Abstract
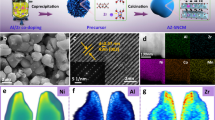
The application of all-solid-state Li-metal batteries with solid oxide electrolytes is hindered by interfacial issues, especially the solid electrolyte/Li-metal interface. This work introduced a uniform indium film layer on the surface of Na+ super ionic conductor (NASICON) solid electrolyte Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5P3O12 (LAGP), which promotes the intimate contact between Li metal and solid electrolyte and hinders the side reactions at the interface. Electrochemical impedance spectra show that the battery with coated solid electrolyte presents a smaller interfacial resistance and maintains stability after a long cycling time. By contrast, the baseline battery with a pure LAGP pellet shows a contact loss after cycling with the vibration of interfacial impedance. The Li symmetric cells with indium-modified solid electrolyte present stable cycling behavior over 400 h at 0.1 and 0.2 mA·cm−2. The all-solid-state Li-metal batteries with a Li anode, indium coating LAGP and two kinds of cathodes, namely carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 (NCM811), are prepared and tested. The CNTs cathode for Li–O2 and Li–air batteries has a higher specific capacity than traditional Li-ion battery cathodes. The Li-NCM811 batteries deliver an initial Coulombic efficiency of about 75%, with 82% capacity retention after 20 cycles.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Y, He P, Zhou H. Rechargeable solid-state Li–air and Li–S batteries: materials, construction, and challenges. Adv Energy Mater. 2018;8(4):1701602.
Yu Z, Zhang X, Fu C, Wang H, Chen M, Yin G, Huo H, Wang J. Dendrites in solid-state batteries: ion transport behavior, advanced characterization, and interface regulation. Adv Energy Mater. 2021;11(18):2003250.
Zhou L, Minafra N, Zeier WG, Nazar LF. Innovative approaches to Li-argyrodite solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Acc Chem Res. 2021;54(12):2717.
Krauskopf T, Richter FH, Zeier WG, Janek J. Physicochemical concepts of the lithium metal anode in solid-state batteries. Chem Rev. 2020;120(15):7745.
Chen R, Li Q, Yu X, Chen L, Li H. Approaching practically accessible solid-state batteries: stability issues related to solid electrolytes and interfaces. Chem Rev. 2020;120(14):6820.
Zhang J, Zheng C, Li L, Xia Y, Huang H, Gan Y, Liang C, He X, Tao X, Zhang W. Unraveling the intra and intercycle interfacial evolution of Li6PS5Cl-based all-solid-state lithium batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2019;10(4):1903311.
Banerjee A, Wang X, Fang C, Wu EA, Meng YS. Interfaces and interphases in all-solid-state batteries with inorganic solid electrolytes. Chem Rev. 2020;120(14):6878.
Wenzel S, Leichtweiss T, Krüger D, Sann J, Janek J. Interphase formation on lithium solid electrolytes—an in situ approach to study interfacial reactions by photoelectron spectroscopy. Solid State Ionics. 2015;278:98.
Wenzel S, Sedlmaier SJ, Dietrich C, Zeier WG, Janek J. Interfacial reactivity and interphase growth of argyrodite solid electrolytes at lithium metal electrodes. Solid State Ionics. 2018;318:102.
Ahmad Z, Viswanathan V. Stability of electrodeposition at solid-solid interfaces and implications for metal anodes. Phys Rev Lett. 2017;119(5): 056003.
Zhou W, Wang S, Li Y, Xin S, Manthiram A, Goodenough JB. Plating a dendrite-free lithium anode with a polymer/ceramic/polymer sandwich electrolyte. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(30):9385.
Hao Y, Wang S, Xu F, Liu Y, Feng N, He P, Zhou H. A design of solid-state Li-S cell with evaporated lithium anode to eliminate shuttle effects. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(39):33735.
Liu Y, Li C, Li B, Song H, Cheng Z, Chen M, He P, Zhou H. Germanium thin film protected lithium aluminum germanium phosphate for solid-state Li batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2018;8(16):1702374.
Han X, Gong Y, Fu KK, He X, Hitz GT, Dai J, Pearse A, Liu B, Wang H, Rubloff G, Mo Y, Thangadurai V, Wachsman ED, Hu L. Negating interfacial impedance in garnet-based solid-state Li metal batteries. Nat Mater. 2017;16(5):572.
Li Y, Xu B, Xu H, Duan H, Lu X, Xin S, Zhou W, Xue L, Fu G, Manthiram A, Goodenough JB. Hybrid polymer/garnet electrolyte with a small interfacial resistance for lithium-ion batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017;56(3):753.
Han SY, Lewis JA, Shetty PP, Tippens J, Yeh D, Marchese TS, McDowell MT. Porous metals from chemical dealloying for solid-state battery anodes. Chem Mater. 2020;32(6):2461.
Yang C, Xie H, Ping W, Fu K, Liu B, Rao J, Dai J, Wang C, Pastel G, Hu L. An electron/ion dual-conductive alloy framework for high-rate and high-capacity solid-state lithium-metal batteries. Adv Mater. 2019;31(3):e1804815.
Huang Y, Shao B, Han F. Li alloy anodes for high-rate and high-areal-capacity solid-state batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2022;10(23):12350.
Luo W, Gong Y, Zhu Y, Fu KK, Dai J, Lacey SD, Wang C, Liu B, Han X, Mo Y, Wachsman ED, Hu L. Transition from superlithiophobicity to superlithiophilicity of garnet solid-state electrolyte. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(37):12258.
Du Y, Liu Y, Yang S, Li C, Cheng Z, Qiu F, He P, Zhou H. A rechargeable all-solid-state Li–CO2 battery using a Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 ceramic electrolyte and nanoscale RuO2 catalyst. J Mater Chem A. 2021;9(15):9581.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, YJ., Fang, RY. & Mitlin, D. NASICON solid electrolyte coated by indium film for all-solid-state Li-metal batteries. Tungsten 4, 316–322 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-022-00183-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-022-00183-0