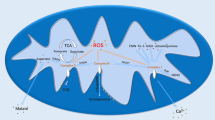
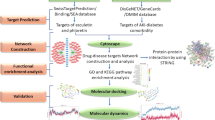
Abstract
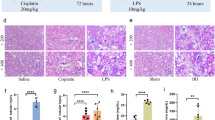
Sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI) is a leading cause of death among septic complications. Tao-Hong-Si-Wu decoction (TSD), a classical recipe from traditional Chinese medicine used for treating ischemic stroke, has been recently reported to alleviate inflammation and inflammation-stimulated injuries related to the pathology of ALI. Here, we first observed the therapeutic effect of TSD on sepsis-induced ALI. Based on integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology analysis (NPA) techniques, we aim to understand the mechanism of TSD alleviating ALI. TSD’s effects were observed in rats modeled by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) and rat macrophages stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Metabolomics analyses were applied to determine the ingredients in the medicine and key metabolites correlated to the NPA for the prediction of TSD targets. Gene and protein expressions of the key predicted targets were evaluated in the lung tissue and macrophages of septic model rat by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, respectively. TSD improved survival rate and protected against lung injury in CLP rats. Eleven endogenous metabolites were related to TSD’s actions. TSD significantly suppressed IL-6 and TNF-α secretions and their gene expressions both in the lung tissue of the model rats and in LPS-stimulated macrophages. TSD also restored decreased lung protein expression of VEGFA in septic model rats. Targeted proteins and their affecting metabolites were finally validated in an external test set of rats. This study shows that metabolomics coupled with NPA is a promising approach to explore potential targets of medicine with complex compositions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors state that all the data supporting the findings are contained within the article and supplementary material.
References
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, Kumar A, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Nunnally ME, Rochwerg B, Rubenfeld GD, Angus DC, Annane D, Beale RJ, Bellinghan GJ, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith C, De Backer DP, French CJ, Fujishima S, Gerlach H, Hidalgo JL, Hollenberg SM, Jones AE, Karnad DR, Kleinpell RM, Koh Y, Lisboa TC, Machado FR, Marini JJ, Marshall JC, Mazuski JE, McIntyre LA, McLean AS, Mehta S, Moreno RP, Myburgh J, Navalesi P, Nishida O, Osborn TM, Perner A, Plunkett CM, Ranieri M, Schorr CA, Seckel MA, Seymour CW, Shieh L, Shukri KA, Simpson SQ, Singer M, Thompson BT, Townsend SR, Van PT, Vincent JL, Wiersinga WJ, Zimmerman JL, Dellinger RP. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43:304–77.
Kempker JA, Martin GS. A global accounting of sepsis. Lancet. 2020;395:168–70.
Seymour CW, Gesten F, Prescott HC, Friedrich ME, Iwashyna TJ, Phillips GS, Lemeshow S, Osborn T, Terry KM, Levy MM. Time to treatment and mortality during mandated emergency care for sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:2235–44.
Klompas M, Calandra T, Singer M. Antibiotics for sepsis—finding the equilibrium. JAMA J Am Med Assoc. 2018;320:1433–4.
Dendoncker K, Libert C. Glucocorticoid resistance as a major drive in sepsis pathology. Cytokine Growth F R. 2017;35:85–96.
Halbach JL, Wang AW, Hawisher D, Cauvi DM, Lizardo RE, Rosas J, Reyes T, Escobedo O, Bickler SW, Coimbra R, De MA. Why antibiotic treatment is not enough for sepsis resolution: an evaluation in an experimental animal model. Infect Immun. 2017;85:e00664-e1617.
Fan TT, Cheng BL, Fang XM, Chen YC, Su F. Application of Chinese medicine in the management of critical conditions: a review on sepsis. Am J Chin Med. 2020;48:1315–30.
Li L, Yang N, Nin L, Zhao Z, Chen L, Yu J, Jiang Z, Zhong Z, Zeng D, Qi H, Xu X. Chinese herbal medicine formula Tao Hong Si Wu decoction protects against cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt and the Nrf2 signaling pathway. J Nat Med. 2015;69:76–85.
