Abstract
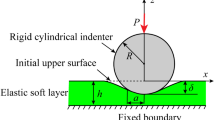
The mechanical properties of biological materials are commonly found through the application of Hertzian theory to force-displacement data obtained through micro-indentation techniques. Due to their soft nature, biological specimens are often subjected to large indentations, resulting in a nonlinear deformation behavior that can no longer be accurately described by Hertzian contact. Useful models for studying the large deformation response of cylindrical specimens under indentation are not readily available, and the morphologies of biological materials are often closer to cylinders than spheres (e.g., cellular processes, fibrin, collagen fibrils, etc.). In this study, a computational model is used to analyze the large deformation indentation of an incompressible hyperelastic cylinder in order to provide a generalized formulation that can be used to extract mechanical properties from indentation into soft cylindrical bodies. The effects of specimen size and indentation depth are examined in order to quantify the deformation at which the proposed force-displacement relationship remains accurate.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lutolf, M.P., Gilbert, P.M., Blau, H.M.: Designing materials to direct stem-cell fate. Nature 462(7272), 433 (2009)
Ethier, C.R., Simmons, C.A.: Introductory Biomechanics: From Cells to Organisms. Cambridge University Press (2007)
Suresh, S., Spatz, J., Mills, J., Micoulet, A., Dao, M., Lim, C., Beil, M., Seufferlein, T.: Connections between single-cell biomechanics and human disease states: gastrointestinal cancer and malaria. Acta biomaterialia 1(1), 15 (2005)
Moeendarbary, E., Weber, I.P., Sheridan, G.K., Koser, D.E., Soleman, S., Haenzi, B., Bradbury, E.J., Fawcett, J., Franze, K.: The soft mechanical signature of glial scars in the central nervous system. Nat. Commun. 8, 14787 (2017)
Suresh, S.: Biomechanics and biophysics of cancer cells. Acta Mater. 55(12), 3989 (2007)
Darling, E.M., Di Carlo, D.: High-throughput assessment of cellular mechanical properties. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 17, 35 (2015)
Zahalak, G., McConnaughey, W., Elson, E.: Determination of cellular mechanical properties by cell poking, with an application to leukocytes. J. Biomech. Eng. 112(3), 283 (1990)
Zahalak, G.I., Wagenseil, J.E., Wakatsuki, T., Elson, E.L.: A cell-based constitutive relation for bio-artificial tissues. Biophys. J. 79(5), 2369 (2000)
Heidemann, S.R., Wirtz, D.: Towards a regional approach to cell mechanics. Trends Cell Biol. 14(4), 160 (2004)
Petersen, N.O., McConnaughey, W.B., Elson, E.L.: Dependence of locally measured cellular deformability on position on the cell, temperature, and cytochalasin b. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 79(17), 5327 (1982)
Binnig, G., Quate, C.F., Gerber, C.: Atomic force microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 56(9), 930 (1986)
McConnaughey, W.B., Petersen, N.O.: An apparatus for stress-strain measurements on living cells. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 51(5), 575 (1980)
Radmacher, M., Tillamnn, R., Fritz, M., Gaub, H.: From molecules to cells: imaging soft samples with the atomic force microscope. Science 257(5078), 1900 (1992)
Hoh, J.H., Schoenenberger, C.A: Surface morphology and mechanical properties of mdck monolayers by atomic force microscopy. J. Cell Sci. 107(5), 1105 (1994)
Vinckier, A., Semenza, G.: Measuring elasticity of biological materials by atomic force microscopy. FEBS Lett. 430(1-2), 12 (1998)
Azeloglu, E.U., Costa, K.D.: Atomic force microscopy in mechanobiology: measuring microelastic heterogeneity of living cells. Atomic Force Microscopy in Biomedical Research, pp. 303–329. Springer (2011)
Lim, C., Zhou, E., Quek, S.: Mechanical models for living cells: a review. J. Biomech. 39(2), 195 (2006)
Sen, S., Subramanian, S., Discher, D.E.: Indentation and adhesive probing of a cell membrane with AFM. Biophys. J. 89(5), 3203 (2005)
Digiuni, S., Berne-Dedieu, A., Martinez-Torres, C., Szecsi, J., Bendahmane, M., Arneodo, A., Argoul, F.: Single cell wall nonlinear mechanics revealed by a multiscale analysis of AFM forceindentation curves. Biophys. J. 108(9), 2235 (2015)
Humphrey, J.D.: Continuum biomechanics of soft biological tissues. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, vol. 459, pp. 3–46. The Royal Society (2003)
Mow, V.C., Guilak, F., Tran-Son-Tay, R., Hochmuth, R.M.: Cell mechanics and cellular engineering. Springer Science & Business Media (2012)
Levental, I., Georges, P.C., Janmey, P.A.: Soft biological materials and their impact on cell function. Soft Matter 3(3), 299 (2007)
Hertz, H.: On the contact of solid elastic bodies and on hardness. J. Math 92, 156 (1881)
Johnson, K.L.: Contact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press (1987)
Williams, J.A., Dwyer-Joyce, R.S.: Contact between solid surfaces. Modern Tribol. Handbook 1, 121 (2001)
Liu, D., Zhang, Z., Sun, L.: Nonlinear elastic load-displacement relation for spherical indentation on rubberlike materials. J. Mater. Res. 25(11), 2197 (2010)
Lin, D.C., Shreiber, D.I., Dimitriadis, E.K., Horkay, F.: Spherical indentation of soft matter beyond the hertzian regime: numerical and experimental validation of hyperelastic models. Biomech. Modeling Mechanobiol. 8 (5), 345 (2009)
Giannakopoulos, A., Triantafyllou, A: Spherical indentation of incompressible rubber-like materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55(6), 1196 (2007)
