothermal synthesis of ultrasmall Pt nanoparticles as highly active electrocatalysts for methanol oxidation. Nanomaterials 5, 2203–2211 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5042203
D. Wu, K. Kusada, Y. Nanba, M. Koyama, T. Yamamoto, T. Toriyama, S. Matsumura, O. Seo, I. Gueye, J. Kim, L.S. RosanthaKumara, O. Sakata, S. Kawaguchi, Y. Kubota, H. Kitagawa, Noble-metal high-entropy-alloy nanoparticles: atomic-level insight into the electronic structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 3365–3369 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c13616
Z. Xu, Z. Zhu, P. Wang, G.K. Meenashisundaram, S.M.L. Nai, J. Wei, Fabrication of porous CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy using binder jetting additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 35, 101441 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADDMA.2020.101441
P. Sreeramagiri, P. Sharma, C. Das, G. Balasubramanian, Examining solid-state sintering of AlCoCrFeNi multi-principal element alloy by molecular simulations. Comput. Mater. Sci. 216, 111875 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2022.111875
T.M. Butler, M.L. Weaver, Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNi multi-component high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 674, 229–244 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2016.02.257
W.R. Wang, W.L. Wang, S.C. Wang, Y.C. Tsai, C.H. Lai, J.W. Yeh, Effects of Al addition on the microstructure and mechanical property of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 26, 44–51 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INTERMET.2012.03.005
Y.F. Kao, T.J. Chen, S.K. Chen, J.W. Yeh, Microstructure and mechanical property of as-cast, -homogenized, and -deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x ≤ 2) high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 488, 57–64 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2009.08.090
C. Li, J.C. Li, M. Zhao, Q. Jiang, Effect of aluminum contents on microstructure and properties of AlxCoCrFeNi alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 504, S515–S518 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2010.03.111
T. Yang, S. Xia, S. Liu, C. Wang, S. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Xue, S. Yan, Y. Wang, Effects of AL addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxCoCrFeNi High-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 648, 15–22 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEA.2015.09.034
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) through the award CMMI-1944040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PS: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Validation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing; CD: Methodology, Investigation; PS: Methodology, Validation, Writing—Review & Editing; GB: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding Acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, P., Das, C., Sreeramagiri, P. et al. Additively Manufactured Lightweight and Hard High-Entropy Alloys by Thermally Activated Solvent Extraction. High Entropy Alloys & Materials (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44210-024-00029-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44210-024-00029-z