Ma Q, Li P-L, Hua Y-L, Ji P, Yao W-L, Zhang X-S, Zhong L-J, Wei Y-M. Effects of Tao-Hong-Si-Wu decoction on acute blood stasis in rats based on a LC-Q/TOF-MS metabolomics and network approach. Biomed Chrom. 2018;32:e4144.
Yuan G, Han A, Wu J, Lu Y, Zhang D, Sun Y, Zhang J, Zhao M, Zhang B, Cui X. Bao Yuan decoction and Tao Hong Si Wu decoction improve lung structural remodeling in a rat model of myocardial infarction: Possible involvement of suppression of inflammation and fibrosis and regulation of the TGF-β1/Smad3 and NF-κB pathways. BioSci Trends. 2018;12:491–501.
Wang X-J, Ren J-L, Zhang A-H, Sun H, Yan G-L, Han Y, Liu L. Novel applications of mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in herbal medicines and its active ingredients: current evidence. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2019;38:380–402.
Pang H, Jia W, Hu Z. Emerging applications of metabolomics in clinical pharmacology. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019;106:544–56.
Liu Z, Triba MN, Amathieu R, Lin X, Bouchemal N, Hantz E, Le Moyec L, Savarin P. Nuclear magnetic resonance-based serum metabolomic analysis reveals different disease evolution profiles between septic shock survivors and non-survivors. Crit Care. 2019;23:169.
Liu Z, Yin P, Amathieu R, Savarin P, Xu G. Application of LC-MS-based metabolomics method in differentiating septic survivors from non-survivors. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:7641–9.
Zhang R, Zhu X, Bai H, Ning K. Network pharmacology databases for traditional Chinese medicine: review and assessment. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:123.
Zhang W, Chen Y, Jiang H, Yang J, Wang Q, Du Y, Xu H. Integrated strategy for accurately screening biomarkers based on metabolomics coupled with network pharmacology. Talanta. 2020;211: 120710.
Zhang X, Li Z, Shen C, He J, Wang L, Di L, Rui B, Li N, Liu Z. Tao-Hong-Si-Wu decoction improves depressive symptoms in model rats via amelioration of BDNF-CREB-arginase I axis disorders. Pharma Biol. 2022;60:1739–50.
Liu Z, Zhang J, Zhang X, Shen C, Yin L, Zhu Y, Li N, Chen F. Metabolic and inorganic elemental profiling analysis of tortoise shell for the identification of tortoise strain. Food Anal Met. 2021;14:742–9.
Zhang J, Yu H, Li S, Zhong X, Wang H, Liu X. Comparative metabolic profiling of Ophiocordyceps sinensis and its cultured mycelia using GC-MS. Food Res Int. 2020;134:109241.
Maier S, Traeger T, Entleutner M, Westerholt A, Kleist B, Huser N, Holzmann B, Stier A, Pfeffer K, Heidecke CD. Cecal ligation and puncture versus colon ascendens stent peritonitis: two distinct animal models for polymicrobial sepsis. Shock. 2004;21:505–11.
Tian G, Li C, Zhai Y, Xu J, Feng L, Yao W, Bao B, Zhang L, Ding A. GC-MS based metabolomic profiling of lung tissue couple with network pharmacology revealed the possible protection mechanism of Pudilan Xiaoyan Oral Liquid in LPS-induced lung injury of mice. Biom Pharm. 2020;124:109833.
Lang B, Urbas A, DeRose P, Liu HK, Travis J, Choquette S, Cole KD. Development of NIST standard reference material 2082, a pathlength standard for measurements in the ultraviolet spectrum. J Res Natl Inst Stand Technol. 2017;122:1–14.
Chen ZQ, Lin T, Liao XZ, Li ZY, Lin RT, Qi XJ, Chen GM, Sun LL, Lin LZ. Network pharmacology based research into the effect and mechanism of Yinchenhao Decoction against Cholangiocarcinoma. Chin Med. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-021-00423-4.
