Abstract
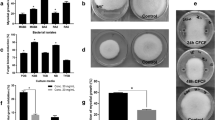
A set of 41 fluorescent pseudomonads isolates was isolated from 290 rhizosphere soil samples collected from six North East states of India with different agroclimatic zones. Differentiations of fluorescent Pseudomonas into different groups was made based on phenotypic characters. Among a subset of 28 isolates, 21 were grouped as Pseudomonas fluorescens Biovar I, 3 as Biovar II, 3 as Biovar III and 1 as Biovar V. The isolates Pf 8, Pf4 and Pf 39 belonging to Biovar I and II showed highest antagonistic potential against Ralstonia solanacearum with 86%, 68% and 64% growth suppression respectively in in vitro modified filter paper disc assay. Further, BLAST analyses of 16S rDNA sequences of representative seven isolates from six states revealed 94–99% similarity with Pseudomonas sp. In addition, three best isolates were used to prepare three substrate based bioformulation to perform an in Planta study. The in Planta study revealed among the tested bioformulations, Pf39-based bioformulation exhibited lowest wilt incidence in tomato and chilli plants. A negative correlation between population densities of R. solanacearum and Pseudomonas spp. as well as between Pseudomonas and percent wilt incidence was observed. Based on these observations Pf39 was found to be the most effective biocontrol agent against R. solanacearum under the experimental conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The 16S rDNA sequences of the Pseudomonas isolates were submitted to GeneBank database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) and the accession numbers obtained are given in the Supplementary file (Table S6).
References
Acea M, Moore C, Alexander M (1988) Survival and growth of bacteria introduced into soil. Soil Biol Biochem 20:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(88)90066-1
Ahemad M, Kibret M (2014) Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: current perspective. J King Saud Univ Sci 26:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JKSUS.2013.05.001
Al-Fadhal FA, Al-Abedy AN, Alkhafije DA (2019) Isolation and molecular identification of Rhizoctonia solani and Fusarium solani isolated from cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) and their control feasibility by Pseudomonas fluorescens and Bacillus subtilis. Egypt J Biol Pest Control 29:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-019-0145-5
Anuratha CS, Gnanamanickam SS (1990) Biological control of bacterial wilt caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum in India with antagonistic bacteria. Plant Soil 124:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010938
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal 6:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2015.11.005
Beneduzi A, Ambrosini A, Passaglia LMP (2012) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): their potential as antagonists and biocontrol agents. Genet Mol Biol 35:1044–1051
Bora LC, Deka SN (2007) Wilt disease suppression and yield enhancement in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) by application of Pseudomonas fluorescens-based biopesticide (Biofor -Pf) in Assam. Indian J Agric Sci 77:490–494
Bora L, Kataki L, Talukdar K et al (2015) Molecular characterizations of microbial antagonists and development of bioformulations for management of bacterial wilt of Naga Chilli (Capsicum chinensJacq.) in Assam. J Exp Biol Agric Sci. https://doi.org/10.18006/jebas.030201
Bossis E, Lemanceau P, Latour X et al (2000) The taxonomy of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Pseudomonas putida : current status and need for revision. Agronomic 20:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2000112
Breed R, Murray EG, Smith N (1957) Bergey’s manual of determintive bacteriology, 9th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity G (2005) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. In: The Proteobacteria, vol 2. Springer, NY
Chakravarty G, Kalita MC (2012) Biocontrol potential of pseudomonas fluorescens against bacterial wilt of Brinjal and its possible plant growth promoting. Eff Ann Biol Res 3:5083–5094
Cirvilleri G, Catara V, Bella P, Marchese E (1999) Isolation and characterization of rhizosphere bacteria of potential interest for biological control of soil borne pathogens. Phytophag Palermo 9:79–87
Costa R, Gomes NCM, Peixoto RS et al (2006) Diversity and antagonistic potential of Pseudomonas spp. associated to the rhizosphere of maize grown in a subtropical organic farm. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2434–2447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.03.003
Das M, Bora L (2000) Biological control of bacterial wilt of tomato caused by Ralstonia solanacearum. J Agric Sci Soc North East India 13:52–55
de Souza R, Ambrosini A, Passaglia LMP (2015) Plant growth-promoting bacteria as inoculants in agricultural soils. Genet Mol Biol 38:401–419. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-475738420150053
Dube HC (2001) Rhizobacteria in biological control and plant growth promotion. J Mycol Plant Pathol 31:9–21
Fatima J, Goswami G, Bora S et al (2018) “ Doi ”, a naturally fermented milk product of Assam contains indigenous Lactobacillus spp. with probiotic attributes. Res J Biotechnol 13:1–15
Ganeshan G, Kumar AM (2005) Pseudomonas fluorescens, a potential bacterial antagonist to control plant diseases. J Plant Interact 1:123–134
Gopalakrishnan S, Sathya A, Vijayabharathi R et al (2015) Plant growth promoting rhizobia: challenges and opportunities. 3 Biotech 5:355–377
