Abstract
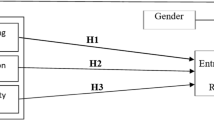
Entrepreneurship plays an important role in driving a nation's economic growth to impact the global economy. The presence and rise of business entities, primarily through digital platforms, have helped maintain Indonesia’s general business circulation and lowered youth unemployment. Efforts to realise this condition begin when students take their studies seriously. However, the level of graduate unemployment is currently high, with the intensity of entrepreneurial intentions being low. This study aims to explore students' entrepreneurial intentions based on the present curriculum, risk awareness, optimism and opportunities mediated and moderated by inspiration and support, respectively. Compared to other papers with similar research, the uniqueness of this paper is that it addresses the moderating and mediating roles of inspiration and support in the correlation of several variables to youth entrepreneurial intention. This study involves 306 students spread throughout Indonesia. The data were collected using a questionnaire and indicators derived from existing measurement instruments. The data analysis, involving mediation and moderation analysis of direct and indirect relationships, was done using the structural equation model-partial least square (SEM-PLS). The results reveal that educational support and inspiration have a direct positive and significant relationship with opportunities for entrepreneurial intention. Further, educational support, relational support and structural support have a positive and significant impact on entrepreneurial intention through the mediation role of opportunities. Student intention in starting a business is closely related to various factors or variables that are mutually sustainable.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adekiya AA, Ibrahim F (2016) Entrepreneurship intention among students. The antecedent role of culture and entrepreneurship training and development. Int J Manag Educ 14(2):116–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2016.03.001
Ahmad NH, Rahman SA, Rajendran NLKA, Halim HA (2020) Sustainable entrepreneurship practices in Malaysian manufacturing SMEs: the role of individual, organisational and institutional factors. World Rev Entrep, Manag Sustain Dev 16(2):153–171
Ahmed T, Chandran VGR, Klobas JE, Liñán F, Kokkalis P (2020) Entrepreneurship education programmes: how learning, inspiration and resources affect intentions for new venture creation in a developing economy. Int J Manag Educ 18(1), Article 100327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2019.100327
Aima MH, Wijaya SA, Carawangsa L, Ying M (2020) Effect of global mindset and entrepreneurial motivation to entrepreneurial self-efficacy and implication to entrepreneurial intention. Dinasti Int J Digital Bus Manag 1(2):302–314
Al-Azawei A, Parslow P, Lundqvist K (2017) The effect of universal design for learning (UDL) application on e-learning acceptance: a structural equation model. Int Rev Res Open Distrib Learn: IRRODL 18(6):54–87
Alshebami AS, Seraj AHA (2021) The antecedents of saving behavior and entrepreneurial intention of Saudi Arabia University students. Educ Sci: Theory Pract 21(2):67–84
Ament C (2018) The ubiquitous security expert: overconfidence in information security
Ardi Z, Hidayat H, Ifdil I, Guspriadi Y, Fauziyyah SA (2021) The development of POTENSIA; The android-based psychological application for mapping and assessments of student mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Interact Mob Technol 15(16)
Awang A, Amran S, Niza Md Nor M, Ibrahim II, Mohd Razali MF (2016) Individual entrepreneurial orientation impact on entrepreneurial intention: intervening effect of PBC and subjective norm. J Entrep, Bus Econ 4(2):36
Bignotti A, Le Roux I (2020) Which types of experience matter? The role of prior start-up experiences and work experience in fostering youth entrepreneurial intentions. Int J Entrep Behav Res 26(6):1181–1198
Chang A, Chang DF, Chen TL (2022) Detecting female students transforming entrepreneurial competency, mindset, and intention into sustainable entrepreneurship. Sustainability (Switzerland) 14(20), Article 12970. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142012970
Chaniago H (2022) The effect innovation cloning to small business success: entrepreneurial perspective. J Innov Entrep 11(1), Article 52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-022-00245-0
