Abstract
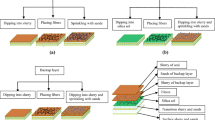
In this study, different amounts of steel fiber were added in the slurry to prepare fiber reinforced shell with improved performances of investment casting shell. The thixotropy of slurry, as well as green strength, fired strength, high-temperature strength, thermal diffusivity and permeability of the shells were all examined. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to identify morphologies and compositions of the shells. The results showed that the viscosity of the slurry increased with the increase of steel fiber content. The addition of 0.4% steel fiber (3 mm in length) resulted in maximum thixotropic loop of the slurry, and the addition of 0.4% steel fiber (4 mm in length) resulted in maximum green strength of 2.45 MPa, fired strength of 5.82 MPa, and strong enough high-temperature strength. XRD data revealed a shell was mainly composed of Zr(SiO4) and mullite. Also, high temperature led to shell mullitization and sintering. SEM observations indicated that reinforcement steel fiber in the shell was mainly achieved by debonding, deforming, and breaking processes. The addition of fiber led to significantly improved heat dissipation ability and permeability of the shell.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.M. Cheah, C.K. Chua, C.W. Lee, Rapid prototyping and tooling techniques: a review of applications for rapid investment casting. Int J Adv Manuf. Technol. 25, 308–320 (2005)
C. Yuan, S. Jones, S. Blackburn, The influence of autoclave steam on polymer and organic fiber modified ceramic shells. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25, 1081–1087 (2005)
Lu. Huang Pengpeng, Y.Q. Gang, Effect of ceramic and nylon fiber content on composite silica sol slurry properties and bending strength of investment casting shell. Materials. 12, 2788–2797 (2019)
Lü. Kai, D. Zehai, L. Xiangdong, Effects of fiber length and mixing routes on fiber reinforced shell for investment casting. Ceram. Int. 45, 6925–6930 (2019)
S. Kumar, D.B. Karunakar, Enhancing the permeability and properties of ceramic shell in investment casting process using ABS powder and needle coke. Inter. Metalcast. 13, 588–596 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-00297-7
Y. Li, X. Liu, K. Lü, X. Du, Preparation of fiber-reinforced shell by airflow placement fiber technology for investment casting. Inter. Metalcast. 13(4), 979–986 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00323-2
D.H. Lu, Z. Wang, Y.H. Jiang, Effect of aluminium silicate fiber modification on crack-resistance of a ceramic mould. China Foundry. 9, 322–327 (2012)
S. Kumar, D.B. Karunakar, Characterization and properties of ceramic shells in investment casting process. Inter. Metalcast. 15, 98–107 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00421-6
S. Pattnaik, M.K. Sutar, Effect of saw dust content on slurry rheology and mechanical properties of the investment casting ceramic shell. Inter. Metalcast. 15, 470–487 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00478-3
M.B. Madan, P. Sarojrani, K. Mihir, Thermo-mechanical analysis of investment casting ceramic shell: a case study. Measurement 147, 1068–1071 (2019)
L. Tian, A. Joe, S.L. Boyan, Investment casting and experimental testing of heat sinks designed by topology optimization. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 127, 396–412 (2018)
D. Anna, N. Krzysztof, G. Jakub, Aluminum inserts for enhancing heat transfer in PCM accumulator. Materials 13, 415–425 (2020)
U. Veit, C. Rüssel, Viscosity and liquidus temperature of quaternary glasses close to an eutectic composition in the CaO-MaO-Al2O3-SiO2 system. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 8280–8292 (2017)
R.A. Eppler, Mechanism of formation of zircon stains. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 53, 457–462 (1970)
K. Lü, X. Liu, Z. Duan, Effect of firing temperature and time on hybrid fiber-reinforced shell for investment casting. Inter. Metalcast. 13, 666–673 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-0280-x
K. Lü, X. Liu, Du. Zhaoxin, Y. Li, Properties of hybrid fibre reinforced shell for investment casting. Ceram. Int. 42, 15397–15404 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51865042); National Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (Grant No. 2021LHMS05003, 2019LH05026 and 2020MS05024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lü, K., Shen, S., Ma, C. et al. Research on Modification of Steel Fiber in Investment Casting shell. Inter Metalcast 16, 1849–1857 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00722-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00722-4