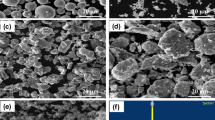
Abstract
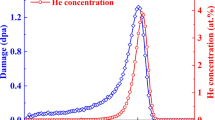
In the present study, samples of a titanium carbide nanoparticle-reinforced nickel alloy (Ni–TiCNP composite) were irradiated with 1 MeV He ions at 700 °C. The evolution of He bubbles and nanohardness was characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and nanoindentation, respectively. TEM images showed that the size and number density of He bubbles in the grains were affected by the He ion fluence. The number density first increased significantly and then decreased with increasing ion dose, while the size exhibited an inverse trend. Moreover, the swelling induced by He bubbles continuously increased with increasing ion dose. He bubbles also formed in the grain boundaries, interior of the TiC nanoparticles, and interfaces between the TiC nanoparticles and Ni matrix. Nanoindentation measurements indicated a decrease in nanohardness after irradiation, which is attributed to the disappearance of intrinsic dislocation lines caused by He ion irradiation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.M. Chen, Carbon neutrality: toward a sustainable future. Innov. 2(3), 100127 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100127
G. Chen, Q. Wang, X. Chu, Accelerated spread of Fukushima’s waste water by ocean circulation. Innov. 2(2), 100119 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100119
M.W. Rosenthal, P.N. Haubenreich, R.B. Briggs, The Development Status of Molten-Salt Breeder Reactors. ORNL-4812 (Oak Ridge National Lab, USA, 1972), pp. 195–218
Y. Zou, X. Wang, P. Lyu et al., Microstructural characteristics of pure nickel foils under argon ion irradiation. Nucl. Tech. 44(8), 080203 (2021). https://doi.org/10.11889/j.0253-3219.2021.hjs.44.080203 (in Chinese)
H.E. McCoy, Status of Materials Development for Molten Salt Reactors. ORNL-TM-5920 (Oak Ridge National Lab, USA, 1978), pp. 1–30
C.-T. Fu, W. Yinling, X.-W. Chu et al., Grain boundary engineering for control of tellurium diffusion in GH3535 alloy. J. Nucl. Mater. 497, 76–83 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2017.10.052
G. Lei, S. Yang, R. Liu et al., The effect of He bubbles on the corrosion properties of nickel-based alloy in molten salt environment. Nucl. Tech. 42(4), 040602 (2019). https://doi.org/10.11889/j.0253-3219.2019.hjs.42.040602 (in Chinese)
H.-S. Bao, Z.-H. Gong, Z.-Z. Chen et al., Evolution of precipitates in Ni–Co–Cr–W–Mo superalloys with different tungsten contents. Rare Met. 39(6), 716–724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01400-w
M. Liu, J. Hou, F. Han et al., Effects of He ion irradiation on the corrosion performance of alloy GH3535 welded joint in molten FLiNaK. Corros. Sci. 146, 172–178 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.10.038
G. Lei, R. Xie, H. Huang et al., The effect of He bubbles on the swelling and hardening of UNS N10003 alloy. J. Alloys Comp. 746, 153–158 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.291
H.F. Huang, W. Zhang, M. De Los Reyes et al., Mitigation of He embrittlement and swelling in nickel by dispersed SiC nanoparticles. Mater. Des. 90, 359–363 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.147
Z. Zhu, H. Huang, J. Liu et al., Helium-induced damage behavior in high temperature nickel-based alloys with different chemical composition. J. Nucl. Mater. 541, 152419 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2020.152419
Z. Zhu, H. Huang, O. Muránsky et al., On the irradiation tolerance of nano-grained Ni–Mo–Cr alloy: 1 MeV He+ irradiation experiment. J. Nucl. Mater. 544, 152694 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2020.152694
Fluoride-salt-cooled high temperature reactor (FHR) materials, fuels and components white paper. UCBTH-12-003. pp 1–163 (2013)
S. Liu, X.-X. Ye, L. Jiang et al., Effect of tungsten content on the microstructure and tensile properties of Ni–xW–6Cr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 655, 269–276 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.01.010
C. Yang, T. Wei, G. Zhu et al., Synergistic effect of Mo2C micro-particles and SiC nanoparticles on irradiation-induced hardening in dispersion-precipitation strengthened NiMo alloys. Scr. Mater. 189, 1–6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.058
C. Yang, H.-F. Huang, M. De Los Reyes et al., Microstructures and tensile properties of ultrafine-grained Ni–(1–3.5) wt% SiCNP composites prepared by a powder metallurgy route. Acta. Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 28(7), 809–816 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-015-0261-5
Y. Li, J. Li, C. Fu et al., Damage characteristics of selective laser melted 304L stainless steel under Xe ion irradiation. Nucl. Tech. 44(7), 9–16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.11889/j.0253-3219.2021.hjs.44.080203 (in Chinese)
X. Zhou, H. Huang, R. Xie et al., The key role of ball milling time in the microstructure and mechanical property of Ni-TiCNP composites. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25(12), 5280–5288 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2403-y
Q. Xu, H.Y. Chen, L.M. Luo et al., Microstructural evolution in W-1%TiC alloy irradiated He ions at high temperatures. Tungsten 1(3), 229–235 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-019-00026-5