Stockert JC, Blázquez-Castro A, Cañete M, Horobin RW, Villanueva Á. MTT assay for cell viability: intracellular localization of the formazan product is in lipid droplets. Acta Histochem. 2012;114:785–96.
Asgharpour F, Moghadamnia AA, Motallebnejad M, Nouri HR. Propolis attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through intracellular ROS and NO levels along with downregulation of IL-1 beta and IL-6 expressions in murine RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Food Biochem. 2019;4:3.
Valledor AF, Comalada M, Santamaria-Babi LF, Lloberas J, Celada A. Macrophage proinflammatory activation and deactivation: a question of balance. Adv Immunol. 2010;108:1–20.
Tretter L, Patocs A, Chinopoulos C. Succinate, an intermediate in metabolism, signal transduction, ROS, hypoxia, and tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1857:1086–101.
Cavaleri F, Bashar E. Potential synergies of β-hydroxybutyrate and butyrate on the modulation of metabolism, inflammation, cognition, and general health. J Nutr Metab. 2018;2018:7195760.
Thomsen HH, Rittig N, Johannsen M, Moller AB, Jorgensen JO, Jessen N, Moller N. Effects of 3-hydroxybutyrate and free fatty acids on muscle protein kinetics and signaling during LPS-induced inflammation in humans: anticatabolic impact of ketone bodies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018;108:857–67.
Zhang Q, Feng F. A novel insight into the potential toxicity mechanisms of Zhi-Zi-Hou-Po decoction by dynamic urinary metabolomics based on UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS. J Chrom B. 2020;1142:122019.
Goossens C, Weckx R, Derde S, Vander Perre S, Derese I, Van Veldhoven PP, Ghesquiere B, Van den Berghe G, Langouche L. Altered cholesterol homeostasis in critical illness-induced muscle weakness: effect of exogenous 3-hydroxybutyrate. Crit Care. 2021;2:5.
De Bandt JP, Cynober L. Therapeutic use of branched-chain amino acids in burn, trauma, and sepsis. J Nutr. 2006;136:308–13.
Zhang L, Tian Y, Yang J, Li J, Tang H, Wang Y. Colon Ascendens Stent Peritonitis (CASP) induces excessive inflammation and systemic metabolic dysfunction in a septic rat model. J Proteome Res. 2018;17:680–8.
Rozova EV, Mankovskaya IN, Belosludtseva NV, Khmil NV, Mironova GD. Uridine as a protector against hypox-ia-induced lung injury. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9418.
Tao T, He T, Mao H, Wu X, Liu X. Non-targeted metabolomic profiling of coronary heart disease patients with Taohong Siwu decoction treatment. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:651.
Noubouossie DF, Reeves BN, Strahl BD, Key NS. Neutrophils: back in the thrombosis spotlight. Blood. 2019;133:2186–97.
Shang J, He Q, Chen Y, Yu D, Sun L, Cheng G, Liu D, Xiao J, Zhao Z. MiR-15a-5p suppresses inflammation and fibrosis of peritoneal mesothelial cells induced by peritoneal dialysis via targeting VEGFA. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:9746–55.
Eremina V, Sood M, Haigh J, Nagy A, Lajoie G, Ferrara N, Gerber H-P, Kikkawa Y, Miner JH, Quaggin SE. Glomerular-specific alterations of VEGF-A expression lead to distinct congenital and acquired renal diseases. J Clin Investig. 2003;111:707–16.
Zou J, Wang N, Liu M, Bai Y, Wang H, Liu K, Zhang H, Xiao X, Wang K. Nucleolin mediated pro-angiogenic role of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A in ischaemic cardiac dysfunction: Post-transcriptional regulation of VEGF-A and MMP-9. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:2692–705.
Ince C. The microcirculation is the motor of sepsis. Crit Care. 2005;9:S13–9.
Barratt SL, Blythe T, Jarrett C, Ourradi K, Shelley-Fraser G, Day MJ, Qiu Y, Harper S, Maher TM, Oltean S, Hames TJ, Scotton CJ, Welsh GI, Bates DO, Millar AB. Differential expression of VEGF-Axxx isoforms is critical for development of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Res Crit Care Med. 2017;196:479–93.