Zhang, M.G., Cao, Y.P., Li, G.Y., Feng, X.Q.: Spherical indentation method for determining the constitutive parameters of hyperelastic soft materials. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 13(1), 1 (2014)
Ding, Y., Xu, G.K., Wang, G.F.: On the determination of elastic moduli of cells by AFM based indentation. Sci. Rep. 7, 45575 (2017)
Bernick, K.B., Prevost, T.P., Suresh, S., Socrate, S.: Biomechanics of single cortical neurons. Acta biomaterialia 7(3), 1210 (2011)
Kang, I., Panneerselvam, D., Panoskaltsis, V.P., Eppell, S.J., Marchant, R.E., Doerschuk, C.M.: Changes in the hyperelastic properties of endothelial cells induced by tumor necrosis factor-α. Biophys. J. 94(8), 3273 (2008)
Mahaffy, R., Shih, C., MacKintosh, F., Käs, J.: Scanning probe-based frequency-dependent microrheology of polymer gels and biological cells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(4), 880 (2000)
Guz, N., Dokukin, M., Kalaparthi, V., Sokolov, I.: If cell mechanics can be described by elastic modulus: study of different models and probes used in indentation experiments. Biophys. J. 107(3), 564 (2014)
Sokolov, I., Iyer, S., Woodworth, C.D.: Recovery of elasticity of aged human epithelial cells in vitro. Nanomed.: Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2(1), 31 (2006)
Codan, B., Del Favero, G., Martinelli, V., Long, C., Mestroni, L., Sbaizero, O.: Exploring the elasticity and adhesion behavior of cardiac fibroblasts by atomic force microscopy indentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 40, 427 (2014)
Berdyyeva, T.K., Woodworth, C.D., Sokolov, I.: Human epithelial cells increase their rigidity with ageing in vitro: direct measurements. Phys. Med. Biol. 50(1), 81 (2004)
Park, S., Koch, D., Cardenas, R., Käs, J., Shih, C.K.: Cell motility and local viscoelasticity of fibroblasts. Biophys. J. 89(6), 4330 (2005)
Sokolov, I., Dokukin, M.E., Guz, N.V.: Method for quantitative measurements of the elastic modulus of biological cells in AFM indentation experiments. Methods 60(2), 202 (2013)
Magdesian, M.H., Sanchez, F.S., Lopez, M., Thostrup, P., Durisic, N., Belkaid, W., Liazoghli, D., Grütter, P., Colman, D.R.: Atomic force microscopy reveals important differences in axonal resistance to injury. Biophys. J. 103(3), 405 (2012)
Charras, G.T., Horton, M.A.: Single cell mechanotransduction and its modulation analyzed by atomic force microscope indentation. Biophys. J. 82(6), 2970 (2002)
Brewe, D.E., Hamrock, B.J.: Elastic compression of spheres and cylinders at point and line contact. J. Lubr. Technol. 99(4), 485 (1977)
Hamrock, B.J., Brewe, D.: Simplified solution for stresses and deformations. J. Lubricat. Technol. 105(2), 171 (1983)
Puttock, M., Thwaite, E.: Elastic Compression of Spheres and Cylinders at Point and Line Contact. Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization, Melbourne Australia (1969)
Horgan, C.O., Smayda, M.G.: The importance of the second strain invariant in the constitutive modeling of elastomers and soft biomaterials. Mech. Mater. 51, 43 (2012)
Mahaffy, R., Park, S., Gerde, E., Käs, J., Shih, C.: Quantitative analysis of the viscoelastic properties of thin regions of fibroblasts using atomic force microscopy. Biophys. J. 86(3), 1777 (2004)
Dimitriadis, E.K., Horkay, F., Maresca, J., Kachar, B., Chadwick, R.S.: Determination of elastic moduli of thin layers of soft material using the atomic force microscope. Biophys. J. 82(5), 2798 (2002)
Chadwick, R.S.: Axisymmetric indentation of a thin incompressible elastic layer. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 62(5), 1520 (2002)
Pereira, C.M., Ramalho, A.L., Ambrósio, J.A.: A critical overview of internal and external cylinder contact force models. Nonlin. Dyn. 63(4), 681 (2011)
Moeendarbary, E., Valon, L., Fritzsche, M., Harris, A.R., Moulding, D.A., Thrasher, A.J., Stride, E., Mahadevan, L., Charras, G.T.: The cytoplasm of living cells behaves as a poroelastic material. Nat. Mater. 12(3), 253 (2013)
Pan, Y., Zhan, Y., Ji, H., Niu, X., Zhong, Z.: Can hyperelastic material parameters be uniquely determined from indentation experiments? RSC Adv. 6(85), 81958 (2016)
Cartagena, A., Raman, A.: Local viscoelastic properties of live cells investigated using dynamic and quasi-static atomic force microscopy methods. Biophys. J. 106(5), 1033 (2014)
Andriotis, O.G., Manuyakorn, W., Zekonyte, J., Katsamenis, O.L., Fabri, S., Howarth, P.H., Davies, D.E., Thurner, P.J.: Nanomechanical assessment of human and murine collagen fibrils via atomic force microscopy cantilever-based nanoindentation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 39, 9 (2014)
Funding
This work was funded by the DoD SMART Scholarship Program and the US Army Research Lab (Aberdeen Proving Ground, MD), under Cooperative Agreement Number W911NF-12-2-0022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Disclaimer
The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official policies, either expressed or implied, of the Army Research Laboratory or the US Government. The US Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Government purposes notwithstanding any copyright notation herein.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dagro, A.M., Ramesh, K.T. Nonlinear contact mechanics for the indentation of hyperelastic cylindrical bodies. Mech Soft Mater 1, 7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42558-019-0006-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42558-019-0006-0