Abstract
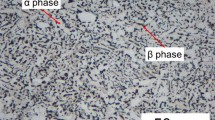
Ultra-short Pulse Laser (USPL) has a wide range of applications in industrial sections. Among them is the workpiece surface pre-structuring before machining to reduce the process forces and temperature. Laser pre-structuring removes a section of workpiece material and induces controlled subsurface damages, improving the achievable Material Removal Rate (MRR) and workpiece machinability. USPL pre-structuring is used in various studies to optimize the conventional machining of titanium alloys. However, there is a lack of understanding of the interaction between USPL and titanium alloys associated with the laser scanning process concerning surface morphology, material removal mechanisms and geometrical features. The present work analyses the interactions between USPL and a titanium alloy as a difficult-to-cut material. A picosecond (ps) laser with a pulse duration of 12 ps was used for material ablation of titanium samples at different average laser powers PL_ave, laser scan velocities vL, and number of pulses Np. The experimental studies were conducted in three categories of multiple pulses, single linear laser scanning and multiple linear laser scanning. For multiple pulses, the influence of pulse energy Ep on material ablation, changing surface morphology and melting formation was highlighted in a more significant role than the number of pulses. At Ep > 62.5 µJ, a substantial volume of melted material at the different number of pulses could be seen. In the case of linear laser scanning, laser input energy EL_input was introduced as a parameter that includes the influence of successive pulses. In the single linear laser scanning, at laser input energy EL_input greater than 125 J/cm2, a tremendous rise in ablation depth was observed that corresponds to the huge melt formation on the surface of the lasered profile. At EL_input < 125 J/cm2, Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures (LIPSS) were observed and most of the lasered profile indicates considerably less or even no melting. In multiple linear laser scanning, lower scan velocities and average laser powers at constant EL_input = 3.9 J/cm2 led to more surface degradation, a more significant rise in ablation depth with the number of laser scanning Ns, deeper ablation depth, narrower lasered profile, less specific energy and MRR.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu D, Chen C, Man B, Meng X, Sun Y, Li F. Evolution and mechanism of the periodical structures formed on Ti plate under femtosecond laser irradiation. Appl Surf Sci. 2016;378:120–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.229.
Kong MC, Wang J. Surface quality analysis of titanium and nickel-based alloys using picosecond laser. Proced CIRP. 2014;13:417–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.04.071.
Kiran Kumar K, Samuel GL, Shunmugam MS. Theoretical and experimental investigations of ultra-short pulse laser interaction on Ti6Al4V alloy. J Mater Process Technol. 2019;263:266–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.08.028.
Yu Z, Hu J, Li K. Investigating the multiple-pulse drilling on titanium alloy in picosecond laser. J Mater Process Technol. 2019;268:10–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.12.027.
Sedao X, Lenci M, Rudenko A, Faure N, Pascale-Hamri A, Colombier JP, et al. Influence of pulse repetition rate on morphology and material removal rate of ultrafast laser ablated metallic surfaces. Opt Lasers Eng. 2019;116:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.12.009.
Mannion P, Magee J, Coyne E, O’Connor GM. Ablation thresholds in ultrafast laser micromachining of common metals in air. In: Glynn TJ, editor. Opto-Ireland 2002: optics and photonics technologies and applications. SPIE; 2002. p. 470.
Zheng B, Jiang G, Wang W, Wang K, Mei X. Ablation experiment and threshold calculation of titanium alloy irradiated by ultra-fast pulse laser. AIP Adv. 2014;4(3):31310. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4867088.
Cheng J, Perrie W, Sharp M, Edwardson SP, Semaltianos NG, Dearden G, et al. Single-pulse drilling study on Au, Al and Ti alloy by using a picosecond laser. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process. 2009;95(3):739–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-5037-6.
Mannion P, Magee J, Coyne E, O’Connor G, Glynn T. The effect of damage accumulation behaviour on ablation thresholds and damage morphology in ultrafast laser micro-machining of common metals in air. Appl Surf Sci. 2004;233(1–4):275–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2004.03.229.
Huerta-Murillo D, García-Girón A, Romano JM, Cardoso JT, Cordovilla F, Walker M, et al. Wettability modification of laser-fabricated hierarchical surface structures in Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Appl Surf Sci. 2019;463:838–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.09.012.
Uhlmann E, Schweitzer L, Kieburg H, Spielvogel A, Huth-Herms K. The effects of laser microtexturing of biomedical grade 5 Ti-6Al-4V dental implants (abutment) on biofilm formation. Proced CIRP. 2018;68:184–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.044.
Shaikh S, Kedia S, Majumdar AG, Subramanian M, Sinha S. In vitro bioactivity and biocompatibility of femtosecond laser-modified Ti6Al4V alloy. Appl Phys A. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2238-5.
Azarhoushang B, Soltani B, Daneshi A. Study of the effects of laser micro structuring on grinding of silicon nitride ceramics. CIRP Ann. 2018;67(1):329–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2018.04.084.
Kadivar M, Shamray S, Soltani B, Daneshi A, Azarhoushang B. Laser-assisted micro-grinding of Si3N4. Precis Eng. 2019;60:394–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2019.09.004.
Azarhoushang B, Soltani B, Zahedi A. Laser-assisted grinding of silicon nitride by picosecond laser. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2017;93(5–8):2517–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0440-9.
