Abstract
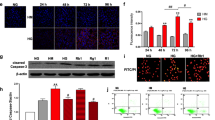
Nephropathy is a chronic complication of diabetes which lacks an effective treatment. “Baitouweng,” a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, is the root of Anemone chinensis Bunge, Ranunculaceae, and is used for its antidiabetes properties. However, the mechanism by which it exerts its effects has not been fully elucidated. Anemoside B4 is the most abundant triterpenoid saponin in this plant with anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis activities. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effect of anemoside B4 on diabetic nephropathy and elucidate the underlying mechanism. Our data showed that anemoside B4 did not affect the proliferation of mesangial cells, but it could significantly inhibit the proliferation induced by high glucose. Mechanistically, anemoside B4 decreased the content of reactive oxygen species and improved glutathione and catalase activity. Also, the activation of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway was inhibited. Therefore, anemoside B4 has a protective activity against diabetic nephropathy with the characteristics of having high safety, low toxicity, and high solubility.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Waili N, Al-Waili H, Al-Waili T, Salom K (2017) Natural antioxidants in the treatment and prevention of diabetic nephropathy; a potential approach that warrants clinical trials. Redox Rep 22:99–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/13510002.2017.1297885
Backe MB, Pedersen ML (2020) Prevalence, incidence, mortality, and quality of care of diagnosed diabetes in Greenland. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107991
Brownlee M (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 414:813–820. https://doi.org/10.1038/414813a
Brunskill EW, Potter SS (2012) Changes in the gene expression programs of renal mesangial cells during diabetic nephropathy. BMC Nephrol 13:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-13-70
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (2015) Chinese Pharmacopoeia, vol. 1, People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing, China
Dubey VK, Patil CR, Kamble SM, Tidke PS, Patil KR, Maniya PJ, Jadhav RB, Patil SP (2013) Oleanolic acid prevents progression of streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropathy and protects renal microstructures in Sprague Dawley rats. J Pharmacol Pharmacother 4:47–52. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-500X.107678
He L, Zhang Y, Kang N, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Zha Z, Yang S, Xu Q, Liu Y (2019) Anemoside B4 attenuates nephrotoxicity of cisplatin without reducing anti-tumor activity of cisplatin. Phytomedicine 56:136–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.10.035
Kaneto H, Katakami N, Kawamori D, Miyatsuka T, Sakamoto K, Matsuoka TA, Matsuhisa M, Yamasaki Y (2007) Involvement of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetes. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:355–366. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2006.1465
Kang N, Shen W, Zhang Y, Su Z, Yang S, Liu Y, Xu Q (2019) Anti-inflammatory and immune-modulatory properties of anemoside B4 isolated from Pulsatilla chinensis in vivo. Phytomedicine 64:152934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152934
Kanwar YS, Sun L, Xie P, Liu FY, Chen S (2011) A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. Annu Rev Pathol-Mech 6:395–423. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092150
Li YH, Zou M, Han Q, Deng LR, Weinshilboum RM (2020) Therapeutic potential of triterpenoid saponin anemoside B4 from Pulsatilla chinensis. Pharmacol Res 160:105079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105079
Lindblom R, Higgins G, Coughlan M, de Haan JB (2015) Targeting mitochondria and reactive oxygen species-driven pathogenesis in diabetic nephropathy. Rev Diabet Stud 12:134–156. https://doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2015.12.134
Ling Y, Lin Z, Zha W, Lian T, You S (2016) Rapid detection and characterisation of triterpene saponins from the root of Pulsatilla chinensis (Bunge) Regel by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. Phytochem Anal 27:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2613
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP, Malik AB (2014) Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 20:1126–1167. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.5149
Mohamed R, Jayakumar C, Chen F, Fulton D, Stepp D, Gansevoort RT, Ramesh G (2016) Low-dose IL-17 therapy prevents and reverses diabetic nephropathy, metabolic syndrome, and associated organ fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:745–765. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014111136
Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Mora-Fernandez C (2008) The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:433–442. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2007091048
Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Mora-Fernandez C, Muros de Fuentes M, Garcia-Perez J (2011) Inflammatory molecules and pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 7:327–340. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2011.51
Ozbek E (2012) Induction of oxidative stress in kidney. Int J Nephrol 2012:465897. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/465897
Prabakaran T, Bodda C, Krapp C, Zhang BC, Christensen MH, Sun C, Reinert L, Cai Y, Jensen SB, Skouboe MK, Nyengaard JR, Thompson CB, Lebbink RJ, Sen GC, van Loo G, Nielsen R, Komatsu M, Nejsum LN, Jakobsen MR, Gyrd-Hansen M, Paludan SR (2018) Attenuation of cGAS-STING signaling is mediated by a p62/SQSTM1-dependent autophagy pathway activated by TBK1. EMBO J 37:e97858. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201797858
Schmid H, Boucherot A, Yasuda Y, Henger A, Brunner B, Eichinger F, Nitsche A, Kiss E, Bleich M, Grone HJ, Nelson PJ, Schlondorff D, Cohen CD, Kretzler M, Renal E, c DNABC, (2006) Modular activation of nuclear factor-kappaB transcriptional programs in human diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 55:2993–3003. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-0477
Song G, Han P, Sun H, Shao M, Yu X, Wang W, Wang D, Yi W, Ge N, Li S, Yi T (2018) astragaloside IV ameliorates early diabetic nephropathy by inhibition of MEK1/2-ERK1/2-RSK2 signaling in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J Int Med Res 46:2883–2897. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060518778711
Tamada S, Asai T, Kuwabara N, Iwai T, Uchida J, Teramoto K, Kaneda N, Yukimura T, Komiya T, Nakatani T, Miura K (2006) Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of chronic renal injury: the role of nuclear factor kappaB activation in the development of renal fibrosis. J Pharmacol Sci 100:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.fmj05003x4
Tan SM, de Haan JB (2014) Combating oxidative stress in diabetic complications with Nrf2 activators: how much is too much? Redox Rep 19:107–117. https://doi.org/10.1179/1351000214Y.0000000087
Xu QM, Shu Z, He WJ, Chen LY, Yang SL, Yang G, Liu YL, Li XR (2012) Antitumor activity of Pulsatilla chinensis (Bunge) Regel saponins in human liver tumor 7402 cells in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine 19:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2011.08.066
Xu Q-M, Shu Z, Zhu W-F, Liu Y-L, Li X-R, Yang S-L (2013) Lupane-type triterpenoidal saponins from Pulsatilla chinensis and their anticomplement activities through the classical pathway. Planta Med 79:506–512. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1328323
Yang YY, Shi LX, Li JH, Yao LY, Xiang DX (2019) Piperazine ferulate ameliorates the development of diabetic nephropathy by regulating endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Mol Med Rep 19:2245–2253. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.9875
Yu SM, Bonventre JV (2018) Acute kidney injury and progression of diabetic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 25:166–180. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2017.12.005zhaozhaozhaozz
Zhu Y, Zhu C, Yang H, Deng J, Fan D (2020) Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg5 against kidney injury via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the MAPK signaling pathway in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Pharmacol Res 155:104746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104746
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J (2001) Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 414:782–787. https://doi.org/10.1038/414782a
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82073912 and 81273402), Suzhou Science and Technology Plan Project (SYS2019032), Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (SJCX19_0811), and a project funded by Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LY-L and XQ-M conceptualized the project; HL did the major experimental work and contributed in the manuscript writing; LN analyzed the data and revised the paper; ZZ-X and LQ-H participated in part of the experimentation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the procedure approved by the Ethical Review Committee for Laboratory Animal Welfare of Soochow University (protocol No. ECS-2019–3021). All the international standards and the ethical guidelines on animal welfare were strictly followed throughout the experimentation.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, H., Ning, L., Zheng-Xia, Z. et al. Anemoside B4 Alleviates the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy In Vitro and In Vivo. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 31, 310–321 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00161-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00161-6