Nedeva C, Menassa J, Puthalakath H. Sepsis: inflammation is a necessary evil. Fron Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:108.
Trebec-Reynolds DP, Voronov I, Heersche JNM, Manolson MF. VEGF-A expression in osteoclasts is regulated by NF-κB induction of HIF-1α. J Cell Biochem. 2010;110:343–51.
Hotchkiss RS, Chang KC, Swanson PE, Tinsley KW, Hui JJ, Klender P, Xanthoudakis S, Roy S, Black C, Grimm E, et al. Caspase inhibitors improve survival in sepsis: a critical role of the lymphocyte. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:496–501.
Cheng C-Y, Ho T-Y, Hsiang C-Y, Tang N-Y, Hsieh C-L, Kao S-T, Lee Y-C. Angelica sinensis exerts angiogenic and anti-apoptotic effects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating p38MAPK/HIF-1α/VEGF-A signaling in rats. Am J Chin Med. 2017;45:1683–708.
Bacanli M, Aydin S, Taner G, Goktas HG, Sahin T, Basaran AA, Basaran N. The protective role of ferulic acid on sepsis-induced oxidative damage in Wistar albino rats. Environ Toxicol Pharm. 2014;38:774–82.
Ibitoye OB, Ajiboye TO. Ferulic acid potentiates the antibacterial activity of quinolone-based antibiotics against Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb Pathogenesis. 2019;126:393–8.
Li Y, Zhu Z, Zhang T, Zhou Y. Ligustrazine attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress in a rat model of arthritis via the Sirt1/NF-κB and Nrf-2/HO-1 pathways. Arch Pharm Res. 2019;42:824–31.
Wang Q-S, Gao T, Cui Y-L, Gao L-N, Jiang H-L. Comparative studies of paeoniflorin and albiflorin from Paeonia lactiflora on anti-inflammatory activities. Pharm Biol. 2014;52:1189–95.
Liu X, Wang J. Anti-inflammatory effects of iridoid glycosides fraction of Folium syringae leaves on TNBS-induced colitis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;133:780–7.
Sun C-Y, Pei C-Q, Zang B-X, Wang L, Jin M. The ability of hydroxysafflor yellow a to attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammatory injury in mice. Phytother Res. 2010;24:1788–95.
Wang J, Wang P, Gui S, Li Y, Chen R, Zeng R, Zhao P, Wu H, Huang Z, Wu J. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A attenuates the apoptosis of peripheral blood CD4(+) T lymphocytes in a Murine model of sepsis. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:613.
Jiang B, Shen RF, Bi J, Tian XS, Hinchliffe T, Xia Y. Catalpol: a potential therapeutic for neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Med Chem. 2015;22:1278–91.
Sun M, Shen X, Ma Y. Rehmannioside A attenuates cognitive deficits in rats with vascular dementia (VD) through suppressing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Biomed Pharm. 2019;120:109492.
Venet F, Monneret G. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14:121–37.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the constructive advice on the study design from Prof. Jinfang Ge and Prof. Rong Li. We also thank Mr. Lan Zhang and Mr. Junlong Li for their help with animal experiences.
Funding
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81873986), Anhui Natural Science Foundation (2008085QH364), the funding of Anhui Medical University (2020xkjT019, 2021lcxk026), and Scientific Research Platform Improvement Project of Anhui Medical University (2022xkjT045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JH: conceptualization, writing—original draft, formal analysis, investigation; LW: data curation, validation, methodology; writing—original draft; YW: methodology, investigation, validation; ZL: conceptualization, project administration; FC: validation, project administration; ZL: conceptualization, data curation, writing—original draft, validation, project administration. All the authors contributed to the review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Wang, L., Wang, Y. et al. Metabolomics Combined with Network Pharmacology Uncovers Effective Targets of Tao-Hong-Si-Wu Decoction for Its Protection from Sepsis-Associated Acute Lung Injury. J. Anal. Test. 7, 172–186 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-023-00248-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-023-00248-0