Abstract
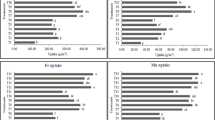
The present field study was conducted on silty loam soil at ‘long-term fertilizer experiment’ Research Farm, Department of Soil Science, CSK HPKV, Palampur (HP), India under a maize–wheat cropping to study the influence of long-term integrated nutrient management (INM) involving chemical fertilizers, organics and lime on the availability of micronutrients (Zn, Fe, Mn and Cu) in soil, yield and uptake of these micronutrients by maize and wheat. Ten fertilizer treatments comprising different amounts of NPK fertilizers, farmyard manure (FYM) and lime, and Natural Farming and control, were replicated thrice in a randomized block design. Soil availability of micronutrients and their plant concentrations were estimated in grain and stover/straw of both the crops. Soil recovery coefficient (SRC) was calculated to find out micronutrients availability in relation to their plant uptake. The continuous use of chemical fertilizers along with organics and lime in maize–wheat cropping system for 47 years has resulted to an increase in the availability of micronutrient cations (Zn, Fe, Mn and Cu). Build-up of soil organic carbon and decrease in soil pH has resulted in the increase of bio-available forms of micronutrients. Low SRC values of Zn, Cu, Fe, and Mn indicated that long-term INM can meet their plant nutritional requirement in maize–wheat cropping system. This study concluded that long-term integration of FYM with NPK fertilizers has an edge over chemical fertilizers alone in regulating the supply of micronutrients in soil–plant system and correcting the micronutrients deficiencies in maize–wheat cropping system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya CN, Rajagopalan K (1956) Effect of application of manures and fertilizers on the organic carbon and nitrogen level. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 4:111
Amipara HV, Jadhav NJ (2017) Long-term effect of farm yard manure and inorganic fertilizers on crop yield and physico-chemical properties of loamy sand soil. Agric Res J 54:505–509
Anonymous (2021) Economic Survey, Economic and Statistics Department, Government of Himachal Pradesh p 74–80
Antil RS, Singh M (2007) Effects of organic manures and fertilizers on organic matter and nutrients status of the soil. Arch Agron Soil Sci 53:519–528
Bharti B, Sharma RP (2017) Long term effect of integrated nutrient management on soil properties and availability of nutrients in a Typic Hapludalfs under maize–wheat cropping. Int J Environ Agric Res 3:43–48
Bhattacharyya R, Prakash V, Kundu S, Ghosh BN, Srivastva AK, Gupta HS (2009) Soil properties and their relationships with crop productivity after 30 years of different fertilization in the Indian Himalayas. Arch Agron Soil Sci 55:641–661
Bhattacharyya R, Pandey AK, Gopinath KA, Mina BL, Bisht JK, Bhatt JC (2016) Fertilization and crop residue addition impacts on yield sustainability under rainfed maize–wheat system in the Himalayas. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 86:21–32
Brar BS, Singh J, Singh G, Kaur G (2015) Effects of long-term application of inorganic and organic fertilizers on soil organic carbon and physical properties in maize–wheat rotation. Agronomy 5:220–238
Chauhan N, Sankhyan NK, Sharma RP, Singh J, Gourav (2020) Effect of long-term application of inorganic fertilizers, farm yard manure and lime on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) productivity, quality and nutrient content in an acid alfisol. J Plant Nutr 43:2569–2578
Chimdi A, Gebrekidan V, Kibret K, Tadesse A (2012) Effects of liming on acidity-related chemical properties of soils of different land use systems in Western Oromia, Ethiopia. World J Agric Sci 8:560–567
Dhiman D, Sharma RP, Sankhyan NK, Sepehya S, Sharma SK, Kumar R (2019) Effect of regular application of fertilizers, manure and lime on soil health and productivity of wheat in an acid Alfisol. J Plant Nutr 42:2507–2521
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedure for agricultural research. Wiley, New York
Hati N, Fisher TR, Upchurch WJ (1979) Liming of acid soil II effect on plant available manganese and iron. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 27:394
Hodgson JF (1963) Chemistry of micronutrient elements in soils. Adv Agron 15:119–150
Hue NV (1992) Correcting soil acidity of a highly weathered ultisols with chicken manure and sewage sludge. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 23:241–264
Isaac RA, Kerber JD (1971) Atomic absorption and flame photometry: Techniques and uses in soil, plant and water analysis. In Instrumental methods for analysis of soils and plant tissue. Madison WI, USA: Walsh, L M Science Society of America
Kaushal V (2002) Studies on long-term effects of chemical fertilizers and amendments on sustainable use of soil in wet temperate zone of western Himalayas. M Sc Thesis. Department of Soil Science, CSKHPKV, Palampur, India. p 99
Khaliq A, Zafar M, Abbasi MK, Hussain I (2017) Soil–plant micronutrients dynamics in response to integrated fertilization under wheat–soybean cropping system at Rawalakot, Pakistan. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:640–653
Kher D (1987) Studies on crop responses and soil properties as influenced by long term term fertilizer experimentation in acid alfisol of Himachal Pradesh. Ph D Thesis. Department of Soil Science, CSKHPKV, Palampur, India. p 239
Kundu DK, Mazumdar SP, Ghosh D, Saha AR, Mazumdar B, Ghorai AK, Behera MS (2016) Long-term effects of fertilizer and manure application on soil quality and sustainability of jute–rice–wheat production system in Indo-Gangetic plain. J Appl Nat Sci 8:1793–1800