Chen H, Tang Y, Han J (2022) Building students’ entrepreneurial competencies in Chinese universities: Diverse learning environment, knowledge transfer, and entrepreneurship education. Sustainability (Switzerland) 14(15):Article 9105. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159105
Costin Y, O’Brien MP, Hynes B (2022) Entrepreneurial education: Maker or breaker in developing students’ entrepreneurial confidence, aptitude and self-efficacy? Ind High Educ 36(3):267–278
Cui J, Sun J, Bell R (2021) The impact of entrepreneurship education on the entrepreneurial mindset of college students in China: the mediating role of inspiration and the role of educational attributes. Int J Manag Educ 19(1):100296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2019.04.001
DeJaeghere J, Baxter A (2014) Entrepreneurship education for youth in sub-Saharan Africa: a capabilities approach as an alternative framework to neoliberalism’s individualizing risks. Prog Dev Stud 14(1):61–76. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464993413504353
Galati F, Bigliardi B, Passaro R, Quinto I (2020) Why do academics become entrepreneurs? How do their motivations evolve? Results from an empirical study. Int J Entrep Behav Res 26(7):1477–1503. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-11-2019-0619
Ghura AS, DeNoble A, Martínez Flores R (2022) Prodensa consulting services: in search of corporate entrepreneurs. Emerald Emerg Markets Case Stud 12(4):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1108/EEMCS-06-2022-0207
Gilang A, Syarifuddin S, Pradana M, Fakhri M, Maisarah N (2019, 10/17) Factors analysis of basic human values at Indonesian Insurance Company. Int J Adv Sci Technol 28(8s):755–763
González-Serrano MH, González-García RJ, Carvalho MJ, Calabuig F (2021) Predicting entrepreneurial intentions of sports sciences students: a cross-cultural approach. J Hospital, Leis, Sport Tour Educ 29, Article 100322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhlste.2021.100322
Greblikaite J, Sroka W, Gerulaitiene N (2016) Involving young people in polish and Lithuanian social enterprises by fostering entrepreneurial skills and abilities as entrepreneurial opportunity at university. Entrep Bus Econ Rev 4(3):131–152. https://doi.org/10.15678/EBER.2016.040310
Hidayat, H., Ardi, Z., & Yuliana, H., S. (2019) Exploration of the need analysis for technopreneurship scientific learning models in higher vocational education. Int J Econ Bus Res 18(3):356–368https://doi.org/10.1504/ijebr.2019.102733
Iqbal J, Yi X, Ashraf MA, Chen R, Ning J, Perveen S, Imran Z (2022) How curriculum delivery translates into entrepreneurial skills: the mediating role of knowledge of information and communication technology. PLOS One 17(5 May), Article e0265880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0265880
Jang Y, Lee WJ, Hadley B (2020) Interactive effects of business environment assessment and institutional programs on opportunity entrepreneurship. Sustainability (Switzerland) 12(13), Article 5280. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135280
Karyaningsih RPD, Wibowo A, Saptono A, Narmaditya BS (2020) Does entrepreneurial knowledge influence vocational students’ intention? Lessons from Indonesia. Entrep Bus Econ Rev 8(4):138–155. https://doi.org/10.15678/EBER.2020.080408
Khan MF, Khurshid S, Amin F, Saqib N (2022) Learning and creativity in virtual communities: nurturing entrepreneurial intentions of Muslim women. Manag Labour Stud 47(4):483–501. https://doi.org/10.1177/0258042X221106601
Kiškis M, Kiškienė A (2021) Entrepreneurship education – a hidden contributor to the decline in entrepreneurship? Int J Entrep 25(5)
Melnyk L, Kubatko O, Matsenko O, Balatskyi Y, Serdyukov K (2021) Transformation of the human capital reproduction in line with Industries 4.0 and 5.0. Probl Perspect Manag 19(2):480–494. https://doi.org/10.21511/ppm.19(2).2021.38
Murphy M, Pacher C (2022) Bridging the gap: brain drain to brain circulation: researching successful strategies to support effective change
Pangarso A, Astuti ES, Raharjo K, Afrianty TW (2020) The impact of absorptive capacity and innovation ambidexterity on sustainable competitive advantage: The case of Indonesian higher education. Entrep Sustain Issues 7(3):2436–2455. https://doi.org/10.9770/jesi.2020.7.3(65)
Prabowo H, Ikhsan RB, Yuniarty Y (2022) Drivers of green entrepreneurial intention: Why does sustainability awareness matter among university students? Front Psychol 13:873140–873140
Pradana M, Kartawinata BR (2020) Indonesian private university students’ entrepreneurial intention. APMBA (Asia Pac Manag Bus Appl) 9(2):111–122
