Abstract
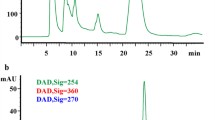
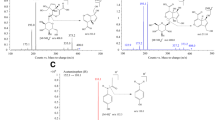
Tilianin was obtained from the medicinal plant Agastache mexicana (Kunth) Lint & Epling, Lamiaceae, a compound that is candidate to develop new multitarget drug for the treatment of metabolic syndrome–related diseases. The main aim of this work is to determine the pharmacokinetic parameters of tilianin after oral administration in Wistar rats to clarify its absorption pattern, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and permeability. A validated sensitive, selective, and reproducible high-performance liquid chromatography method was developed: r2 = 0.9992, 5.8 min of retention time, recovery of 100.2%, and LOD and LOQ were 1.86 and 5.63 μg/ml, respectively. By non-compartmental analysis, pharmacokinetic parameters were obtained, such as Tmax (1.00 h), Cmax (29.01 μg/ml), T1/2 (3.33 h), MRT (2.91 h), AUC0–t (62.25 µg h/ml), AUC0–∞ (92.47 µg h/ml), Kel (0.21 1/h), and Vd/F (2,788.05 ml). It was also determined that tilianin is deposited at 5 h in the pancreas, liver, and lung. The protonated [M + H]+ ion peaks of main metabolites were obtained by LC–MS at m/z 285.1 and 625.2, corresponding to acacetin and tilianin-glucuronic acid conjugation, respectively. In addition, tilianin was not excreted and metabolized through urine. Tilianin had a lower permeability pattern than furosemide and naproxen using everted gut model (1.43 × 10−6 cm/s). The pharmacokinetic study showed a long-lasting terminal half-life, and rapid absorption of tilianin in rodents. These results support the search to develop tilianin as a new drug for the treatment of metabolic syndrome.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bass AS, Cartwright ME, Mahon C, Morrison R, Snyder R, McNamara P, Bradley P, Zhou YY, Hunter J (2009) Exploratory drug safety: a discovery strategy to reduce attrition in development. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 60:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vascn.2009.04.194
Benjamin B, Barman TK, Chaira T, Paliwal JK (2010) Integration of physicochemical and pharmacokinetic parameters in lead optimization: a physiological pharmacokinetic model based approach. Curr Drug Discov Technol 7:143–153. https://doi.org/10.2174/157016310793180558
Berrin JG, McLauchlan WR, Needs P, Williamson G, Puigserver A, Kroon PA, Juge N (2002) Functional expression of human liver cytosolic β-glucosidase in Pichia pastoris. Insights into its role in the metabolism of dietary glucosides. Eur J Biochem 269:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0014-2956.2001.02641.x
Berrin JG, Czjzek M, Kroon PA, McLauchlan WR, Puigserver A, Williamson G, Juge N (2003) Substrate (aglycone) specificity of human cytosolic beta-glucosidase. Biochem J 373:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20021876
Bijsterbosch MK, Duursma AM, Bouma JM, Gruber M, Nieuwenhuis P (1981) Plasma clearance and endocytosis of mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase in the rat. Biochem J 200:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2000115
Boersma MG, van der Woude H, Bogaards J, Boeren S, Vervoort J, Cnubben NH, van Iersel ML, van Bladeren PJ, Rietjens IM (2002) Regioselectivity of phase II metabolism of luteolin and quercetin by UDP-glucuronosyl transferases. Chem Res Toxicol 15:662–670. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx0101705
Chawla S, Ghosh S, Sihorkar V, Nellore R, Shantha-Kumar TR, Srinivas NR (2006) High-performance liquid chromatography method development and validation for simultaneous determination of five model compounds, antipyrine, metoprolol, ketoprofen, furosemide and phenol red, as a tool for the standardization of rat in situ intestinal permeability studies using timed wavelength detection. Biomed Chromatogr 20:349–357. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.570
Courts FL, Williamson G (2009) The C-glycosyl flavonoid, aspalathin, is absorbed, methylated and glucuronidated intact in humans. Mol Nutr Food Res 53:1104–1111. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200800569
Dai P, Luo F, Wang Y, Jiang H, Wang L, Zhang G, Zhu L, Hu M, Wang X, Lu L, Liu Z (2015a) Species- and gender-dependent differences in the glucuronidation of a flavonoid glucoside and its aglycone determined using expressed UGT enzymes and microsomes. Biopharm Drug Dispos 36:622–635. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.1989
Dai P, Zhu L, Luo F, Lu L, Li Q, Wang L, Wang Y, Wang X, Hu M, Liu Z (2015b) Triple recycling processes impact systemic and local bioavailability of orally administered flavonoids. AAPS J 17:723–736. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-015-9732-x