Li BY, Zhou DM, Cang L, Zhang HL, Fan XH, Qin SW (2007) Soil micronutrient availability to crops as affected by long term inorganic and organic fertilizer applications. Soil Tillage Res 96:166–173
Liang Q, Chen H, Gong Y, Fan M, Yang H, Lal R, Kuzyakov Y (2012) Effects of 15 years of manure and inorganic fertilizers on soil organic carbon fractions in a maize–wheat system in the North China Plain. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 92:21–33
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Majhi S, Thakur R, Pal SK, Upasani RR, Puran AN, Kujur AN (2018) Long-term influence of nutrient management on productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays)–wheat (Triticum aestivum) cropping system. Indian J Agron 63:14–20
Mishra B, Sharma A, Singh SK, Prasad J, Singh BP (2008) Influence of continuous application of amendments to maize–wheat cropping system on dynamics of soil microbial biomass in Alfisol of Jharkhand. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 56:71–85
Mohrana PC, Sharma BM, Biswas DR (2017) Changes in the soil properties and availability of micronutrients after six-year application of organic and chemical fertilizers using stcr-based targeted yield equations under pearl millet-wheat cropping system. J Plant Nutr 40:165–176
Parven H, Kumar S, Shambhavi S, Kumar S, Kumar R, Kumari D (2020) Long term effect of integrated nutrient management on secondary and micronutrient of alluvial soils. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 9:1990–1999
Puniya R, Pandey PC, Bisht PS, Singh DK, Singh AP (2019) Effect of long-term nutrient management practices on soil micronutrient concentrations and uptake under a rice-wheat cropping system. J Agric Sci 157:226–234
Rutkowska B, Szulc W, Sosulski T, Stępień W (2014) Soil micronutrient availability to crops affected by long-term inorganic and organic fertilizer applications. Plant Soil Environ 60:198–203
Saha S, Saha BN, Ray M, Mukhopadhyay SK, Halder P, Das A, Chatterjee S, Pramanick M (2018) Integrated nutrient management (INM) on yield trends and sustainability, nutrient balance and soil fertility in a long-term (30 years) rice-wheat system in the Indo-Gangetic plains of India. J Plant Nutr 41:2365–2375
Saha S, Saha B, Seth T, Dasgupta S, Ray M, Pal B, Pati S, Mukhopadhyay SK, Hazra G (2019) Micronutrients availability in soil–plant system in response to long-term integrated nutrient management under rice–wheat cropping system. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:712–724
Sharma SP, Subehia SK, Sharma PK (2002). Long-term effects of chemical fertilizers on soil quality, crop productivity and sustainability. Research Bulletin CSK Himachal Pradesh Krishi Vishvavidyalaya p 33
Sharma U, Kumar P (2016) Micronutrient research in India: extent of deficiency, crop responses and future challenges. Int J Adv Res 4:1402–1406
Shirale ST, Kide DS, Meshram NA (2014) Long-term effect of organic manuring and inorganic fertilizers for enhancing yield and soil properties under soybean (Glycine max L.)- safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) cropping sequence in Vertisol. Asian J Soil Sci 9:130–136
Singh P, Saini SP (2021) Micronutrients availability in soil–plant system as influenced by long-term integrated nutrient management under rice–wheat cropping. J Plant Nutr 45:457–470
Singh AK, Sarkar AK, Kumar A, Singh BP (2009) Effect of long-term use of mineral fertilizers, lime and farmyard manure on crop yield, available plant nutrient and heavy metal status in an acidic loam soil. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 57:362–365
Sudhir K, Srikanth K, Jayaprakash SM (2002) Sustained crop production under long term fertilizer use in red soil in India. In: 17th WCSS, 14–21 August 2002, Thailand, vol 108, pp 1–10
Swarup A (2010) Integrated plant nutrient supply and management strategies for enhancing soil quality, input use efficiency and crop productivity. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 58:25–31
Takkar PN, Bhumbla DR (1976) Iron a contributing factor to soil acidity. Bull Indian Soc Soil Sci 17:501
Thakur A, Sharma RP, Sankhyan NK, Sepehya S (2022) Effect of 46years’ application of fertilizers, FYM and lime on physical, chemical and biological properties of soil under maize wheat system in an acid Alfisol of northwest Himalayas. Soil Use Manag 39:357–367
Verma G, Sharma RP, Sharma SP, Subehia SK, Shambhavi S (2012) Changes in soil fertility status in maize–wheat system due to long-term use of chemical fertilizers and amendments in an Alfisol. Plant Soil Environ 58:529–533
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff (wet acid) method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Welch RM, Graham RD (2004) Breeding for micronutrients in staple food crops from a human nutrition perspective. J Exp Bot 55:353–364
Zhang S, Li Z, Yang X (2015) Effects of long-term inorganic and organic fertilization on soil micronutrient status. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 46:1778–1790
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly thankful to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research for funding the study under the All-Indian Coordinated Research Project on Long-Term Fertilizer Experiments and CSK Himachal Pradesh Agricultural University, Palampur for providing essential facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Communicated by Márton Jolánkai.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Suri, D., Sharma, R.P., Sankhyan, N.K. et al. Micronutrient availability in soil–plant system as influenced by 47 years long application of chemical fertilizers, organics and lime under maize–wheat cropping in an acid Alfisol. CEREAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-023-00450-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-023-00450-x