Abstract
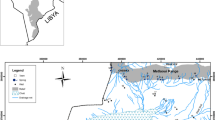
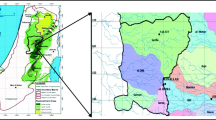
Groundwater quality indicators were mapped and integrated with spatial information about the surrounding environment for groundwater protection management. Three sampling campaigns were conducted at 17 springs in the Natuv surface water basin in Western Ramallah/Palestine (48 samples). The samples were analyzed for physico–chemical parameters: major ions, trace elements, and total and fecal coliform bacteria. Analyses included physical parameters pH, temperature, and EC, and concentrations of chemical constituents Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl–, HCO3–, NO3–, and SO42–. Results were used in a regional water-quality trend assessment and the spring water was found to be polluted in the springs located inside the populated areas. Relationships between different hydrochemical parameters reflect the carbonate nature of the western aquifers. Spring water in the study area is found to be circum neutral to slightly alkaline with average pH ranging from 6.4 to 8.3 and the EC values ranging from 410 to 1307 μS/cm. The average concentrations of anions and cations in all water samples are within WHO standards, with the exception of calcium in some samples. Some samples contain concentrations of trace elements Co, Zn, Sr, Mn, B, Al, Cu, Fe, and Ba, above WHO standards. Hydrochemical analyses show that most springs in the study area have a water type of Ca–Mg–HCO3−. New measurements were uploaded along with historical water quality data to the online mapping and data management system myObservatory, where they could be added to, accessed, and analyzed by multiple users including decision-makers in the study area.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Saada M, Sauter M (2012) Studying the flow dynamics of a karst aquifer system with an equivalent porous medium model. Groundw J 51(4):641–650
Grimalt J, Fernández P, Berdié L, Vilanova R, Catalan J, Psenner R, Hofer R, Appleby P, Rosseland B, Lien L, Massabuau J, Battarbee R (2001) Selective trapping of organo-chlorine compounds in mountain lakes of temperate areas. Environ Sci Technol 35:2690–2697
Keeler BL, Polasky S, Brauman KA, Johnson KA, Finlay JC, O’Neill A, Kovacs K, Dalzell B (2012) Linking water quality and well-being for improved assessment and valuation of ecosystem services. PNAS 109(45):18619–18624. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1215991109
Meteorological service (2017) Meteorological data in the West Bank. Meteorological Dep., Meteorological reports of the years 2012–2017, Ramallah, Palestine
Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics-PCBS (2014) Projected mid-year population for Ramallah & Al Bireh Governorate by locality. 18-07-2014, http://www.PCBS.org/population/popu_list.aspex/doi
Qannam Z (1997) Environmental status and water quality evaluation of the groundwater resources in Bethlehem-Hebron region/Palestine, MSc Thesis. University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan
Rofe & Raffety (1965) Geological and hydrological report, Jerusalem, and district water supply. Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, Central Water Authority, London, 79 p
Shalash I, Ghanem M (2007) Hydrochemistry of Natuv Drainage basin in Ramallah area/West Bank. Envir Geol J 55(4):359–367
SUSMAQ-NAT (2003) Field measurement campaign for Wadi Natuv recharge estimation: background, design and workshop. Palestinian water authority, Palestine, no 48, vol 3
Todd D (1980) Groundwater Hydrology. Wiley, New York, Geneva
US Geological Survey (2006) Water-quality characteristics, including sodium-adsorption ratios, for four sites in the Powder River drainage basin, Wyoming and Montana, water years 2001–2004. Sci Investig Rep 2006–5113:5–6
World Health Organization (2007) Guidelines for drinking-water quality — WHO standards, vol 2
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use irrigation waters. US Dep. Agric. Circ. 969, Washington, p 19
Acknowledgements
This research is funded through Al Falah Foundation as a cooperative work between the University of California—Berkeley and Birzeit University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper has been selected from the 1st Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration, Tunisia 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghanem, M., Jebreen, H., Sege, J. et al. Investigation of spring water quality in the Natuv catchment, Palestine: a component for the regional environmental management system. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 4, 2 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-018-0091-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-018-0091-8