Damle B, LaBadle R, Crownover P, Glue P (2007) Pharmacokinetic interactions of efavirenz and voriconazole in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 65:523530. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.03085.x
Day AJ, Gee JM, DuPont MS, Johnson IT, Williamson G (2003) Absorption of quercetin-3-glucoside and quercetin-4’-glucoside in the rat small intestine: the role of lactase phlorizin hydrolase and the sodium-dependent glucose transporter. Biochem Pharmacol 65:1199–1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00039-x
Du Y, Xi M, Li Y, Zheng R, Ding X, Li X, Zhang X, Wang L, Xing J, Hong B (2023) Tilianin improves lipid profile and alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice through up-regulation of SREBP2-mediated LDLR expression. Phytomedicine 109:154577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154577
Estrada-Reyes R, López-Rubalcava C, Ferreyra-Cruz OA, Dorantes-Barrón AM, Heinze G, Moreno-Aguilar J, Martínez-Vázquez M (2014) Central nervous system effects and chemical composition of two subspecies of Agastache mexicana; an ethnomedicine of Mexico. J Ethnopharmacol 153:98–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.12.057
Flores-Flores A, Hernández-Abreu O, Rios MY, León-Rivera I, Aguilar-Guadarrama B, Castillo-España P, Perea-Arango I, Estrada-Soto S (2016) Vasorelaxant mode of action of dichloromethane-soluble extract from Agastache mexicana and its main bioactive compounds. Pharm Biol 54:2807–2813. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2016.1184690
García-Díaz JA, Navarrete-Vázquez G, García-Jiménez S, Hidalgo-Figueroa S, Almanza-Pérez JC, Alarcón-Aguilar FJ, Gómez-Zamudio J, Cruz M, Ibarra-Barajas M, Estrada-Soto S (2016) Antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and anti-inflammatory effects of tilianin in streptozotocin-nicotinamide diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 83:667–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.023
González-Trujano ME, Ventura-Martínez R, Chávez M, Díaz-Reval I, Pellicer F (2012) Spasmolytic and antinociceptive activities of ursolic acid and acacetin identified in Agastache mexicana. Planta Med 78:793–796. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1298416
González-Trujano ME, Ponce-Muñoz H, Hidalgo-Figueroa S, Navarrete-Vázquez G, Estrada-Soto S (2015) Depressant effects of Agastache mexicana methanol extract and one of major metabolites tilianin. Asian Pac J Trop Med 8:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60312-6
Guo X, Cao W, Yao J, Yuan Y, Hong Y, Wang X, Xing J (2015) Cardioprotective effects of tilianin in rat myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep 11:2227–2233. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2954
Gupta SC, Sundaram C, Reuter S, Aggarwal BB (2010) Inhibiting NF-κB activation by small molecules as a therapeutic strategy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1799:775–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.05.004
Hartmann A, Krebber R, Daube G, Hartmann K (2008) Pharmacokinetics of pradofloxacin and doxycycline in serum, saliva, and tear fluid of cats after oral administration. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 31:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2885.2007.00932.x
Havsteen BH (2002) The biochemistry and medical significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol Ther 96:67–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0163-7258(02)00298-x
Hernández-Abreu O, Castillo-España P, León-Rivera I, Ibarra-Barajas M, Villalobos-Molina R, González-Christen J, Vergara-Galicia J, Estrada-Soto S (2009) Antihypertensive and vasorelaxant effects of tilianin isolated from Agastache mexicana are mediated by NO/cGMP path way and potassium channel opening. Biochem Pharmacol 78:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.03.016
Hernández-Abreu O, Durán-Gómez L, Best-Brown R, Villalobos-Molina R, Rivera-Leyva JC, Estrada-Soto S (2011) Validated liquid chromatographic method and analysis of content of tilianin on several extracts obtained from Agastache mexicana and its correlation with vasorelaxant effect. J Ethnopharmacol 138:487–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.041
Hernández-Abreu O, Torres-Piedra M, García-Jiménez S, Ibarra-Barajas M, Villalobos-Molina R, Montes S, Rembao D, Estrada-Soto S (2013) Dose-dependent antihypertensive determination and toxicological studies of tilianin isolated from Agastache mexicana. J Ethnopharmacol 146:187–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.12.029
Hong JJ, Choi JH, Oh SR, Lee HK, Park JH, Lee KY, Kim JJ, Jeong TS, Oh GT (2001) Inhibition of cytokine-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression; possible mechanism for anti-atherogenic effect of Agastache rugosa. FEBS Lett 495:142–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02379-1