J.F. Ziegler, M.D. Ziegler, J.P. Biersack, SRIM—the stopping and range of ions in matter (2010). Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 268(11), 1818–1823 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2010.02.091
W. Kesternich, Helium trapping at dislocations, precipitates and grain boundaries. Radiat. Eff. 78(1–4), 261–273 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1080/00337578308207376
A. Liu, H. Huang, J. Liu et al., Improvement of helium swelling resistance of nickel-based alloy via proper SiCNP dispersion. Mater. Today Commun. 26, 102011 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102011
X.L. Zhou, H.F. Huang, R. Xie et al., Helium ion irradiation behavior of Ni-1wt.%SiCNP composite and the effect of ion flux. J. Nucl. Mater. 467, 848–854 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2015.11.004
L.K. Mansur, Theory and experimental background on dimensional changes in irradiated alloys. J. Nucl. Mater. 216, 97–123 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3115(94)90009-4
J. Gao, H. Huang, X. Liu et al., A special coarsening mechanism for intergranular helium bubbles upon heating: a combined experimental and numerical study. Scr. Mater. 147, 93–97 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.01.006
J. Gao, L. Bao, H. Huang et al., Evolution law of helium bubbles in hastelloy N alloy on post-irradiation annealing conditions. Materials 9(10), 832 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9100832
H. Trinkaus, B.N. Singh, Helium accumulation in metals during irradiation—where do we stand? J. Nucl. Mater. 323(2), 229–242 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2003.09.001
M. Klimenkov, R. Lindau, U. Jäntsch et al., Effect of irradiation temperature on microstructure of ferritic-martensitic ODS steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 493, 426–435 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2017.06.024
L.M. Luo, Z.H. Zhao, G. Yao et al., Recent progress on preparation routes and performance evaluation of ODS/CDS-W alloys for plasma facing materials in fusion devices. J. Nucl. Mater. 548, 152857 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2021.152857
J. Chen, P. Jung, W. Hoffelner et al., Dislocation loops and bubbles in oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic steel after helium implantation under stress. Acta Mater. 56(2), 250–258 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.09.016
A. Hasegawa, M. Ejiri, S. Nogami et al., Effects of helium on ductile-brittle transition behavior of reduced-activation ferritic steels after high-concentration helium implantation at high temperature. J. Nucl. Mater. 386–388, 241–244 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.12.102
W.D. Nix, H. Gao, Indentation size effects in crystalline materials: a law for strain gradient plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46(3), 411–425 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5096(97)00086-0
G.M. Pharr, E.G. Herbert, Y. Gao, The indentation size effect: a critical examination of experimental observations and mechanistic interpretations. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 40(1), 271–292 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-matsci-070909-104456
J. Wang, Z. Ma, C. Liu et al., Helium bubble evolution and deformation of single crystal α-Fe. J. Mater. Sci. 54(2), 1785–1796 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2915-y
H.C. Chen, D.H. Li, R.D. Lui et al., Ion irradiation induced disappearance of dislocations in a nickel-based alloy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 377, 94–98 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2016.04.030
Q. Han, Y. Li, G. Ran et al., In-situ TEM observation of the evolution of helium bubbles & dislocation loops and their interaction in Pd during He+ irradiation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 87, 108–119 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.01.069
Y. Li, G. Ran, Y. Guo et al., The evolution of dislocation loop and its interaction with pre-existing dislocation in He+-irradiated molybdenum: in-situ TEM observation and molecular dynamics simulation. Acta Mater. 201, 462–476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.022
Y. Li, L. Wang, G. Ran et al., In-situ TEM investigation of 30 keV he+ irradiated tungsten: Effects of temperature, fluence, and sample thickness on dislocation loop evolution. Acta Mater. 206, 116618 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116618
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Min Liu, Yong-Feng Yan, Zhen-Bo Zhu and He-Fei Huang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Min Liu and He-Fei Huang commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was suported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11705264, 11975304, 12022515, and 12175323).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Yan, YF., Zhu, ZB. et al. Influence of He ion irradiation on the microstructure and hardness of Ni–TiCNP composites. NUCL SCI TECH 32, 121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-021-00961-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-021-00961-4