Abstract
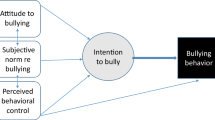
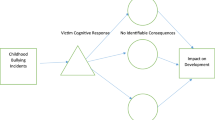
To understand the underlying cognitive processes of youth involved in bullying has been of interest in bullying literature. The mechanisms of moral disengagement have gained considerable attention in research as an underlying motive for why youth engage in bullying behaviors. The current study focused on developing a new moral disengagement measure that would incorporate the eight mechanisms of moral disengagement with bullying behaviors. The current study investigated the new measure’s psychometric properties. Factor analyses of the data resulted in a single-factor 14-item measure with evidence of good fit. Further evidence of reliability and validity for the test score interpretation was provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, RJ, upon reasonable request.
References
Allison, K. R., & Bussey, K. (2017). Individual and collective moral influences on intervention in cyberbullying. Computers in Human Behavior, 74, 7–15.
Almeida, A., Correia, I., & Marinho, S. (2009). Moral disengagement, normative beliefs of peer group, and attitudes regarding roles in bullying. Journal of School Violence, 9(1), 23–36.
Atlas, R. S., & Pepler, D. J. (1998). Observations of bullying in the classroom. Journal of Educational Research, 92, 78–82.
Bandura, A. (1989). Human agency in social cognitive theory. American Psychologist, 44(9), 1175.
Bandura, A. (2002). Selective moral disengagement in the exercise of moral agency. Journal of Moral Education, 31(2), 101–119.
Bandura, A., Barbaranelli, C., Caprara, G. V., & Pastorelli, C. (1996). Mechanisms of moral disengagement in the exercise of moral agency. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 71(2), 364–374.
Barchia, K., & Bussey, K. (2010). The psychological impact of peer victimization: Exploring social-cognitive mediators of depression. Journal of Adolescence, 33(5), 615–623.
Bartlett, M. S. (1954). A note on multiplying factors for various chi-squared approximations. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 16, 296–298.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107(2), 238–246.
Brown, C. (2014). High school cyberbullying and cyber victimization: Measurement, grade and gender differences, overlap with traditional bullying and victimization, and social emotional outcomes (Publication No. 3624767) [Doctoral dissertation, Northern Illinois University]. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing.
Brown, C. F., Demaray, M. K., & Secord, S. M. (2014). Cyber victimization in middle school and relations to social emotional outcomes. Computers in Human Behavior, 35, 12–21.
Bussey, K., Fitzpatrick, S., & Raman, A. (2015). The role of moral disengagement and self-efficacy in cyberbullying. Journal of School Violence, 14(1), 30–46.
Caravita, S. C., Gini, G., & Pozzoli, T. (2012). Main and moderated effects of moral cognition and status on bullying and defending. Aggressive Behavior, 38(6), 456–468.
Child, D. (2006). The essentials of factor analysis (3rd ed.). Continuum.
Curran, P. J., West, S. G., & Finch, J. F. (1996). The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychological Methods, 1(1), 16–29.
Day, S., & Lazuras, L. (2016). The Cyberbullying-Specific Moral Disengagement Questionnaire (CBMDQ-15).
DeVellis, R. F. (2003). Scale development: Theory and applications (2nd ed.). Sage Publications.
Eid, M., Gollwitzer, M., & Schmitt, M. (2011). Statistik und Forschungsmethoden Lehrbuch. Beltz.
Evans, C., & Smokowski, P. (2016). Understanding weaknesses in bullying research: How school personnel can help strengthen bullying research and practice. Children and Youth Services Review. 69.
Gini, G., Pozzoli, T., & Hymel, S. (2014). Moral disengagement among children and youth: A meta-analytic review of links to aggressive behavior. Aggressive Behavior, 40(1), 56–68.
Gladden, R., Vivolo-Kantor, A., Hamburger, M., & Lumpkin, C. (2014). Bullying surveillance among youths: Uniform definitions for public health and recommended data elements, Version 1.0.
Haddock, A. D., & Jimerson, S. R. (2017). An examination of differences in moral disengagement and empathy among bullying participant groups. Journal of Relationships Research, 8, 1–15.
Horn, J. L. (1965). A rationale and test for the number of factors in factor analysis. Psychometrika, 30, 179–185.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. A. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6, 1–55.
Hymel, S., Rocke-Henderson, N., & Bonanno, R. A. (2005). Moral disengagement: A framework for understanding bullying among adolescents. Journal of Social Sciences, 8(1), 1–11.
Kaiser, H. F. (1974). An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika, 39, 31–36.
Lo Cricchio, M. G., García-Poole, C., Te Brinke, L. W., Bianchi, D., & Menesini, E. (2021). Moral disengagement and cyberbullying involvement: A systematic review. The European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 18, 271–311.