Hung WL, Chang WS, Lu WC, Wei GJ, Wang Y, Ho CT, Hwang LS (2018) Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, tissue distribution and excretion of tangeretin in rat. J Food Drug Anal 26:849–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2017.08.003
Ibarra-Alvarado C, Rojas A, Mendoza S, Bah M, Gutiérrez DM, Hernández-Sandoval L, Martínez M (2010) Vasoactive and antioxidant activities of plants used in Mexican traditional medicine for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Pharm Biol 48:732–739. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880200903271280
Jiang H, Ashraf GM, Liu M, Zhao K, Wang Y, Wang L, Xing J, Alghamdi BS, Li Z, Liu R (2021) Tilianin ameliorates cognitive dysfunction and neuronal damage in rats with vascular dementia via p-CaMKII/ERK/CREB and ox-CaMKII-Dependent MAPK/NF-κB pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:6673967. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6673967
Kashimura J, Nagai Y (2007) Inhibitory effect of palatinose on glucose absorption in everted rat gut. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 53:87–89. https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.53.87
Khattulanuar FS, Sekar M, Fuloria S, Gan SH, Rani NNIM, Ravi S, Chidambaram K, Begum MY, Azad AK, Jeyabalan S, Dhiravidamani A, Thangavelu L, Lum PT, Subramaniyan V, Wu YS, Sathasivam KV, Fuloria NK (2022) Tilianin: a potential natural lead molecule for new drug design and development for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders. Molecules 27:673. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030673
Li J, Xu S (2022) Tilianin attenuates MPP+-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Ther Med 23:293. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2022.11223
Liu Z, Guan C, Li C, Zhang N, Yang C, Xu L, Zhou B, Zhao L, Luan H, Man X, Xu Y (2022) Tilianin reduces apoptosis via the ERK/EGR1/BCL2L1 pathway in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury mice. Front Pharmacol 13:862584. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.862584
Ma LY, Liu RH, Xu XD, Yu MQ, Zhang Q, Liu HL (2010) The pharmacokinetics of C-glycosyl flavones of hawthorn leaf flavonoids in rat after single dose oral administration. Phytomedicine 17:640–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2009.12.010
Monroy-Ortiz C, Castillo-España E (2007) Plantas medicinales utilizadas en el Estado de Morelos, 2nd ed. Cuernavaca, Morelos, Mexico, pp. 154–156
Murota K, Terao J (2003) Antioxidative flavonoid quercetin: implication of its intestinal absorption and metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys 417:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-9861(03)00284-4
Nam KW, Kim J, Hong JJ, Choi JH, Mar W, Cho MH, Kim YM, Oh SR, Lee HK, Nam KH, Oh GT (2005) Inhibition of cytokine-induced IkappaB kinase activation as a mechanism contributing to the anti-atherogenic activity of tilianin in hyperlipidemic mice. Atherosclerosis 180:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.11.022
Nam KH, Choi JH, Seo YJ, Lee YM, Won YS, Lee MR, Lee MN, Park JG, Kim YM, Kim HC, Lee CH, Lee HK, Oh SR, Oh GT (2006) Inhibitory effects of tilianin on the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in low density lipoprotein receptor deficiency mice. Exp Mol Med 38:445–452. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.52
Nemeth K, Plumb GW, Berrin JG, Juge N, Jacob R, Naim HY, Williamson G, Swallow DM, Kroon PA (2003) Deglycosylation by small intestinal epithelial cell β-glucosidases is a critical step in the absorption and metabolism of dietary flavanoid glycosides in humans. Eur J Nutr 42:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-003-0397-3
NOM-177-SSA1–2003 (2013) NORMA Oficial Mexicana. In Spanish. https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5314833&fecha=20/09/2013#gsc.tab=0. Accessed 13 Nov 2023
O’Leary KA, Day AJ, Needs PW, Mellon FA, O’Brien NM, Williamson G (2003) Metabolism of quercetin-7- and quercetin-3-glucuronides by an in vitro hepatic model: the role of human b-glucuronidase, sulfotransferase, catechol-O-methyltransferase and multi-resistant protein 2 (MRP2) in flavonoid metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol 65:479–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(02)01510-1
Peng J, Qi Q, You Q, Hu R, Liu W, Feng F, Wang G, Guo Q (2009) Subchronic toxicity and plasma pharmacokinetic studies on wogonin, a natural flavonoid, in Beagle dogs. J Ethnopharmacol 124:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2009.04.031