Hojati F, Azarhoushang B, Daneshi A, Biermann D. Laser pre-structure-assisted micro-milling of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08774-4.
Standard Specification for Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS R56400).
Soltani B, Azarhoushang B, Zahedi A. Laser ablation mechanism of silicon nitride with nanosecond and picosecond lasers. Opt Laser Technol. 2019;119: 105644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105644.
Wang Y, Yu Z, Li K, Hu J. Study on the effect of surface characteristics of short-pulse laser patterned titanium alloy on cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation. Mater Sci Eng C. 2021;128: 112349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.112349.
Soltani B, Hojati F, Daneshi A, Azarhoushang B. Simulation of the laser-material interaction of ultrashort pulse laser processing of silicon nitride workpieces and the key factors in the ablation process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2021;114(11–12):3719–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07111-5.
Hohlfeld J, Müller JG, Wellershoff S-S, Matthias E. Time-resolved thermoreflectivity of thin gold films and its dependence on film thickness (Appl. Phys. B 64, 387F–390 (1997)). Appl Phys B. 1997;65(4–5):681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400050333.
Vogel A, Noack J, Hüttman G, Paltauf G. Mechanisms of femtosecond laser nanosurgery of cells and tissues. Appl Phys B. 2005;81(8):1015–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-005-2036-6.
Schmidt V, Husinsky W, Betz G. Dynamics of laser desorption and ablation of metals at the threshold on the femtosecond time scale. Phys Rev Lett. 2000;85(16):3516–9. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.3516.
Siegel J, Solis J, Afonso CN, Vega F, Bankmann J, Martı́nez-Sacristán O, et al. Evidence for surface initiated solidification in Ge films upon picosecond laser pulse irradiation. J Appl Phys. 2001;89(7):3642–9. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1347958.
Rajeev PP, Sengupta S, Das A, Taneja P, Ayyub P, Kaw PK, et al. Laser absorption in short-lived metal and nanoplasmas. Appl Phys B. 2005;80(8):1015–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-005-1827-0.
Anisimov SI, Kapeliovich BL, Perelman TL. Electron emission from metal surfaces exposed to ultrashort laser pulses. J Exp Theoret Phys. 1974;66:3757–67.
Lin Z, Zhigilei LV, Celli V. Electron-phonon coupling and electron heat capacity of metals under conditions of strong electron-phonon nonequilibrium. Phys Rev B. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.77.075133.
Ahuir-Torres JI, Arenas MA, Perrie W, de Damborenea J. Influence of laser parameters in surface texturing of Ti6Al4V and AA2024-T3 alloys. Opt Lasers Eng. 2018;103:100–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2017.12.004.
Tan S, Wu J, Zhang Y, Wang M, Ou Y. A model of ultra-short pulsed laser ablation of metal with considering plasma shielding and non-fourier effect. Energies. 2018;11(11):3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113163.
Amoruso S, Bruzzese R, Wang X, O’Connell G, Lunney JG. Multidiagnostic analysis of ultrafast laser ablation of metals with pulse pair irradiation. J Appl Phys. 2010;108(11): 113302. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3516491.
Perez D, Lewis LJ. Molecular-dynamics study of ablation of solids under femtosecond laser pulses. Phys Rev B. 2003. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.67.184102.
Yu Z, Yang G, Zhang W, Hu J. Investigating the effect of picosecond laser texturing on microstructure and biofunctionalization of titanium alloy. J Mater Process Technol. 2018;255:129–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.12.009.
Bonse J, Krüger J, Höhm S, Rosenfeld A. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. J Laser Appl. 2012;24(4):42006. https://doi.org/10.2351/1.4712658.
Vorobyev AY, Guo C. Direct observation of enhanced residual thermal energy coupling to solids in femtosecond laser ablation. Appl Phys Lett. 2005;86(1):11916. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1844598.
Lopez J, Faucon M, Devillard R, Zaouter Y, Hönninger C, Mottay E, et al. Parameters of influence in surface ablation and texturing of metals using high-power ultrafast laser. J Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2015. https://doi.org/10.2961/jlmn.2015.01.0001.
Liu E, Chen X, Jin Y, Chen Y, Xu J, Shan D, et al. Surface morphology evolution and tribological behavior in nanosecond pulsed laser polishing of S136 mold steel. J Mark Res. 2023;22:3230–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.12.153.
Lasemi N, Pacher U, Zhigilei LV, Bomatí-Miguel O, Lahoz R, Kautek W. Pulsed laser ablation and incubation of nickel, iron and tungsten in liquids and air. Appl Surf Sci. 2018;433:772–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.082.
Dai Y, He M, Bian H, Lu B, Yan X, Ma G. Femtosecond laser nanostructuring of silver film. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process. 2012;106(3):567–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-011-6705-5.
Vorobyev AY, Kuzmichev VM, Kokody NG, Kohns P, Dai J, Guo C. Residual thermal effects in Al following single ns- and fs-laser pulse ablation. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process. 2006;82(2):357–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3412-0.
Zhao W, Yu Z. Self-cleaning effect in high quality percussion ablating of cooling hole by picosecond ultra-short pulse laser. Opt Lasers Eng. 2018;105:125–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.01.011.
Funding
Thanks to Ministry of Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung BMBF in Connected Health in Medical Mountains (CoHMed) project for the fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hojati, F., Obergfell, D., Azarhoushang, B. et al. On interaction between laser and Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 24, 78 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-023-00837-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-023-00837-x