Abstract
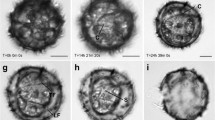
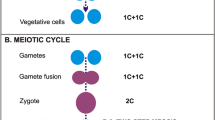
The lifecycle of red tide forming dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans (Ehrenberg) McCartney was investigated from the estuarine waters of Cochin and also from their clonal cultures. Reproductive divisions including asexual binary fission and sexual isogamete formation were studied. Certain vegetative cells were observed to undergo binary fission. Gametocyte mother cells underwent meiosis followed by several synchronous mitotic divisions which resulted in the production of 256–1024 mature spindle-shaped haploid isogametes attached on the surface of the gametocyte mother cell body. After several hours, gametes were observed to fuse and form diploid zygotes. The zygote underwent differentiation from spindle to spherical, with a reduction in the flagellar number and develops into a minuscule trophont. These trophonts later attained maturity as the cell size increased. The life cycle of Noctiluca scintillans thus appear to be a diplontic type. Hence, the study illustrates different life cycle stages of N. scintillans based on both in-situ and clonal culture studies. In-situ life cycle study is first of its kind in the reproductive biology of the species.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzelius BA (1963) The nucleus of Noctiluca scintillans. J Cell Biol 19:229–238
Calkins GN (1899) Mitosis in Noctiluca miliaris and its bearing on the nuclear relations of the Protozoa and Metazoa. J Morph 15:711–768
Doflein F (1916) Lehrbuch der Protozoankunde. Eine Darstellung der Naturgeschichte der protozoen mit besonderer Berucksichtingung der parasitischen und pathogenen Formen. Fischer Jena 4:1–1198
Dym M, Fawcett DW (1971) Further observations on the number of spermatogonia, spermatocytes, and spermatids connected by intercellular bridges in the mammalian testis. Biol Rep 4:195–215
Elbrächter M, Hoppenrath M (2009) Dinoflagellates/Dinophyceae. In: Hoppenrath M, Elbrächter M, Drebes G (Eds) Marine phytoplankton. Kleine Senckenberg-Reihe. E. Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuggart, pp 113–206
Fukuda Y, Endoh H (2006) New details from the complete life cycle of the red tide dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans (Ehrenburg) McCartney. Eur J Protistol 42:209–219
Gomes HdR, Goes J, Matondkar SGP, Buskey EJ, Basu S, Parab S, Thoppil P (2014) Massive outbreaks of Noctiluca scintillans blooms in the Arabian Sea due to spread of hypoxia. Nat Commun 5:4862 pp
Haeckel E (1873) Zur Morphologic der Infusorein. Jena. Z Med Naturwiss 7:516 – 61, pls.27–28
Ishikawa C (1893) Studies of reproductive elements. Noctiluca miliaris, Sur.; its division and spore-formation. J Im Coll Sci Tokyo 6:297–334
Kofoid CA, Swezy O (1921) The free-living unarmored dinoflagellate. Mem Univ Calif 5:1-562, pls. 1–12.
Lirdwitayaprasit T (2002) Culture of green Noctiluca under laboratory conditions: I. Feeding behavior and sexual reproduction. In: Proceedings of the Fifth IOC/WESTPAC International Science Symposium, 27–31 August 2001, Seoul, Republic of Korea, Available from: http://www.kocean.or.kr/upfile/WESTPAC_symposium/reports/%5BBP02%5DBiolLirdwitayaprasit.pdf
Macartney J (1810) Observation in luminous animals. Phil Trans R Soc Lond 1:238 – 93, pls. 14–15
Padmakumar KB, Sreerenjima G, Fanimol CL, Menon NR, Sanjeevan VN (2010) Preponderance of heterotrophic Noctiluca scintillans during a multi-species diatom bloom along southwest coast of India. Int J Oceans Oceanogr 4:55–63
Padmakumar KB, Lathika CT, Sudhakar M, Bijoy Nandan S (2016) Extensive outbreaks of heterotrophic dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans blooms along the coastal waters of South Eastern Arabian Sea. Harmful Algae News 52:10–12
Padmakumar KB, Lathika CT, Vimalkumar KG, Asha Devi CR, Maneesh TP, Anilkumar V, Gupta GVM, Sudhakar M (2017) Hydrobiological responses of the North Eastern Arabian Sea during late winter and early spring inter-monsoons and the repercussions on open ocean blooms. J Mar Biol Assoc U K 97(7):1467–1478
Sato MS, Suzuki M, Hayashi H (1998) The density of a homogeneous population of cells controls resetting of the program for swarmer formation in the unicellular marine microorganism Noctiluca scintillans. Exp Cell Res 245:290–293
Schnepf E, Drebes G (1993) Anisogamy in the dinoflagellate Noctiluca? Helgol Meeresunters 47:265–273
Smayda TJ (1997) Harmful algal blooms: their ecotoxicology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1137–1153
Taylor FJR (1987) The biology of dinoflagellates. Blackwell Scient Publication, Boston, 785 pp
Umani SF, Beran A, Parlato S, Virgillo D, Zollet T, De Olozabal A, Lazzarini B, Cabrini M (2004) Noctiluca scintillans Macartney in the Northern Adriatic Sea: long-term dynamics, relationships with temperature and eutrophication, and role in the food web. J Plankton Res 26(5):545–561
Von Dassow P, Montresor M (2011) Unveiling the mysteries of phytoplankton life cycles: patterns and opportunities behind complexity. J Plankton Res 33:3–12
Zhang S, Liu H, Guo C, Harrison PJ (2016) Differential feeding and growth of Noctiluca scintillans on monospecific and mixed diets. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 549:27–40
Zingmark RG (1970) Sexual reproduction in the dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Suriray. J Phycol 6:122–126
Acknowledgements
This investigation was carried out as a part of the Seed Money for New research Initiatives (SMNRI) programme under the State Plan Grant (2017-18) of Cochin University of Science and Technology (CUSAT), Kerala, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sathish, ., Thomas, L.C. & Padmakumar, K.B. Vegetative and Sexual Reproduction of Bloom-forming Dinoflagellate Noctiluca Scintillans (Ehrenberg) McCartney from Tropical Cochin Estuary (Southwest coast of India): In-situ and Laboratory Studies. Thalassas 37, 31–37 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-020-00247-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-020-00247-3