Pradana M, Wardhana A, Wijayangka C, Kartawinata BR, Wahyuddin S (2020) Indonesian university students’ entrepreneurial intention: a conceptual study. J Crit Rev 7(7):571–573. https://doi.org/10.31838/jcr.07.07.101
Qader AA, Zhang J, Ashraf SF, Syed N, Omhand K, Nazir M (2022) Capabilities and opportunities: linking knowledge management practices of textile-based SMEs on sustainable entrepreneurship and organizational performance in China. Sustainability (Switzerland) 14(4), Article 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042219
Riyanti BPD, Suryani AO, Sandroto CW, Soeharso SY (2022) The construct and predictive validity testing of Indonesian entrepreneurial competence inventory-situational judgment test model. J Innov Entrep 11(1), Article 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-022-00202-x
Ruiz-Palomino P, Martínez-Cañas R (2021) From opportunity recognition to the start-up phase: the moderating role of family and friends-based entrepreneurial social networks. Int Entrep Manag J 17(3):1159–1182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-020-00734-2
Sampene AK, Li C, Khan A, Agyeman FO, Opoku RK (2022) Yes! I want to be an entrepreneur: a study on university students’ entrepreneurship intentions through the theory of planned behavior. Curr Psychol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03161-4
Schlaegel C, Koenig M (2014) Determinants of entrepreneurial intent: a meta-analytic test and integration of competing models. Entrep: Theory Pract 38(2):291–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.12087
Sherkat A, Chenari A (2022) Assessing the effectiveness of entrepreneurship education in the universities of Tehran province based on an entrepreneurial intention model. Stud High Educ 47(1):97–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2020.1732906
Valencia-Arias A, Arango-Botero D, Sánchez-Torres JA (2022) Promoting entrepreneurship based on university students’ perceptions of entrepreneurial attitude, university environment, entrepreneurial culture and entrepreneurial training. High Educ, Skills Work-Based Learn 12(2):328–345. https://doi.org/10.1108/HESWBL-07-2020-0169
Wach K, Wojciechowski L (2016) Entrepreneurial intentions of students in Poland in the view of Ajzen’s theory of planned behaviour. Entrep Bus Econ Rev 4(1):83–94. https://doi.org/10.15678/EBER.2016.040106
Wardana LW, Handayati P, Narmaditya BS, Wibowo A, Patma TS, Suprajan SE (2020a) Determinant factors of young people in preparing for entrepreneurship: Lesson from Indonesia. J Asian Finance, Econ Bus 7(8):555–566. https://doi.org/10.13106/jafeb.2020.vol7.no8.555
Wardana LW, Narmaditya BS, Wibowo A, Mahendra AM, Wibowo NA, Harwida G, Rohman AN (2020b) The impact of entrepreneurship education and students' entrepreneurial mindset: the mediating role of attitude and self-efficacy. Heliyon 6(9), Article e04922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04922
Welter C, Scrimpshire A (2021) The missing capital: The case for psychological capital in entrepreneurship research. J Bus Ventur Insights 16, Article e00267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbvi.2021.e00267
Xiao, Z., Chen, X., Dong, M. C., & Gao, S. (2022). Institutional support and firms’ entrepreneurial orientation in emerging economies. Long Range Plann 55(1), Article 102106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2021.102106
Yang Y (2020) Exploration and practice of maker education mode in innovation and entrepreneurship education. Front Psychol 11, Article 1626. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01626
Yu Y, Luo J (2018) Dispositional optimism and well-being in college students: self-efficacy as a mediator. Soc Behav Pers 46(5):783–792. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.6746
Zamrudi Z, Yulianti F (2020) Sculpting factors of entrepreneurship among university students in Indonesia. Entrep Bus Econ Rev 8(1):33–50.https://doi.org/10.15678/EBER.2020.080102
Funding
The study was supported by a grant from the Lembaga Penelitian dan Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat (LPPM) Universitas Negeri Padang, Indonesia. The authors would like to thank Lembaga Penelitian dan Pengabdian Masyarakat Universitas Negeri Padang for funding this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ardi, Z., Yulastri, A., Hidayat, H. et al. Enhancing entrepreneurial intention through curriculum, risk awareness, optimism and opportunities: the mediating and moderating roles of entrepreneur inspiration and support. J. Soc. Econ. Dev. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40847-024-00339-3
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40847-024-00339-3