Pferschy-Wenzig EM, Bauer R (2015) The relevance of pharmacognosy in pharmacological research on herbal medicinal products. Epilepsy Behav 52:344–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.05.037
Ross JA, Kasum CM (2002) Dietary flavonoids: bioavailability, metabolic effects, and safety. Annu Rev Nutr 22:19–34. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.22.111401.144957
Sánchez-Recillas A, Mantecón-Reyes P, Castillo-España P, Villalobos-Molina R, Ibarra-Barajas M, Estrada-Soto S (2014) Tracheal relaxation of five medicinal plants used in Mexico for the treatment of several diseases. Asian Pac J Trop Med 7:179–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60017-1
Sesink AL, Arts IC, de Boer VC, Breedveld P, Schellens JH, Hollman PC, Russel FG (2005) Breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp1/Abcg2) limits net intestinal uptake of quercetin in rats by facilitating apical efflux of glucuronides. Mol Pharmacol 67:1999–2006. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.104.009753
Ventura-Martínez R, Rodríguez R, González-Trujano ME, Ángeles-López GE, Déciga-Campos M, Gómez C (2017) Spasmogenic and spasmolytic activities of Agastache mexicana ssp. mexicana and A. mexicana ssp. xolocotziana methanolic extracts on the guinea pig ileum. J Ethnopharmacol 196:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.023
Walle T (2004) Absorption and metabolism of flavonoids. Free Radic Biol Med 36:829–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.01.002
Wang TT, Li W, Yuan Y, Wang L-P, Wang X-C (2013) Study on intestinal absorption of tilianin in rats of single-pass perfusion model. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 38:1079–1082
Wang X, Morris ME (2008) Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the flavonoid 7,8-benzoflavone in rats. J Pharm Sci 97:4546-4556. http://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21296
Xiao J, Cao H, Chen T, Yang F, Liu C, Xu X (2011) Molecular property-binding affinity relationship of flavonoids for common rat plasma proteins in vitro. Biochimie 93:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2010.08.013
Xiong C, Yan B, Xia S, Yu F, Zhao J, Bai H (2021) Tilianin inhibits the human ovarian cancer (PA-1) cell proliferation via blocking cell cycle, inducing apoptosis and inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Saudi J Biol Sci 28:4900–4907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.033
Yao J, Li Y, Jin Y, Chen Y, Tian L, He W (2021) Synergistic cardioptotection by tilianin and syringin in diabetic cardiomyopathy involves interaction of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 and PGC1a/SIRT3 pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 96:107728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107728
Yu-Chi H, Shiuan-Pey L, Shang-Yuan T, Miau-Hwa K, Yun-Chia C, Pei-Dawn LC (2011) Flavonoid pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution after repeated dosing of the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis in rats. Planta Med 77:455–460. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1250433
Zhan-Ling X, Ming-Yue X, Hai-Tao W, Qing-Xuan X, Ming-Yang L, Chun-Peng J, Fang G, Ning Z (2018) Pharmacokinetics of eight flavonoids in rats assayed by UPLC-MS/MS after oral administration of Drynariae rhizoma extract. J Anal Methods Chem 2018:4789196. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4789196
Funding
This work was supported by SEP-CONACYT (Ciencia Básica A1-S-13540), CONACYT FORDECYT-PRONACES (Ciencia de Frontera 377882/2020), and IN210222, PAPIIT, DGAPA, UNAM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OH-A: performed the experiments, data analysis, drafted the manuscript; SE-S: project design, drafted and revised the final manuscript, funding acquisition; JCR-L: conceptualization, supervision in the validation of the analytical method by HPLC; AP-L: performed the LC–MS analysis; GÁ-V: data analysis and interpretation, technical assistance, and revised the manuscript; RV-M: drafted and revised the final manuscript, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Animal protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Protocol 1497, F.E.S. Iztacala, U.N.A.M.).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
In memory of Professor Ismael León-Rivera, may he rest in peace.
Taken in part from the PhD thesis of O. Hernández-Abreu.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández-Abreu, O., Estrada-Soto, S., Rivera-Leyva, J.C. et al. Pharmacokinetic Study of Tilianin After Oral Administration in Wistar Rats by HPLC. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-024-00541-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-024-00541-8