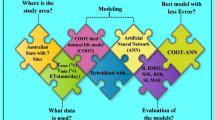
Abstract
Accurate monitoring and estimation of evaporation of a region is significant for proper planning and management of water resources management. Hence, the prediction of future alteration in evaporation is so critical in the development of irrigation systems, therefore; the current study aims to develop a hybrid artificial neural network that is coupled with COOT algorithm (ANN–COOT) to prediction the monthly evaporation in three stations in Iran. Utilizing different input combinations of monthly temperature (Tmin and Tmax), sunshine hours (SSH), wind speed (WS) and relative humidity (RH) datasets, the performance of the proposed ANN–COOT hybrid model results was compared with standalone ANN model. Statistical performances were calculated and comparison plots were made in the training and testing phases to find the most accurate model for evaporation prediction. Compared with the results of different input combinations, the hybrid ANN–COOT4 model at all three stations were found superior with input combinations of Tmin, Tmax, SSH, RH, WS. The testing results revealed that the lowest root mean square error (RMSE) (18.43 mm, 19.36 mm and 8.19 mm) and highest coefficient of correlation (R) (0.99, 0.97 and 0.99) and the highest Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NS) (0.98, 0.93 and 0.99) attained by the ANN–COOT4 hybrid model (relative to other ANN and ANN–COOT models) tested for three selected stations in Shiraz, Kish and Gorgan sites. In respect to the predictive efficiency, the developed ANN–COOT hybrid model, improved the modeling performance at extreme points, which outperforms conventional ANN model, indicating its capability in the prediction of monthly evaporation.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the first author on reasonable request.
References
Ahi Y, Coşkun Dilcan Ç, Köksal DD, Gültaş HT (2022) Reservoir evaporation forecasting based on climate change scenarios using artificial neural network model. Water Resour Manag 37(6):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03365-0
Ahmadi F, Mehdizadeh S, Mohammadi B, Pham QB, Doan TN, Vo ND (2021) Application of an artificial intelligence technique enhanced with intelligent water drops for monthly reference evapotranspiration estimation. Agric Water Manag 244:106622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106622
Arya Azar N, Kardan N, Ghordoyee Milan S (2021) Developing the artificial neural network–evolutionary algorithms hybrid models (ANN–EA) to predict the daily evaporation from dam reservoirs. Eng Comput 39(2):1375–1393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01523-3
Ashrafzadeh A, Ghorbani MA, Biazar SM, Yaseen ZM (2019) Evaporation process modelling over northern Iran: application of an integrative data-intelligence model with the krill herd optimization algorithm. Hydrol Sci J 65(15):1843–1856. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1676428
Boden TA, Krassovski M, Yang B (2013) The AmeriFlux data activity and data system: an evolving collection of data management techniques, tools, products and services. Geosci Instrum Methods Data Syst 2:165–176. https://doi.org/10.5194/gi-2-165-2013
Dong L, Zeng W, Wu L, Lei G, Chen H, Srivastava AK, Gaiser T (2021) Estimating the pan evaporation in Northwest China by coupling CatBoost with bat algorithm. Water 13(3):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030256
El Bilali A, Abdeslam T, Ayoub N, Lamane H, Ezzaouini MA, Elbeltagi A (2023) An interpretable machine learning approach based on DNN, SVR, extra tree, and XGBoost models for predicting daily pan evaporation. J Environ Manag 327:116890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116890
Ghaemi A, Rezaie-Balf M, Adamowski J, Kisi O, Quilty J (2019) On the applicability of maximum overlap discrete wavelet transform integrated with MARS and M5 model tree for monthly pan evaporation prediction. Agric for Meteorol 278:107647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.107647
Goyal MK, Bharti B, Quilty J, Adamowski J, Pandey A (2014) Modeling of daily pan evaporation in sub tropical climates using ANN, LS-SVR, Fuzzy Logic, and ANFIS. Expert Syst Appl 41(11):5267–5276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.02.047
Kaveh A, Bakhshpoori T (2016) Water evaporation optimization: a novel physically inspired optimization algorithm. Comput Struct 167:69–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2016.01.008
Lu X, Ju Y, Wu L, Fan J, Zhang F, Li Z (2018) Daily pan evaporation modeling from local and cross-station data using three tree-based machine learning models. J Hydrol 566:668–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.09.055
Mizoguchi Y, Miyata A, Ohtani Y, Hirata R, Yuta S (2008) A review of tower flux observation sites in Asia. J for Res 14(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-008-0101-9
Mohammadi B, Mehdizadeh S (2020) Modeling daily reference evapotranspiration via a novel approach based on support vector regression coupled with whale optimization algorithm. Agric Water Manag 237:106145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106145
Naruei I, Keynia F (2021) A new optimization method based on COOT bird natural life model. Expert Syst Appl 183:115352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115352
Nourani V (2017) An emotional ANN (EANN) approach to modeling rainfall-runoff process. J Hydrol 544:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.11.033
Özden A, İşeri İ (2023) COOT optimization algorithm on training artificial neural networks. Knowl Inf Syst 65(8):3353–3383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-023-01859-w
Seifi A, Riahi H (2020) Estimating daily reference evapotranspiration using hybrid gamma test-least square support vector machine, gamma test-ANN, and gamma test-ANFIS models in an arid area of Iran. J Water Clim Change 11(1):217–240. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2018.003
Sheng W, Li R, Yan T, Tseng M-L, Lou J, Li L (2023) A hybrid dynamic economics emissions dispatch model: Distributed renewable power systems based on improved COOT optimization algorithm. Renew Energy 204(34):493–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.01.010
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the National Meteorological Organization for providing necessary data that are used for carrying out this research work.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alempour Rajabi, F., Ahmadi, E., Ragab Ibrahim, O. et al. Modeling Monthly Evaporation in Different Climates Using ANN–COOT Hybrid Algorithm. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-023-01338-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-023-01338-w