Modecki, K. L., Minchin, J., Harbaugh, A. G., Guerra, N. G., & Runions, K. C. (2014). Bullying prevalence across contexts: A meta-analysis measuring cyber and traditional bullying. Journal of Adolescent Health, 55(5), 602–611.
Morris, R. G., & Copes, H. (2012). Exploring the temporal dynamics of the neutralization/delinquency relationship. Criminal Justice Review, 37, 442–460.
Newton, N., & Bussey, K. (2012). The age of reason: An examination of psychosocial factors involved in criminal decision making. Legal and Criminological Psychology, 17, 75–88.
Nunnally, J. C., & Bernstein, I. H. (1994). Psychometric theory (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
Obermann, M.-L. (2011). Moral disengagement in self-reported and peer-nominated school bullying. Aggressive Behavior, 37, 133–144.
Paciello, M., Ballarotto, G., Cerniglia, L., & Muratori, P. (2020). Does the interplay of callous-unemotional traits and moral disengagement underpin disruptive behavior? A systematic review. Adolescent Health, Medicine and Therapeutics, 11, 9–20.
Paciello, M., Fida, R., Tramontano, C., Lupinetti, C., & Caprara, G. V. (2008). Stability and change of moral disengagement and its impact on aggression and violence in late adolescence. Child Development, 79(5), 1288–1309.
Pelton, J., Gound, M., Forehand, R., & Brody, G. (2004). The moral disengagement scale: Extension with an American minority sample. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 26(1), 31–39.
Pornari, C. D., & Wood, J. (2010). Peer and cyber aggression in secondary school students: The role of moral disengagement, hostile attribution bias, and outcome expectancies. Aggressive Behavior, 36(2), 81–94.
Pozzoli, T., Gini, G., & Vieno, A. (2012). Individual and class moral disengagement in bullying among elementary school children. Aggressive Behavior, 38(5), 378–388.
R Core Team (2021). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/.
Raboteg-Šarić, Z., & Bartaković, S. (2019). Empathy and moral disengagement as predictors of bystander roles in school bullying. Central European Journal of Paediatrics, 15(2), 161–176.
Ribeaud, D., & Eisner, M. (2010). Are moral disengagement, neutralization techniques, and self-serving cognitive distortions the same? Developing a unified scale of moral neutralization of aggression. International Journal of Conflict and Violence, 4, 298–315.
Romera, E. M., Herrera-López, M., Ortega-Ruiz, R., & Camacho, A. (2023). The moral disengagement scale-24: Factorial structure and cross-cultural comparison in Spanish and Colombian adolescents. Psychology of Violence, 13(1), 13–22.
Rubio-Garay, F., Amor, P. J., & Carrasco, M. A. (2017). Dimensionality and psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the Mechanisms of Moral Disengagement Scale (MMDS-S). Revista de Psicopatología y Psicología Clínica, 22(1).
Schmitt, T. A., & Sass, D. A. (2011). Rotation criteria and hypothesis testing for exploratory factor analysis: Implications for factor pattern loadings and interfactor correlations. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 71(1), 95–113.
Steiger, J.H., & Lind, J.C. (1980). Statistically based tests for the number of common factors. Psychometric Society.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using Multivariate Statistics (5th ed.). New York: Allyn and Bacon.
Tay, L., & Jebb, A. (2017). Scale development. In S. Rogelberg (ed.), The SAGE Encyclopedia of Industrial and Organizational Psychology (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Thornberg, R., & Jungert, T. (2013). Bystander behavior in bullying situations: Basic moral sensitivity, moral disengagement and defender self-efficacy. Journal of Adolescence, 36, 475–483.
Thornberg, R., & Jungert, T. (2014). School bullying and the mechanisms of moral disengagement. Aggressive Behavior, 40, 99–108.
Thornberg, R., Wänström, L., Pozzoli, T., & Hong, J. S. (2019). Moral disengagement and school bullying perpetration in middle childhood: A short-term longitudinal study in Sweden. Journal of School Violence, 18(4), 585–596.
Wolke, D., Copeland, W. E., Angold, A., & Costello, E. J. (2013). Impact of bullying in childhood on adult health, wealth, crime, and social outcomes. Psychological Science, 24(10), 1958–1970.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have participated sufficiently in the conception and design of this work or the analysis and interpretation of the data, as well as the writing of the manuscript, to take public responsibility for it. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
All participating individuals were given information on the study procedures and terms of consent prior to participating in the study. The current study followed the American Psychology Association (APA)’s Ethics Code as the standard for conducting research.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, R., Demaray, M.K. & Styck, K.M. Development of the Moral Disengagement Bullying Behavior Scale. Int Journal of Bullying Prevention (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42380-023-00206-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42380-023-00206-5