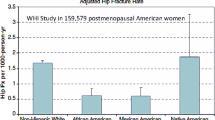
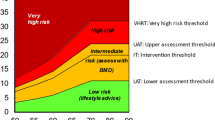
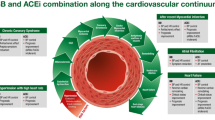
Abstract
Osteoporosis is a chronic disease that often requires long-term treatment for many years. The clinician should know about all the drugs that are currently being used for treatment in osteoporosis and their mechanism of action, efficacy, safety profile, mode of administration and number of years they can be given safely without causing significant adverse effects. The categories of drugs that are currently being used for osteoporosis are antiresorptives such as oral and intravenous bisphosphonates, denosumab, and anabolics like teriparatide. This article will focus on the combination therapy of denosumab and teriparatide and will discuss how this combination is better than other class of drugs when given alone or in combination in osteoporosis patients especially those who are at high risk of fragility fractures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Tsai, J. N., Uihlein, A. V., Burnett-Bowie, S. M., Neer, R. M., Derrico, N. P., Lee, H., Bouxsein, M. L., & Leder, B. Z. (2016). Effects of two years of teriparatide, denosumab, or both on bone microarchitecture and strength (DATA-HRpQCT study). The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 101(5), 2023–2030.
Tsai, J. N., Uihlein, A. V., Lee, H., et al. (2013). Teriparatide and denosumab, alone or combined, in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: The DATA study randomised trial. The Lancet, 382, 50–56.
Leder, B. Z., Tsai, J. N., Uihlein, A. V., et al. (2014). Two years of denosumab and teriparatide administration in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (the DATA extension study): A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 99, 1694–1700.
Tsai, J. N., Lee, H., David, N. L., Eastell, R., & Leder, B. Z. (2019). Combination denosumab and high dose teriparatide for postmenopausal osteoporosis (DATA-HD): a randomised, controlled phase 4 trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 7(10), 767–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30255-4. Epub 2019 Aug 22.
Ramchand, S. K., David, N. L., Lee, H., Bruce, M., Bouxsein, M. L., Leder, B. Z., & Tsai, J. N. (2021). Effects of combination denosumab and high-dose teriparatide administration on bone microarchitecture and estimated strength: The DATA-HD HR-pQCT study. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 36, 41–51.
Black, D. M., Greenspan, S. L., Ensrud, K. E., et al. (2003). The effects of parathyroid hormone and alendronate alone or in combination in postmenopausal osteoporosis. New England Journal of Medicine, 349, 1207–1215.
Finkelstein, J. S., Wyland, J. J., Lee, H., & Neer, R. M. (2010). Effects of teriparatide, alendronate, or both in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 95, 1838–1845.
Cosman, F., Eriksen, E. F., Recknor, C., et al. (2011). Effects of intravenous zoledronic acid plus subcutaneous teriparatide [rhPTH(1–34)] in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 26, 503–511.
Finkelstein, J. S., Leder, B. Z., Burnett, S. M., et al. (2006). Effects of teriparatide, alendronate, or both on bone turnover in osteoporotic men. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 91, 2882–2887.
Nakamura, Y., Suzuki, T., Kamimura, M., et al. (2017). Two-year clinical outcome of denosumab treatment alone and in combination with teriparatide in Japanese treatment-naive postmenopausal osteoporotic women. Bone Research, 5, 16055.
Wang, W. Y., Chen, L. H., Ma, W. J., & You, R. X. (2023). Drug efficacy and safety of denosumab, teriparatide, zoledronic acid, and ibandronic acid for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 27(17), 8253–8268. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202309_33586
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, M.K., Kumar, L. & Marwah, S. Combination Therapy of Denosumab and Teriparatide in Osteoporosis. JOIO 57 (Suppl 1), 147–149 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-023-01051-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-023-01051-w