Abstract
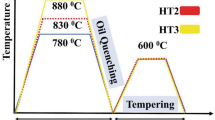
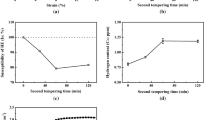
The effect of tempering on carbides and hydrogen embrittlement in E690 high strength marine structural steel has been investigated. The steel was tempered at 600 °C for 1–3 h. Detailed characterization was carried out to characterize the microstructure, especially the dislocation density and grain size. The hydrogen permeation test and thermal desorption spectroscopy test were also implemented. The dislocation density decreases, the amount of carbide increases, and carbides (M23C6 and MX) coarsen with the tempering time increasing. After tempered at 600 °C for 3 h, the diffusible hydrogen trapped by lattice and dislocation decreases while the non-diffusible hydrogen trapped by carbides increases, leading to the best hydrogen embrittlement resistance, although hydrogen diffuses rapidly due to the reduction of dislocation density. And the fracture mode changes from a combination of brittle cleavage and ductile dimpled fracture to fully ductile dimple fracture under hydrogen charging condition. Moreover, a phenomenon that hydrogen accelerates the dislocations movement of the steel during deformation was observed, which is related to the fact that hydrogen enhanced localized plasticity mechanism.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.C. Ma, Z.Y. Liu, C.W. Du, H.R. Wang, C.Y. Li, X.G. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 642 (2015) 22–31.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, ISIJ Int. 56 (2016) 24–36.
A. Nagao, C.D. Smith, M. Dadfarnia, P. Sofronis, I.M. Robertson, Acta Mater. 60 (2012) 5182–5189.
B.A. Szost, R.H. Vegter, P.E.J. Rivera-Díaz-Del-Castillo, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44 (2013) 4542–4550.
C. Park, N. Kang, M. Kim, S. Liu, Mater. Lett. 235 (2019) 193–196.
C. Park, N. Kang, S. Liu, Corro. Sci. 128 (2017) 33–41.
L. Li, B. Song, Z. Cai, Z. Liu, X. Cui, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 742 (2019) 712–721.
A. Nagao, K. Hayashi, K. Oi, S. Mitao, ISIJ Int. 52 (2012) 213–221.
H. Fuchigami, H. Minami, M. Nagumo, Phil. Mag. Lett. 86 (2006) 21–29.
E. Quadrini, Mater. Chem. Phys. 15 (1986) 155–165.
M. Nagumo, Met. Sci. Technol. 20 (2004) 940–950.
R.A. Oriani, Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 8 (1978) 327–357.
J.P. Hirth, Metall. Trans. A 11 (1980) 861–890.
H.K. Birnbaum, P. Sofronis, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 176 (1994) 191–202.
I.M. Robertson, H.K. Birnbaum, Acta Metall. 34 (1986) 353–366.
J. Von Pezold, L. Lymperakis, J. Neugebeauer, Acta Mater. 59 (2011) 2969–2980.
M. Maxelon, A. Pundt, W. Pyckhout-Hintzen, J. Barker, R. Kirchheim, Acta Mater. 49 (2001) 2625–2634.
K. Takai, H. Shoda, H. Suzuki, M. Nagumo, Acta Mater. 56 (2008) 5158–5167.
K. Sakaki, T. Kawase, M. Hirato, M. Mizuno, H. Araki, Y. Shirai, M. Nagumo, Scripta Mater. 55 (2006) 1031–1034.
P. Zhou, W. Li, X.J. Jin, J. Electrochem. Soc. 164 (2017) D394–D400.
X. Zhu, W. Li, H.S. Zhao, L. Wang, X.J. Jin, Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 39 (2014) 13031–13040.
M. Koyama, E. Akiyama, Y.K. Lee, D. Raabe, K. Tsuzaki, Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 42 (2017) 12706–12723.
P.W. Zhou, W. Li, H.S. Zhao, X.J. Jin, Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 43 (2018) 10905–10914.
Y. Li, W. Li, J.C. Hu, H.M. Song, X.J. Jin, Int. J. Plast. 88 (2017) 53–69.
Z.Y. Liang, X. Wang, W. Huang, M.X. Huang, Acta Mater. 88 (2015) 170–179.
R.A. Renzetti, H.R.Z. Sandim, R.E. Bolmaro, P.A. Suzuki, A. Möslang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 534 (2012) 142–146.
T. Ungár, A. Borbély, Appl. Phys. Lett. 69 (1996) 3173–3175.
G. Ribárik, T. Ungár, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528 (2010) 112–121.
T. Ungár, I. Dragomir, A. Borbély, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 32 (1999) 992–1002.
Y.T. Xu, Y.H. Nie, M. Wang, W. Li, X.J. Jin, Acta Mater. 131 (2017) 110–122.
W.Y. Choo, J.Y. Lee, Metall. Trans. A 13 (1982) 135–140.
D.F. Araújo, E.O. Vilar, J. Palma Carrasco, Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 39 (2014) 12194–12200.
E. Fallahmohammadi, F. Bolzoni, L. Lazzari, Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 38 (2013) 2531–2543.
R.A. Oriani, Fusion Technol. 26 (1994) 235–266.
Q.Q. Cui, J.S. Wu, D.H. Xie, X.G. Wu, Y.H. Huang, X.G. Li, Materials 10 (2017) 721.
J.X. Xu, C. Yu, H. Lu, Y. Wang, C.L. Luo, G.Y. Xu, J.P. Suo, J. Nucl. Mater. 516 (2019) 135–143.
R. Valentini, A. Solina, S. Matera, P. De Gregorio, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27 (1996) 3773–3780.
A. Drexler, T. Depover, K. Verbeken, W. Ecker, J. Alloy. Compd. 789 (2019) 647–657.
T. Yokota, T. Shiraga, ISIJ Int. 43 (2003) 534–538.
H.J. Seo, J.N. Kim, J.W. Jo, C.S. Lee, Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 46 (2021) 19670–19681.
A. Turk, Acta Mater. 194 (2020) 118–133.
T. Neeraj, R. Srinivasan, J. Li, Acta Mater. 60 (2012) 5160–5171.
P. Sofronis, J. Mech. Phys. Solid. 43 (1995) 1385–1407.
P.J. Ferreira, I.M. Robertson, H.K. Birnbaum. Mater. Sci. Forum. 207–209 (1996) 93–96.
Y.Z. Chen, Scripta Mater. 68 (2013) 743–746.
R. Kirchheim, Scripta Mater. 62 (2010) 67–70.
R. Kirchheim, Acta Mater. 55 (2007) 5129–5138.
R. Kirchheim, Acta Mater. 55 (2007) 5139–5148.
P. Novak, R. Yuan, B.P. Somerday, P. Sofronis, R.O. Ritchie, J. Mech. Phys. Solid. 58 (2010) 206–226.
M.L. Martin, I.M. Robertson, P. Sofronis, Acta Mater. 59 (2011) 3680–3687.
A. Nagao, M. Dadfarnia, B.P. Somerday, P. Sofronis, R.O. Ritchie, J. Mech. Phys. Solid. 112 (2018) 403–430.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the generous financial support from National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2016YFB0300601), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U1564203, 51831002 and 51571141). The authors also gratefully acknowledge the support sponsored by Program of Shanghai Academic Research Leader 18XD1402200 and provided by Shanghai Key Laboratory of Materials Laser Processing and Modification, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Besides, this research was supported by the TESCAN CHINA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Y., Li, W., Zhou, Pw. et al. Effect of tempering on carbides and hydrogen embrittlement in E690 high strength marine structural steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 29, 1669–1682 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00745-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00745-z