Goswami G, Bora SSS, Parveen A et al (2017a) Identification and functional properties of dominant lactic acid bacteria isolated from Kahudi, a traditional rapeseed fermented food product of Assam, India. J Ethn Foods 4:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jef.2017.08.008
Goswami G, Deka P, Das P et al (2017b) Diversity and functional properties of acid-tolerant bacteria isolated from tea plantation soil of Assam. 3 Biotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0864-9
Haas D, Défago G (2005) Biological control of soil-borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:307–319
Hassanein W, Amara U, Khalid R, Salahel D (2009) The antagonistic activities of some metabolites produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Sh8. J Appl Sci Res 5:404–414
Hayat R, Ali S, Amara U et al (2010) Soil beneficial bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion: a review. Ann Microbiol 60:579–598
Jakobek JL, Lindgren PB (1993) Generalized induction of defense responses in bean is not correlated with the induction of the hypersensitive reaction. Plant Cell 5:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.5.1.49
Kabdwal BC, Sharma R, Tewari R et al (2019) Field efficacy of different combinations of Trichoderma harzianum, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus against the major diseases of tomato in Uttarakhand (India). Egypt J Biol Pest Control 29:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-018-0103-7
Karuna K, Khan ANA (1994) Biological control of wilt of tomato caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum using antagonistic bacteria. Indian Phytopathol 54:12–15
Kataky M, Tamuli A, Teron R (2016) Efficacy of biocontrol agents in controlling bacterial wilt on naga king chilli (Capsicum chinense Jacq.). Int J Appl Pure Sci 02:2394–5532
Khan MR, Siddiqui ZA (2019) Potential of Pseudomonas putida, Bacillus subtilis, and their mixture on the management of Meloidogyne incognita, Pectobacterium betavasculorum, and Rhizoctonia solani disease complex of beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.). Egypt J Biol Pest Control 29:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-019-0174-0
King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE (1954) Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med 44:301–307
Kipgen TL, Majumdar D, Tyagi W et al (2016) Characterization of fluorescent Pseudomonads from maize and rice rhizosphere of Meghalaya and screened for their antagonistic ability against Ralstonia solanacearum. Bioscan 11:699–704
Kuarabachew H, Assefa F, Hiskias Y (2007) Evaluation of Ethiopian isolates of Pseudomonas fluorescens as biocontrol agent against potato bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia (Pseudomonas) solanacearum. Acta Agric Slov 902:125–135
Lorck H (1948) Production of hydrocyanic acid by bacteria. Physiol Plant 1:142–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1948.tb07118.x
Lottmann J, Berg G (2001) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of antagonistic bacteria associated with roots of transgenic and non-transgenic potato plants. Microbiol Res 156:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1078/0944-5013-00086
Louws FJ, Fulbright DW, Stephens CT, de Bruijn FJ (1994) Specific genomic fingerprints of phytopathogenic Xanthomonas and Pseudomonas pathovars and strains generated with repetitive sequences and PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2286–2295
Lucy M, Reed E, R. Glick B, (2004) Applications of free living plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 86:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ANTO.0000024903.10757.6e
Maroniche GA, Rubio EJ, Consiglio A, Perticari A (2016) Plant-associated fluorescent Pseudomonas from red lateritic soil: beneficial characteristics and their impact on lettuce growth. J Gen Appl Microbiol 257:248–257. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.2016.04.006
McSpadden Gardener BB, Schroeder KL, Kalloger SE et al (2000) Genotypic and phenotypic diversity of phlD-containing Pseudomonas strains isolated from the rhizosphere of wheat. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1939–1946
Moazezikho A, Charehgani H, Abdollahi M, Rezaei R (2020) Evidence of inhibitory effect of Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0 and aqueous extracts on tomato plants infected with Meloidogyne javanica (Tylenchida: Heteroderidae). Egypt J Biol Pest Control 30:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-020-00217-0
Naik MK, Rani GSD (2008) Advances in soil borne plant diseases. New India Publishing Agency, New Delhi
Naik PR, Raman G, Narayanan KB, Sakthivel N (2008) Assessment of genetic and functional diversity of phosphate solubilizing fluorescent pseudomonads isolated from rhizospheric soil. BMC Microbiol 8:230. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-8-230
O’Sullivan DJ, O’Gara F (1992) Traits of fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. involved in suppression of plant root pathogens. Microbiol Rev 56:662–676
Palleroni NJ (1994) Pseudomonas classification. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 64:231–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00873084
Payne SM (1994) Detection, isolation, and characterization of siderophores. Methods Enzymol 235:329–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(94)35151-1
Pieterse CMJ, Zamioudis C, Berendsen RL et al (2014) Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 52:347–375. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102340
