Abstract
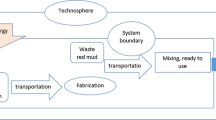
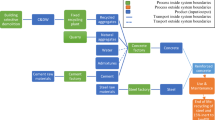
Construction and demolition waste (CDW) management is essential for the sustainable development of a country. Recycled concrete aggregates (RCA) manufactured from CDW can replace a significant portion of natural aggregates in concrete as per various research studies conducted. Nowadays, various alternate waste materials are being utilised to minimise the environmental footprint of concrete. The manufactured sand (MS) is also one of the alternate materials being used in concrete production. There are significant studies available world-wide, which estimated associated environmental impacts of RCA; however, author could not find comparative study on environmental impact of RCA and manufactured sand (MS) production using optimization techniques in Indian perspective. Therefore, this study assessed the environmental impacts of producing 1-ton RCA from reclaimed concrete and MS from granite stone. Seven mid-point environmental impact (EI) categories of ReCePe method, i.e. global warming potential, human-toxicity potential, particulate matter formation potential, terrestrial acidification potential, freshwater eutrophication potential, photochemical ozone formation potential and resource use-fossil were calculated and interpreted. Analytic hierarchy process (AHP) optimization technique was used for calculating the weightage of EI categories. Hotspot and sensitivity analysis were performed to know the relevance and sensitivity of EI categories. As per the observation, CO2 emission and primary energy consumption in 1-ton RCA were 10% and 18.5% less than 1-ton MS. The suspended particulate matter and noise level in RCA were 25% higher and 9% lesser than MS. Transportation and crushing were the main contributors to EIs. This study may help in taking a calculative decision regarding utilization of RCA and MS as river sand replacement in concrete.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the manuscript.
References
Attalla MI, Day SJ, Lange T, Lilley W, Morgan S (2008) NOx emissions from blasting operations in open-cut coal mining. Atmos Environ 42:7874–7883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.07.008
Attri GK, Gupta RC, Shrivastava S (2020) Impact of recycled concrete aggregate on mechanical and durability properties of concrete paver blocks. Mater Today Proc 42:975–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.977
Beccali M, Cellura M, Iudicello M, Mistretta M (2010) Life cycle assessment of Italian citrus-based products. Sensitivity analysis and improvement scenarios. J Environ Manage 91:1415–1428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.02.028
Behera M, Bhattacharyya SK, Minocha AK, Deoliya R, Maiti S (2014) Recycled aggregate from C&D waste & its use in concrete - a breakthrough towards sustainability in construction sector: a review. Constr Build Mater 68:501–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.07.003
Blengini GA, Garbarino E (2010) Resources and waste management in Turin (Italy): the role of recycled aggregates in the sustainable supply mix. J Clean Prod 18:1021–1030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2010.01.027
Blengini GA, Garbarino E, Šolar S, Shields DJ, Hámor T, Vinai R, Agioutantis Z (2012) Life cycle assessment guidelines for the sustainable production and recycling of aggregates: the sustainable aggregates resource management project (SARMa). J Clean Prod 27:177–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.01.020
Butera S, Christensen TH, Astrup TF (2015) Life cycle assessment of construction and demolition waste management. Waste Manag 44:196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.07.011
Coelho A, De Brito J (2013) Economic viability analysis of a construction and demolition waste recycling plant in Portugal - Part II: Economic sensitivity analysis. J Clean Prod 39:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.05.006
Ding T, Xiao J, Tam VWY (2016) A closed-loop life cycle assessment of recycled aggregate concrete utilization in China. Waste Manag 56:367–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.05.031
Estanqueiro B, Dinis Silvestre J, de Brito J, Duarte Pinheiro M (2018) Environmental life cycle assessment of coarse natural and recycled aggregates for concrete. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 22:429–449. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2016.1197161
Grosse-Sommer AP, Grünenwald TH, Paczkowski NS, van Gelder RNMR, Saling PR (2020) Applied sustainability in industry: the BASF eco-eEfficiency toolbox. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120792
