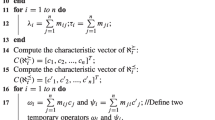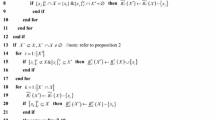Abstract
Many collected data from real world applications often evolve when new attributes or objects are inserted or old ones are removed. The set approximations of ordered information systems (OIS) need to be updated from time to time for further data reduction, analysis, or decision-making. Incremental approaches are feasible and efficient techniques for updating approaches when any variation occurs. In this paper, considering OIS for multi-criteria classification problems, we discuss the principles of incrementally updating approximations in dominance relation based method in four different types of dynamic environments which combine the changes of both attribute set and object set. In each dynamic environment, the corresponding updating principles and algorithm are given with detail proofs. The experimental results and analysis on UCI data sets show that the proposed incremental approach outperforms the non-incremental method and the integration of current incremental algorithms in the implementation efficiency.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanco-Fernández Y, Pazos-Arias J, Gil-Solla A, Ramos-Cabrer M et al (2008) A flexible semantic inference methodology to reason about user preferences in knowledge-based recommender systems. Knowl Based Syst 21(4):305–320
Blaszczynski J, Greco S, Slowinski R (2009) Monotonic variable consistency rough set approaches. Int J Approx Reason 50(7):979–999
Chakhar S, Saad I (2012) Dominance-based rough set approach for groups in multicriteria classification problems. Decis Support Syst 54(1):372–380
Chen J, Wang GY, Hu J (2008) Positive domain reduction based on dominance relation in inconsistent system. Comput Sci 35(3):216–218
Chen HY, Zhou LG, Han B (2011) On compatibility of uncertain additive linguistic preference relations and its application in the group decision making. Knowl Based Syst 24(6):816–823
Chen HM, Li TR, Ruan D (2012) Maintenance of approximations in incomplete ordered decision systems while attribute values coarsening or refining. Knowl Based Syst 31:140–161
Chen HM, Li TR, Ruan D, Lin JH, Hu CX (2013) A rough-set based incremental approach for updating approximations under dynamic maintenance environments. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(2):274–284
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Słowinski R (1998) A new rough set approach to evaluation of bankruptcy risk. In: Zopounidis C (ed) operational tools in the management of financial risks. Kluwer Academic, New York, pp 121–136
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowingski R (1999) Rough approximation of a preference relation by dominance relation. Eur J Oper Res 117(1):63–83
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowingski R (2001) Rough sets theory for multicriteria decision analysis. Eur J Oper Res 129(1):1–47
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowingski R (2002) Rough approximation by dominance relations. Int J Intell Syst 17(2):153–171
Hu QH, Che XJ, Zhang L (2012) Rank entropy based decision trees for monotonic classification. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(11):2052–2064
Huang B (2011) Graded dominance interval-based fuzzy objective information systems. Knowl Based Syst 24(7):1004–1012
Huang B, Zhuang YL, Li HX, Wei DK (2013) A dominance intuitionistic fuzzy-rough set approach and its applications. Appl Math Model 37(12–13):7128–7141
Huang Y, Li TR, Luo C, Fujita H et al (2017) Matrix-based dynamic updating rough fuzzy approximations for data mining. Knowl Based Syst 119:273–283
Huang Q, Li TR, Huang Y, Yang X et al (2020) Dynamic dominance rough set approach for processing composite ordered data. Knowl Based Syst 187:104829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.06.037
Inuiguchi M, Yoshioka Y, Kusunoki Y (2009) Variable-precision dominance-based rough set approach and attribute reduction. Int J Approx Reason 50(8):1199–1214
Jelonek J, Lukasik E, Naganowski A, Slowinski R (2004) Inducing Jury’s preferences in terms of acoustic features of violin sounds. Artif Intell Soft Comput 3070:492–497
Jing Y, Li T, Huang J, Chen H, Horng S (2017) A group incremental reduction algorithm with varying data values. Int J Intell Syst 32(9):900–925
Jing Y, Li TR, Fujita H, Wang B et al (2018) An incremental attribute reduction method for dynamic data mining. Inf Sci 465:202–218
Li SY, Li T (2015) Incremental update of approximations in dominance-based rough sets approach under the variation of attribute values. Inf Sci 294:348–361
Li TR, Ruan D, Geert W, Song J, Xu Y (2007) A rough sets based characteristic relation approach for dynamic attribute generalization in data mining. Knowl Based Syst 20(5):485–494
Li SY, Li TR, Liu D (2013) Incremental updating approximations in dominance-based rough sets approach under the variation of the attribute set. Knowl Based Syst 40:17–26
Li Y, Liu XQ, Hou JJ (2014) Incrementally updating method in dominance-based rough set approach. Int J Intell Inf Manag Sci 3(1):18–22
Li SY, Li TR, Jie H (2015) Update of approximations in composite information systems. Knowl Based Syst 83:138–148
Li Y, Jin YF, Wu T, Guo N et al (2016) Incrementally updating approximations approach in dominance-based rough set for multi-criteria classification problems. Comput Sci 43(12):71–78
Li Y, Jin YF, Sun XD (2018) Incremental method of updating approximations in DRSA under variations of multiple object. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 9:295–308
Liang JY, Wang F, Dang CY, Qian YH (2014) A group incremental approach to feature selection applying rough set technique. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(2):294–308
Luo C, Li TR, Chen HM, Liu D (2013) Incremental approaches for updating approximations in set-valued ordered information systems. Knowl Based Syst 50:218–233
Luo C, Li TR, Chen HM (2014) Dynamic maintenance of approximations in set-valued ordered decision systems under the attribute generalization. Inf Sci 257:210–228
Newman DD, Hettich S, Blake C, Merz C (1998) UCI repository of machine learning databases, University of California, Department of Information and Computer Science, Irvine, CA. Website: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/index.php
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough Sets. Int J Inf Comput Sci 11(3):289–296
Qian YH, Dang CY, Liang JY, Tang DW (2009) Set-valued ordered information systems. Inf Sci 179(16):2809–2832
Wang F, Liang J, Qian YH (2013) Attribute reduction: a dimension incremental strategy. Knowl Based Syst 39:95–108
Wang S, Li TR, Luo C, Fujita H (2016) Efficient updating rough approximations with multi-dimensional variation of ordered data. Inf Sci 372:690–708
Wang S, Li TR, Luo C, Chen HM, Fujita H (2019) Domain-wise approaches for updating approximations with multi-dimensional variation of ordered information systems. Inf Sci 478:100–124
Wang S, Li TR, Luo C, Hu J, Fujita H et al (2020) A novel approach for efficient updating approximations in dynamic ordered information systems. Inf Sci 507:197–219
Xu Y, Wang L, Zhang R (2011) A dynamic attribute reduction algorithm based on 0–1 integer programming. Knowl Based Syst 24(8):1341–1347
Yang X, Qi Y, Yu D, Yu H, Yang J (2015) α-dominance relation and rough sets in interval-valued information systems. Inf Sci 294:334–347
Zhang X, Chen D, Tsang ECC (2017) Generalized dominance rough set models for the dominance intuitionistic fuzzy information systems. Inf Sci 378:1–25
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by NSFC (no. 61976141); NSF of Hebei Province (no. F2018201096); NSF of Guangdong Province (no. 2018A0303130026), the Key Science and Technology Foundation of the Educational Department of Hebei Province (ZD 2019021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wu, X. & Hua, Q. Update of approximations in ordered information systems under variations of attribute and object set. Adv. in Comp. Int. 2, 16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43674-021-00011-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43674-021-00011-x