Raaijmakers JM, Vlami M, de Souza JT (2002) Antibiotic production by bacterial biocontrol agents. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81:537–547
Rai A, Nabti E (2017) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: importance in vegetable production. In: Zaidi A, Khan M (eds) Microbial strategies for vegetable production. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54401-4_2
Rainey PB, Bailey MJ, Thompson IP (1994) Phenotypic and genotypic diversity of fluorescent pseudomonads isolated from field-grown sugar beet. Microbiology (Reading). 140(Pt 9):2315–2331. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-140-9-2315
Rajwar A, Sahgal M (2016) Phylogenetic relationships of fluorescent pseudomonads deduced from the sequence analysis of 16S rRNA. Pseudomonas-specific and rpoD genes. 3 Biotech 6:80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0386-x
Ramamoorthy V, Viswanathan R, Raguchander T et al (2001) Induction of systemic resistance by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in crop plants against pests and diseases. Crop Prot 20:1–11
Ramos-Solano B, García JAL, Garcia-Villaraco A et al (2010) Siderophore and chitinase producing isolates from the rhizosphere of Nicotiana glauca Graham enhance growth and induce systemic resistance in Solanum lycopersicum L. Plant Soil 334:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0371-9
Rathore R, Vakharia DN, Rathore DS (2020) In vitro screening of different Pseudomonas fluorescens isolates to study lytic enzyme production and growth inhibition during antagonism of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cumini, wilt causing pathogen of cumin. Egypt J Biol Pest Control 30:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-020-00259-4
Reddy P, Rao K (2009) Biological and PCR-RAPD characterization of Pseudomonas fluorescens produced antifungal compounds inhibit the rice fungal pathogens in vitro. EJEAF Chem 8:1062–1067
Santoro MV, Bogino PC, Nocelli N et al (2016) Analysis of plant growth-promoting effects of fluorescent pseudomonas strains isolated from Mentha piperita rhizosphere and effects of their volatile organic compounds on essential oil composition. Front Microbiol 7:1085. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01085
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9
Singh N, Phukan T, Sharma PL et al (2018) An innovative root inoculation method to study Ralstonia solanacearum Pathogenicity in Tomato Seedlings. Phytopathology 108:436–442. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-08-17-0291-R
Soni R, Kapoor R, Kaur M (2016) Evaluation of Siderophore production and antimicrobial activity by fluorescent pseudomonas diversity associated with Rhizosphere of Apple and Pear. Int J Agric Environ Biotechnol Cit. https://doi.org/10.5958/2230-732X.2016.00140.6
Srivastava R, Khalid A, Singh US, Sharma AK (2010) Evaluation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, fluorescent Pseudomonas and Trichoderma harzianum formulation against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici for the management of tomato wilt. Biol Control 53:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2009.11.012
Thakuria D, Talukdar NC, Goswami C et al (2004) Characterization and screening of bacteria from rhizosphere of rice grown in acidic soils of Assam. Curr Sci 86:978–985
van Peer R, Niemann G, Schippers B (1991) Induced resistance and phytoalexin accumulation in biological control of Fusarium wilt of carnation by Pseudomonas sp. strain WCS417r. Phytopathology 91:728–734
Vidhyasekaran P, Muthamilan M (1995) Development of formulations of Pseudomonas fluorescens for control of chickpea wilt. Plant Dis 79:782–786. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-79-0782
Weller DM (1988) Biological control of soilborne plant pathogens in the rhizosphere with bacteria. Annu Rev Phytopathol 26:379–407. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.26.090188.002115
Weller DM, Cook RJ (1983) Suppression of take-all of wheat by seed treatments with fluorescent pseudomonads. Phytopathology 73:463–469
Zheng J, Sutton JC, Yu H (2000) Interactions among Pythium aphanidermatum, roots, root mucilage, and microbial agents in hydroponic cucumbers. Can J Plant Pathol 22:368–379. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060660009500455
Acknowledgements
The first author received Moulana Azad National Fellowship for Minority Students under University Grant Commission (UGC), India. The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions that help improve the manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TLK and LCB: conceived the idea; TLK, LCB, PKB, MB, KCP: study design, supervision of experiments and revising the draft manuscript; TLK: sample collection, Isolation and screening of the isolates, pot experiment; GG and TLK: molecular characterization, writing the draft manuscript. All the authors have read the manuscript and agreed to submit in this journal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors have given their consent to publish this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kipgen, T.L., Bora, L.C., Goswami, G. et al. Isolation and characterization of fluorescent Pseudomonas with bio-control potential against Ralstonia solanacearum. Indian Phytopathology 74, 1055–1064 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-021-00400-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-021-00400-9