Hossain MU, Poon CS, Lo IMC, Cheng JCP (2016) Comparative environmental evaluation of aggregate production from recycled waste materials and virgin sources by LCA. Resour Conserv Recycl 109:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.02.009
Huppes G, Van Oers L (2011) Evaluation of weighting methods for measuring the EU-27 overall environmental impact. JRC Scientific and Technical Reports. https://doi.org/10.2788/88465
ISO 14031:2021 Environmental management — Environmental performance evaluation — Guidelines
ISO14040:2006 Environmental management — Life cycle assessment — Principles and framework
ISO 14044:2006, Environmental management — Life cycle assessment — Requirements and guidelines
Kittipongvises S (2017) Assessment of environmental impacts of limestone quarrying operations in Thailand. Environ Clim Technol 20:67–83. https://doi.org/10.1515/rtuect-2017-0011
Kumar G, Shrivastava S, Gupta RC (2020) Paver blocks manufactured from construction & demolition waste. Mater Today Proc 27:311–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.11.039
Kumar Attri G, Gupta RC, Shrivastava S (2020) Effect of demolished concrete and stone crusher dust on properties of M-40 grade paver blocks. Mater Today Proc 44:4330–4336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.553
Kumar G, Shrivastava S, Gupta RC (2019) Materials today : proceedings Paver blocks manufactured from construction & demolition waste. Mater. Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.11.039
McGinnis MJ, Davis M, De La Rosa A, Weldon BD, Kurama YC (2017) Quantified sustainability of recycled concrete aggregates. Mag Concr Res 69:1203–1211. https://doi.org/10.1680/jmacr.16.00338
Mittal ML (2010) Estimates of emissions from coal fired thermal power plants in India. Energy 39:1–22
Nunes KRA, Mahler CF, Valle R, Neves C (2007) Evaluation of investments in recycling centres for construction and demolition wastes in Brazilian municipalities. Waste Manag 27:1531–1540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.09.007
Pollutant N, Review I, Committee S (2021) National Pollutant Inventory Review Report 2021
RILEM, 2013. RILEM TC 217-PRE: use of recycling materials. In: Progress in recycling in the built environment. Springer (978–94–007–4904–8; 2013)
Rosado LP, Vitale P, Penteado CSG, Arena U (2017) Life cycle assessment of natural and mixed recycled aggregate production in Brazil. J Clean Prod 151:634–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.068
Saghafi MD, Teshnizi ZAH (2011) Building deconstruction and material recovery in Iran: an analysis of major determinants. Procedia Eng 21:853–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.2087
Sala S, Cerutti AK, Pant R (2018) Development of a weighting approach for the environmental footprint. Publ Off Eur Union. https://doi.org/10.2760/945290
Silva RV, de Brito J, Dhir RK (2017) Availability and processing of recycled aggregates within the construction and demolition supply chain: a review. J Clean Prod 143:598–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.070
Simion IM, Fortuna ME, Bonoli A, Gavrilescu M (2013) Comparing environmental impacts of natural inert and recycled construction and demolition waste processing using LCA. J Environ Eng Landsc Manag 21:273–287. https://doi.org/10.3846/16486897.2013.852558
TIFAC (2011) Utilization of waste from construction industry. Delhi, India
Yi S, Kurisu KH, Hanaki K (2011) Life cycle impact assessment and interpretation of municipal solid waste management scenarios based on the midpoint and endpoint approaches. Int J Life Cycle Assess 16:652–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-011-0297-3
Zampori L, Saouter E, Schau E, Cristobal J, Castellani V, Sala S (2016) Guide for interpreting life cycle assessment result. Publ Off Eur Union. https://doi.org/10.2788/171315
Zhao W, Leeftink RB, Rotter VS (2010) Evaluation of the economic feasibility for the recycling of construction and demolition waste in China-The case of Chongqing. Resour Conserv Recycl 54:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.09.003Fig.1CDWgeneration
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to study conception and design. Conceptualization and methodology: Gyanendra Kumar, Sandeep Shrivastava and Ramesh Chandra Gupta; formal analysis and investigation: Gyanendra Kumar; writing — original draft preparation, review and editing: Gyanendra Kumar and Sandeep Shrivastava; supervision: Sandeep Shrivastava and Ramesh Chandra Gupta.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attri, G., Gupta, R.C. & Shrivastava, S. Comparative Environmental Impacts of Recycled Concrete Aggregate and Manufactured Sand Production. Process Integr Optim Sustain 6, 737–749 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-022-00244-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-022-00244-4